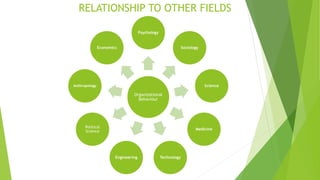
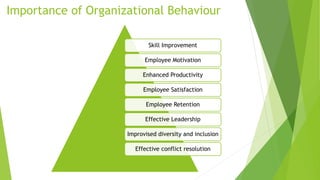
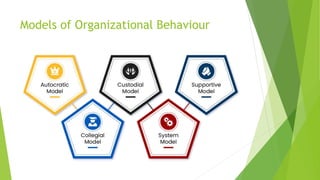
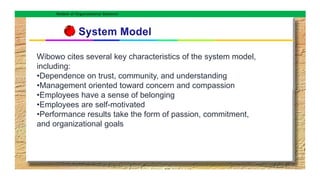
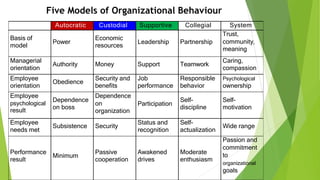
This document discusses five models of organizational behavior: autocratic, custodial, supportive, collegial, and system. It provides characteristics of each model, including their basis of power/control, managerial orientation, employee orientation, employee psychological results, and performance results. The system model emphasizes ethics, integrity, trust and community over economic goals. It aims to motivate self-actualized workers who find meaning and passion through achieving organizational goals.