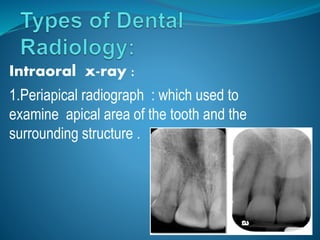
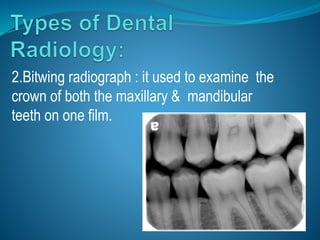
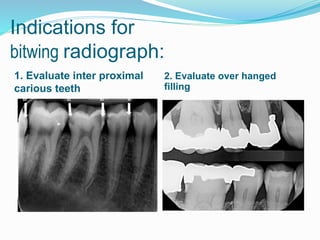
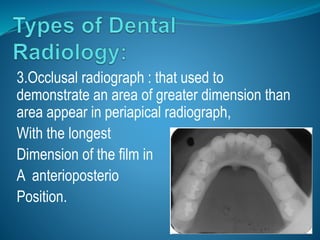
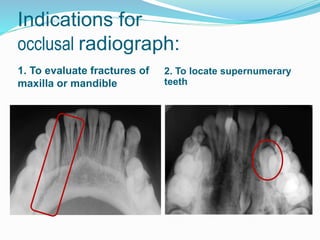
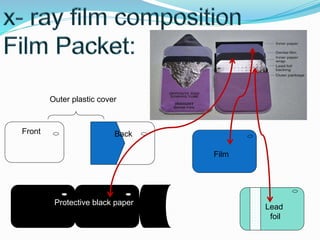
Radiation comes in two forms - particulate and electromagnetic. Dental radiographs use x-rays to produce images of teeth and surrounding structures. There are three main types of intraoral dental x-rays: periapical for the tooth apex, bitewing between teeth, and occlusal for larger areas. Dental films contain a silver halide emulsion layered between a transparent base and protective coating to capture x-ray images.