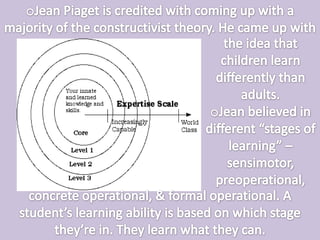
Constructivism is a learning theory based on the idea that learners actively construct their own understanding and knowledge through experiences and reflection. According to the theory, children learn best through hands-on experiences and by figuring things out on their own or with peers. The main principles of constructivism were developed by Jean Piaget, who believed that children learn differently than adults and progress through distinct stages of cognitive development at their own pace. Teachers following constructivist practices take on the role of facilitators who provide opportunities for student exploration and experimentation rather than simply lecturing.