Embed presentation
Downloaded 37 times

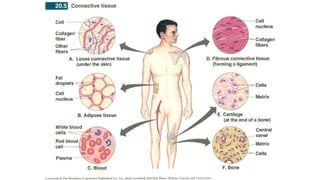
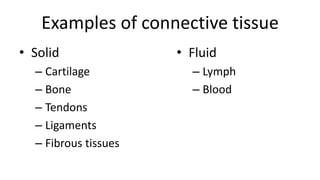

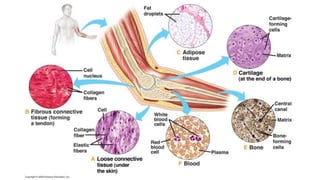
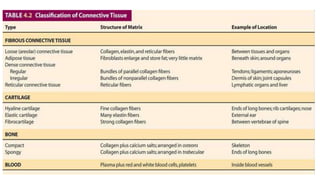
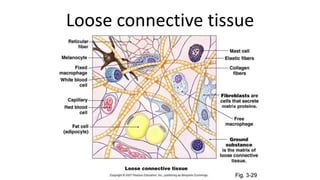
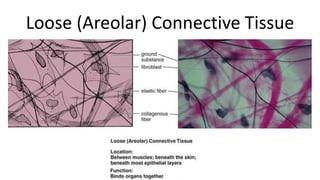

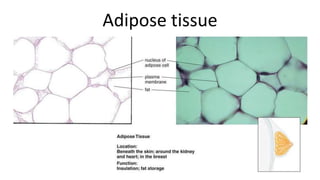

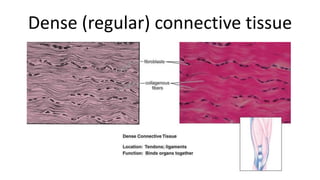
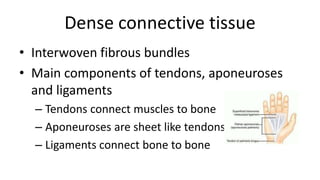
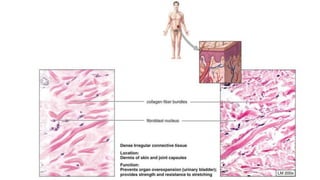
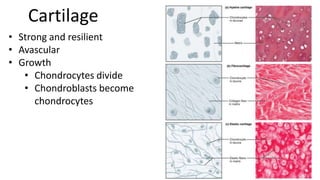
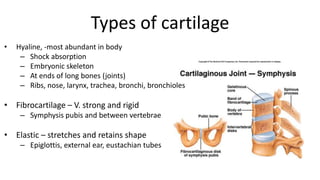
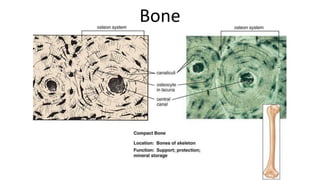
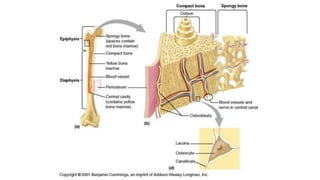
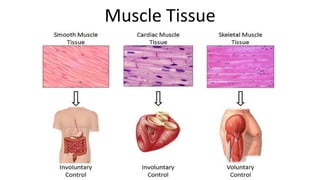
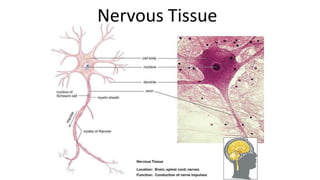
This document discusses the three main types of tissues in the body: connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. It provides examples of different connective tissues, including both solid tissues like cartilage, bone, tendons, and ligaments, as well as fluid tissues like lymph and blood. Connective tissues function to provide protection, support, compartmentalization, and binding organs together. Within connective tissue, there are loose connective tissues like areolar tissue composed of collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers, as well as adipose tissue which functions for insulation. Dense connective tissues have interwoven bundles and form tendons, aponeuroses, and ligaments. Cartilage is also discussed, including the different



















