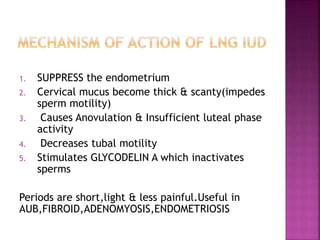
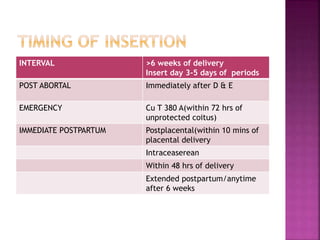
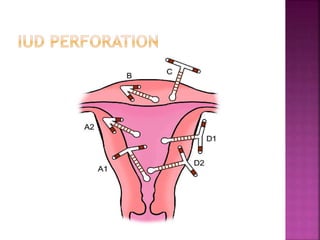
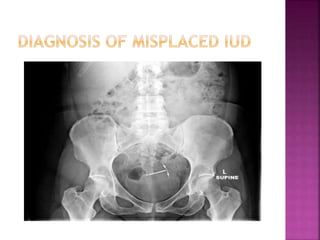
The document provides a comprehensive overview of intrauterine devices (IUDs), including their types, mechanisms of action, insertion procedures, contraindications, and complications. It outlines the differences between copper and hormonal IUDs, their benefits, non-contraceptive uses, and potential side effects. Additionally, the document discusses guidelines for insertion timing, removal, and follow-up care, emphasizing the safety and effectiveness of IUDs as a contraceptive method.