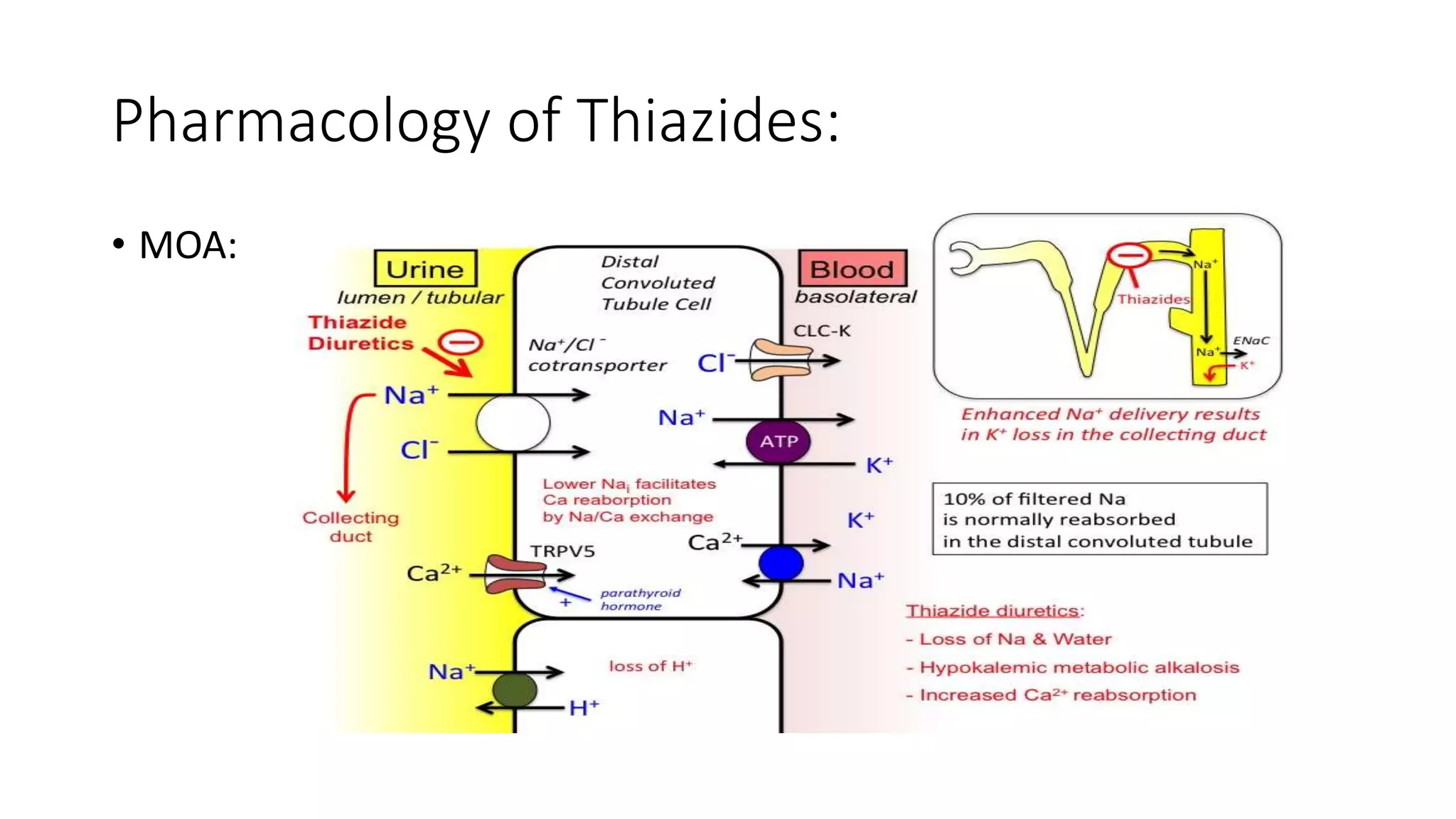
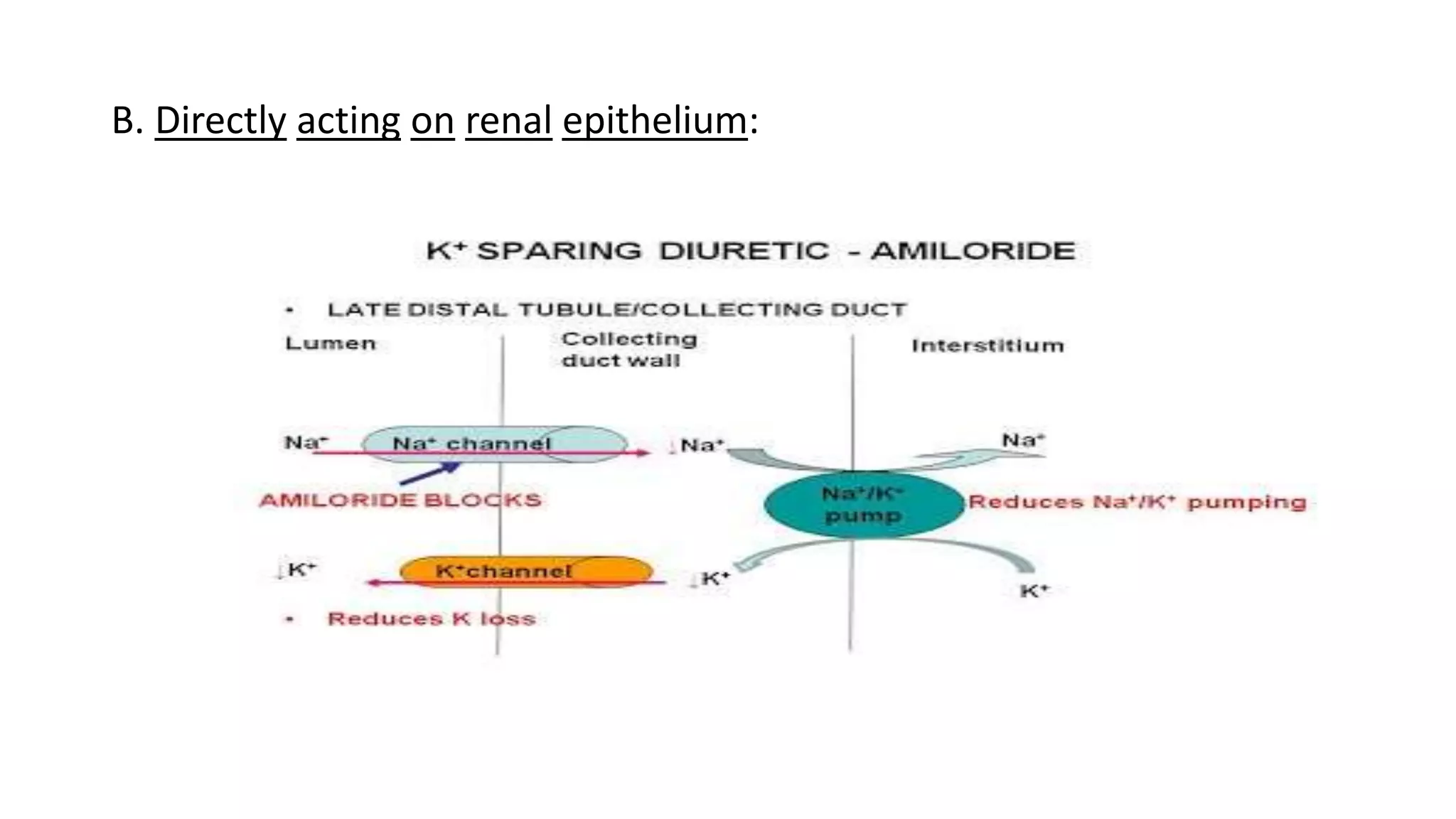
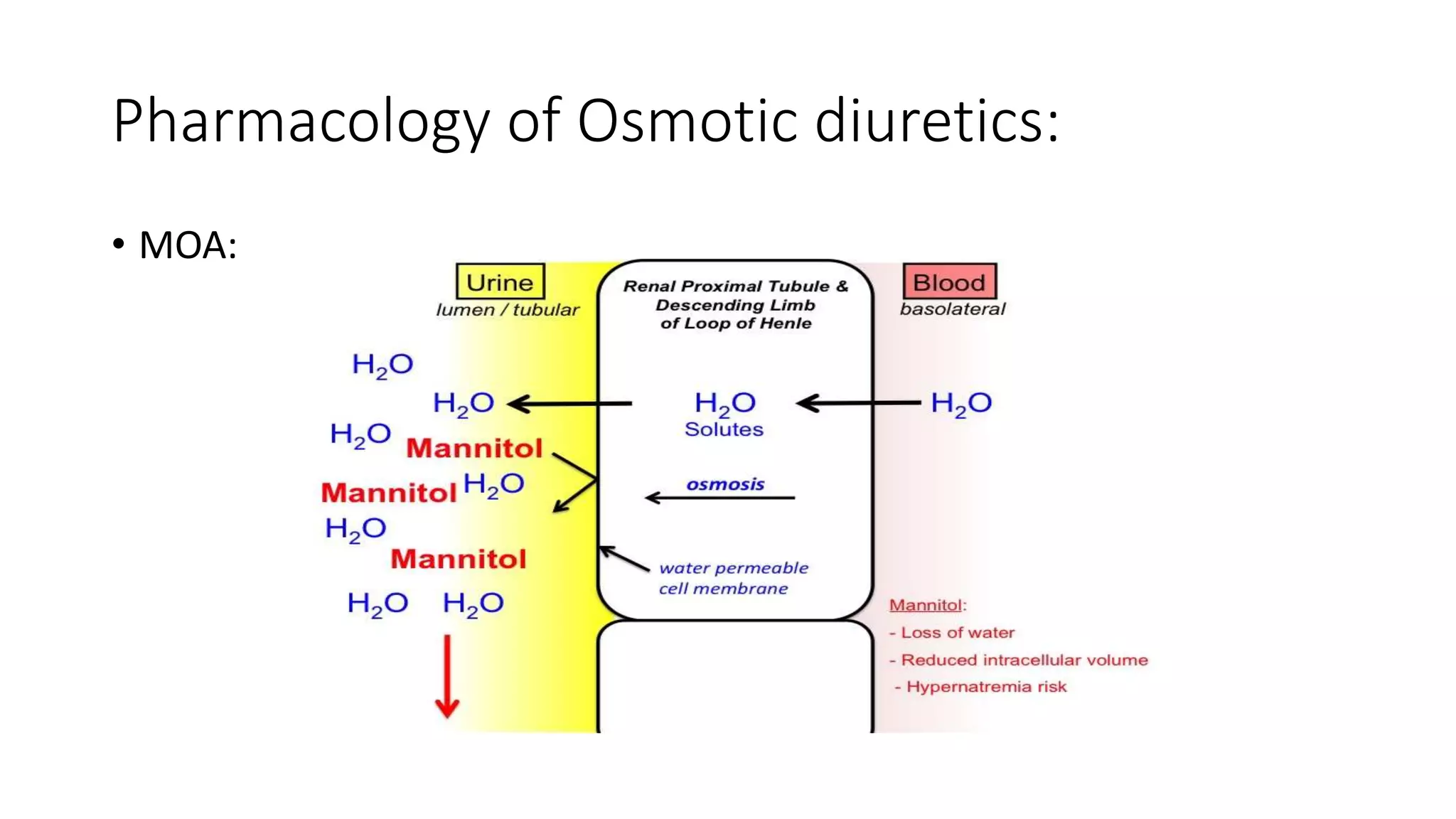
The document presents a seminar on diuretics, detailing their classifications, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, uses, and side effects. Diuretics, known as water pills, are utilized to treat conditions such as hypertension and edema by promoting urine formation through various mechanisms across different diuretic classes. Side effects vary by class and may include electrolyte imbalances and ototoxicity.