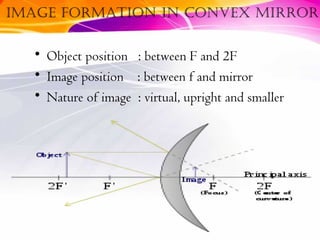
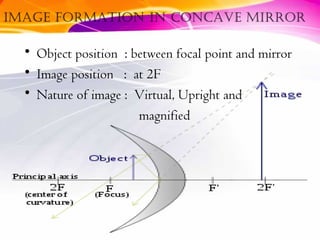
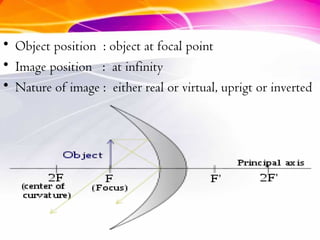
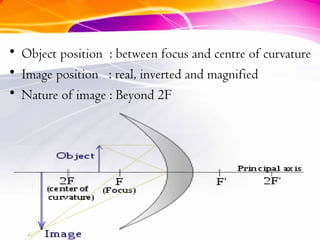
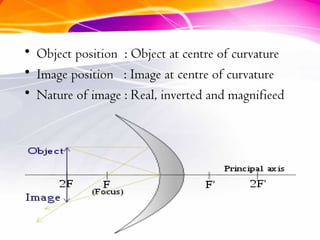
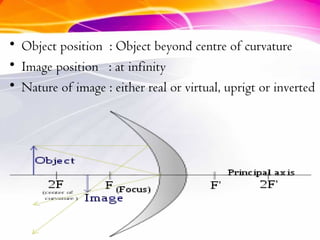
This document discusses curved mirrors and their properties. It notes that curved mirrors have surfaces shaped like parts of spheres and defines convex and concave mirrors. Convex mirrors bulge outward and produce virtual images, while concave mirrors bulge inward and can produce real or virtual images depending on the object position. Examples of uses of each type of mirror are provided, such as passenger side car mirrors using convex mirrors and telescopes and makeup mirrors using concave mirrors. The key differences in image formation between convex and concave mirrors are also summarized.