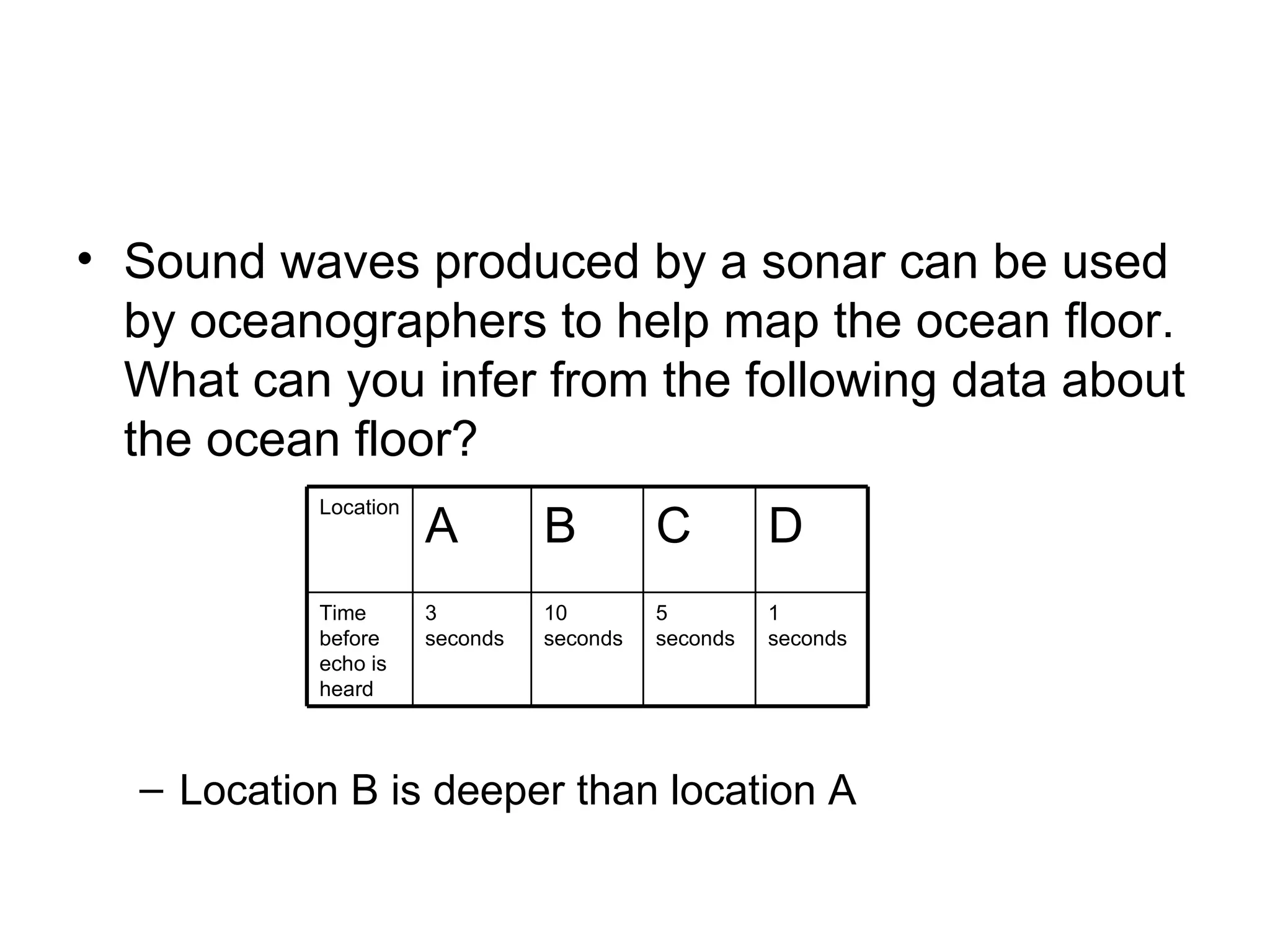
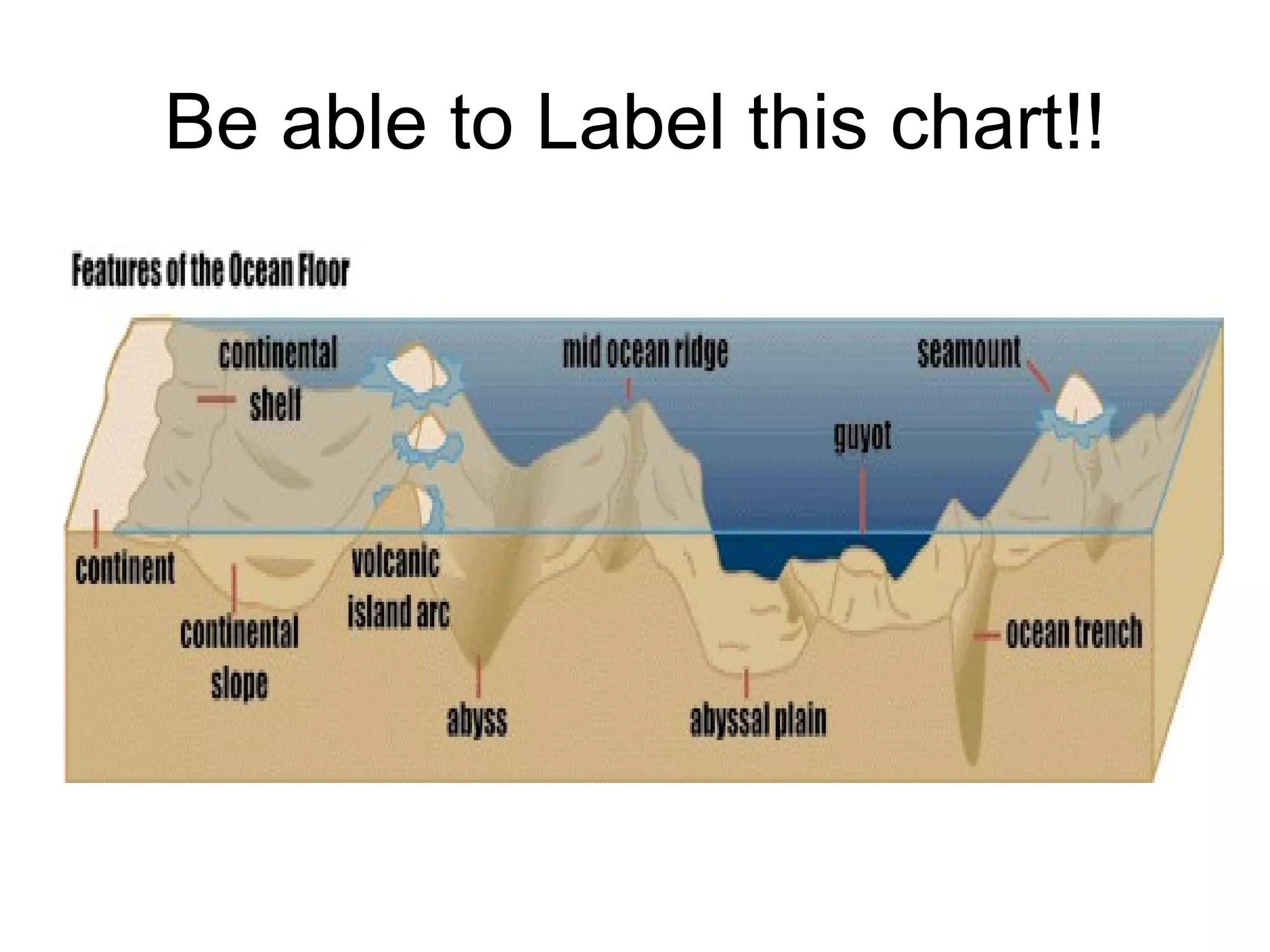
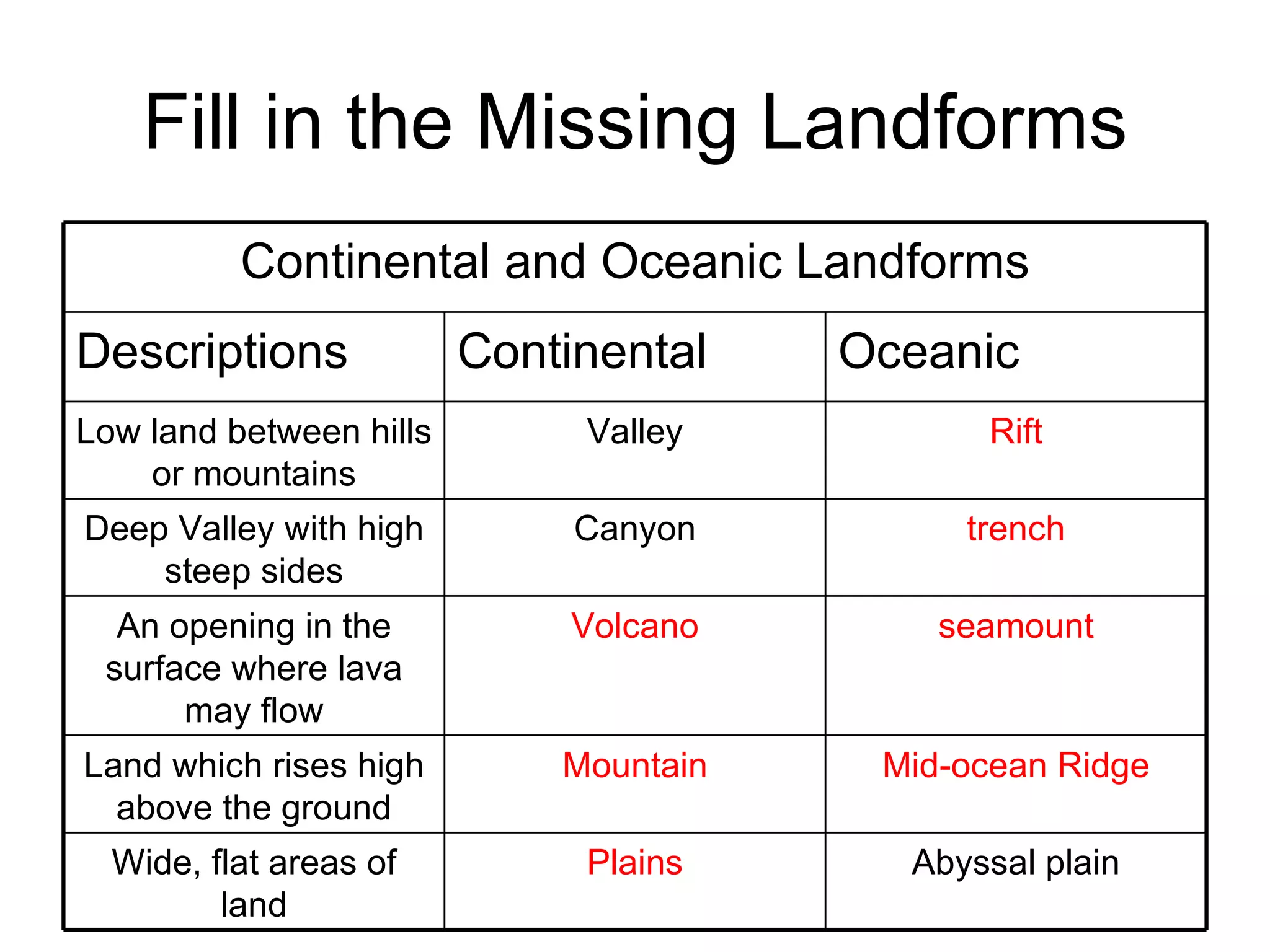
Natural processes like weathering, erosion, deposition, landslides, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and floods can affect Earth's land and oceans in both constructive and destructive ways. Constructive processes build up landforms through deposition and volcanism, while destructive processes like weathering and erosion break down landforms. Weathering is the breakdown of rocks by water, ice, plants, and temperature changes. Erosion is the movement of sediments by wind, water and ice. Deposition occurs when sediments are dropped by wind, water or ice to build up new landforms.