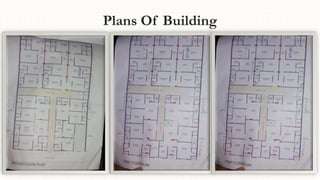
The document details a site visit to a triple-story building under construction, observing various materials and their specifications, such as bricks, aggregates, cement, and concrete mixes. Key structural insights include the building's frame structure, the progress of construction on each floor, and specific design features of the flats. The observation also mentions the design and dimensions of individual flats, including room sizes and an open kitchen layout.