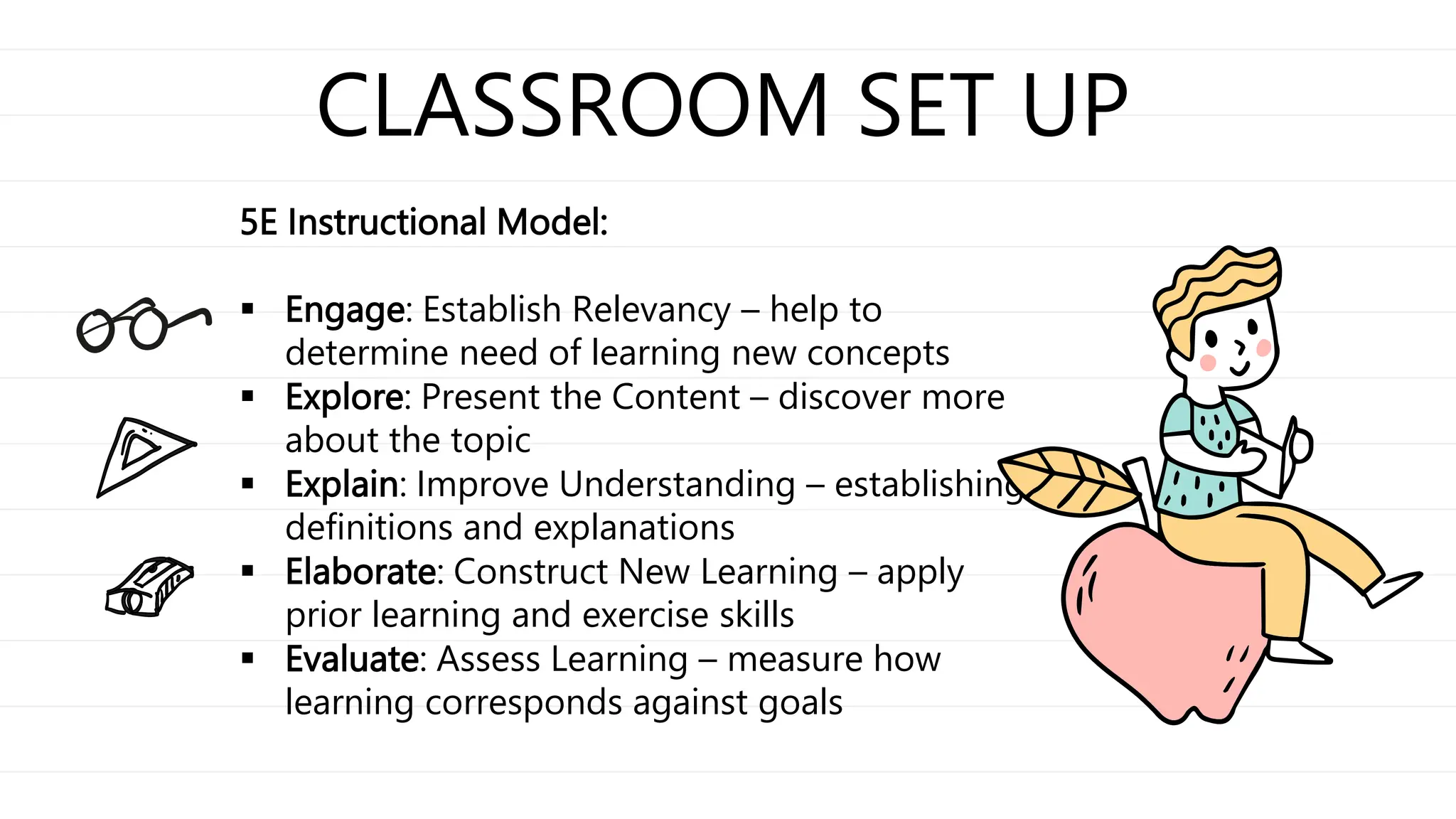
Constructivism is a theory that learners construct knowledge through experiences and reflecting on those experiences. The curriculum in a constructivist classroom is project-based and emphasizes social learning and problem-solving. The teacher acts as a guide by asking questions to help students develop their own understandings, and coaches and scaffolds students as they learn. Students are actively engaged in their own learning by working collaboratively, posing their own questions, and taking responsibility for constructing their own knowledge. The classroom is set up to engage students in hands-on exploration of topics using a 5E instructional model.