Embed presentation
Download to read offline


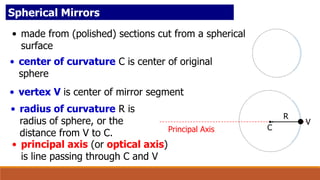
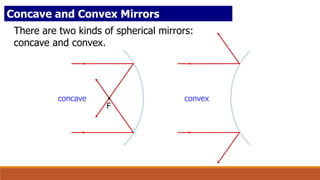
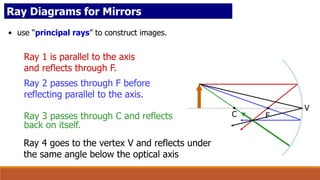

A concave mirror is a spherical mirror where the reflective surface is curved inward like the inside of a sphere. Ray diagrams can be used to find the image location by tracing the reflection of principal rays off the mirror through the center of curvature and focal point. The characteristics of an image formed by a concave mirror depend on the position of the object relative to the focal point of the mirror.





