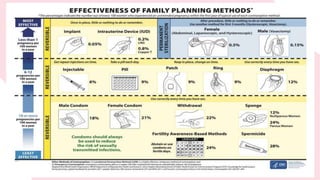
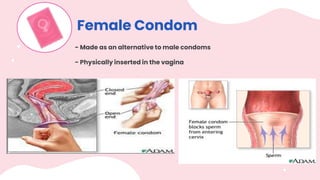
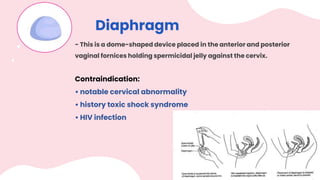
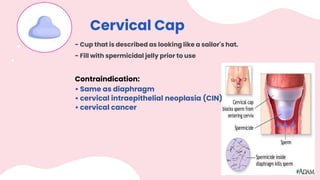
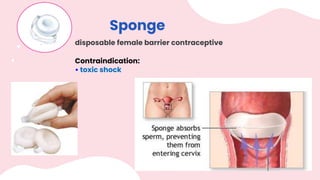
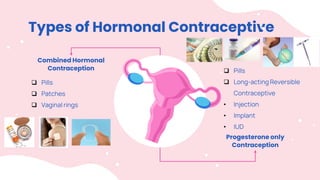
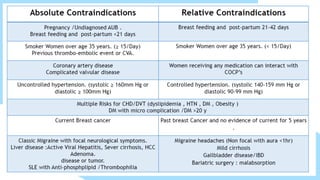
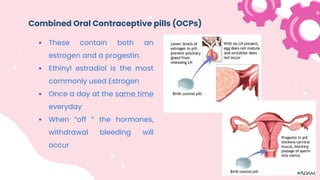
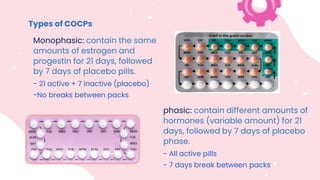
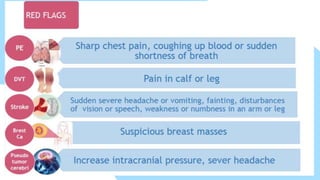
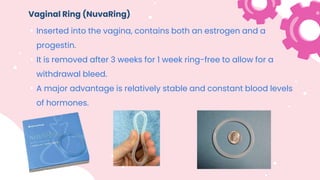
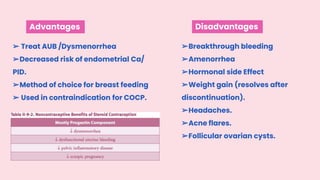
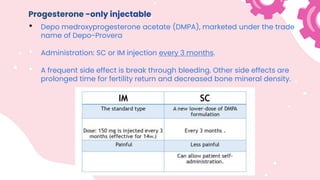
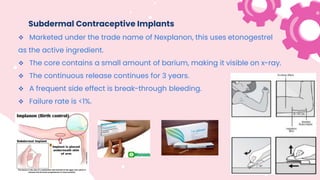
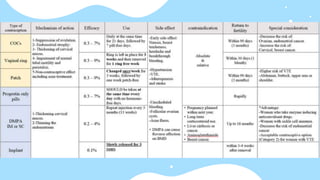
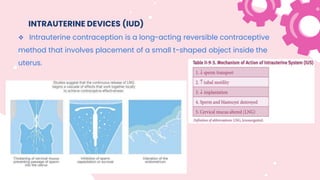
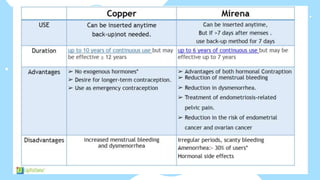
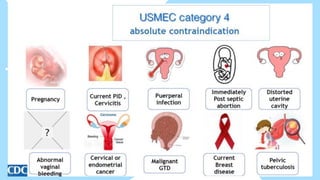
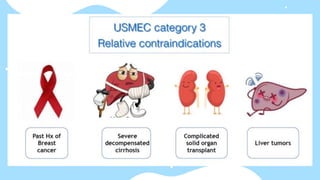
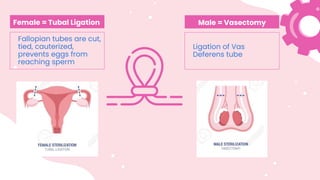
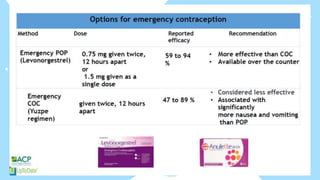
This document summarizes different types of contraceptive methods including behavioral methods, barrier methods, hormonal methods, sterilization, and emergency contraception. Behavioral methods include withdrawal and fertility awareness. Barrier methods discussed are male/female condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, and spermicides. Hormonal methods covered combined oral contraceptives, patches/rings, progesterone only pills and injections, implants, and IUDs. Sterilization involves tubal ligation for females and vasectomy for males. Emergency contraception uses high doses of hormones to prevent ovulation.