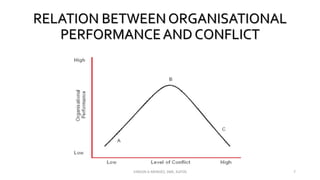
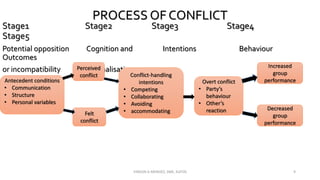
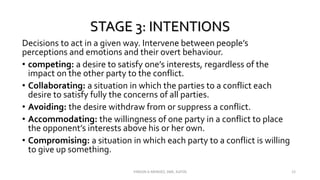
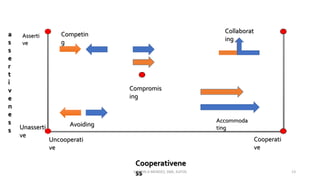
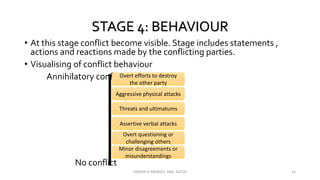
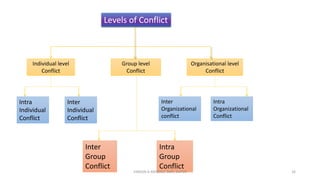
The document discusses the concept of conflict, defining it as the perception of differences in opinions, interests, or goals that negatively affect something a party cares about. It notes conflict is natural and can be functional or dysfunctional. The document outlines various views on conflict and describes the stages of conflict from potential incompatibility to outcomes. It also discusses types of conflict at the individual, group, and organizational levels and methods for managing conflict, including resolution techniques like problem solving, compromise, and altering human or structural variables.