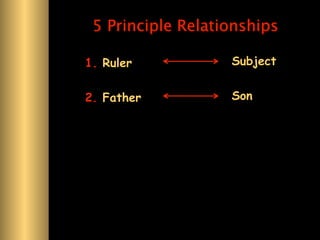
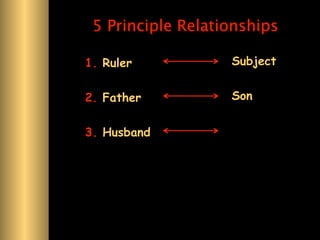
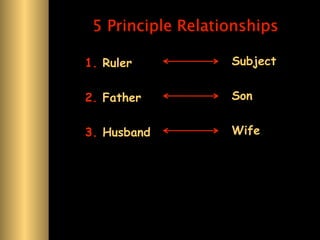
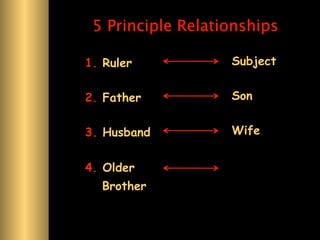
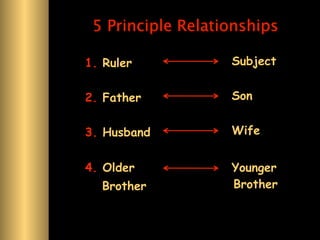
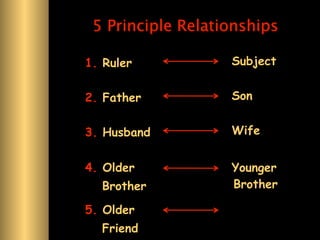
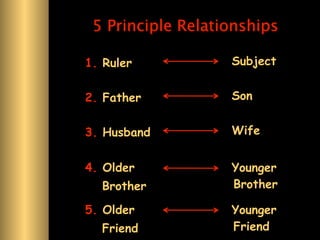
The document provides information about Confucianism and its key figures Confucius and Mencius. Confucius lived from 551-479 BCE in ancient China and became a teacher. He authored the Analects, which focuses on interpersonal relationships and government. Major Confucian principles include li, ren, shu, yi, and xiao. Mencius was a disciple of Confucius who believed people are inherently good and that education, not punishment, can correct bad behavior. Confucianism emphasizes social hierarchies, rituals, and cohesion.