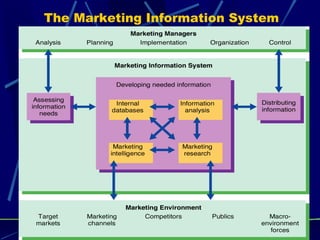
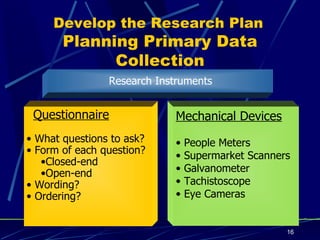
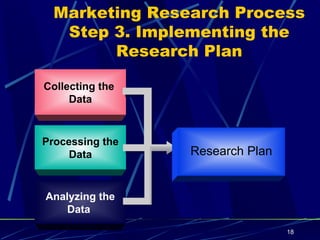
A marketing information system (MIS) consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, analyze, and distribute market information to help managers make decisions. The key functions of an MIS are to assess information needs, develop needed internal and external information through marketing research and intelligence, and distribute the right information to managers on time. The marketing research process involves defining problems, developing a research plan using secondary and primary data collection methods, implementing the research plan, and interpreting and reporting findings.