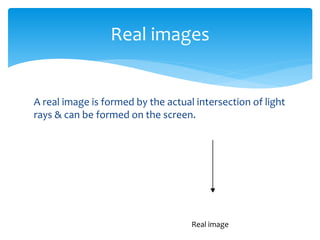
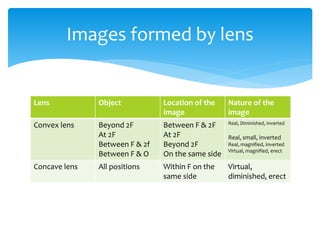
Light can travel through a vacuum and enables us to see. It exhibits rectilinear propagation, reflecting regularly off smooth surfaces and irregularly off rough surfaces. Images can be real, formed by the actual intersection of light rays, or virtual, formed behind a mirror but not by the actual intersection of rays. Spherical mirrors can be concave or convex and have defined optical characteristics. Concave mirrors form enlarged images close to the mirror and diminished ones further away. Convex mirrors always form diminished, erect images. Lenses come in converging and diverging types and also have specific optical properties depending on the position of objects in relation to the focal point.