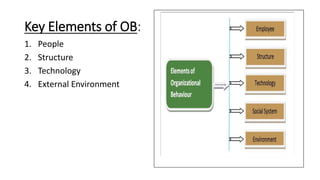
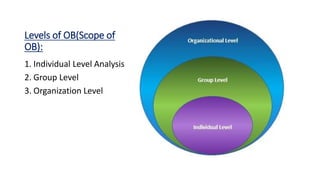
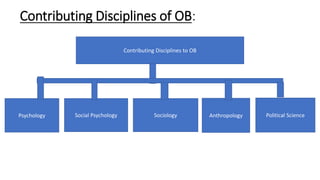
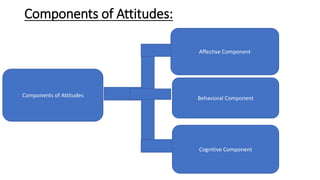
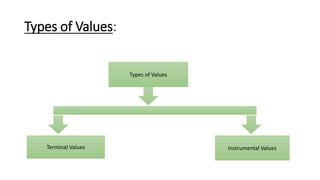
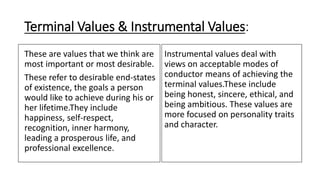
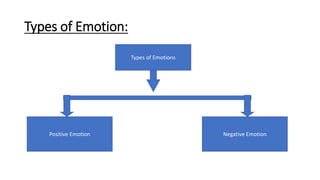
The document provides an introduction to organizational behavior. It defines OB as the study of human behavior in organizations. It discusses the key elements, importance, assumptions, levels, and contributing disciplines of OB. It also covers emerging trends, challenges, and models in OB. Specific topics summarized include attitudes, values, beliefs, and emotions.