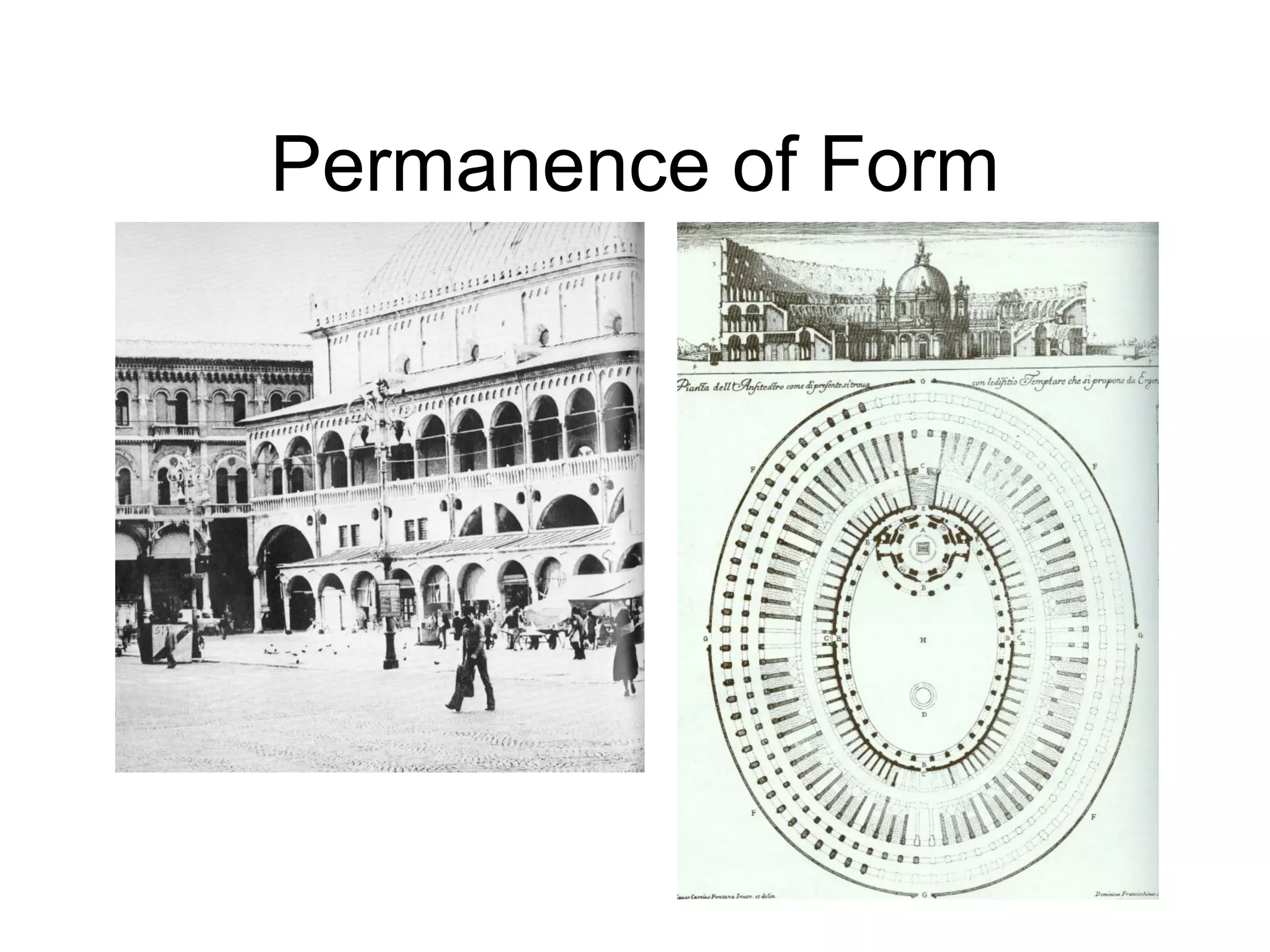
Aldo Rossi's 'The Architecture of the City' critiques functionalism and modernism, advocating for understanding cities through history, memory, and the permanence of form. It emphasizes the significance of autonomous monuments and collective memory in urban design, positioning architecture as a bridge between memory and society. Rossi's works illustrate that cities evolve over time, retaining their identity through adaptable forms and recognizable types.