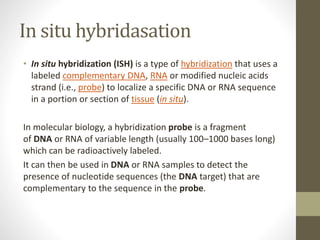
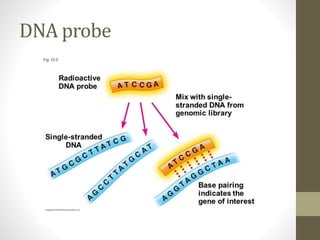
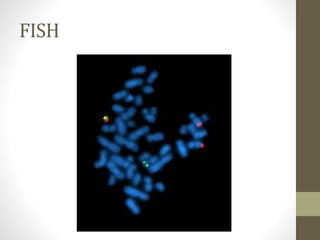
Physical mapping involves determining the locations of identifiable landmarks on DNA molecules, such as restriction enzyme cutting sites or genes, and measuring their distances in base pairs. One physical mapping method is fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), which detects the positions of markers or genes on chromosomes by hybridizing fluorescent probes to chromosomal DNA on slides under a microscope. Another major approach is restriction fragment overlapping based physical mapping using bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs). BAC-based physical mapping does not require chromosome slide preparation like FISH and can map hundreds or thousands of genes to contigs.