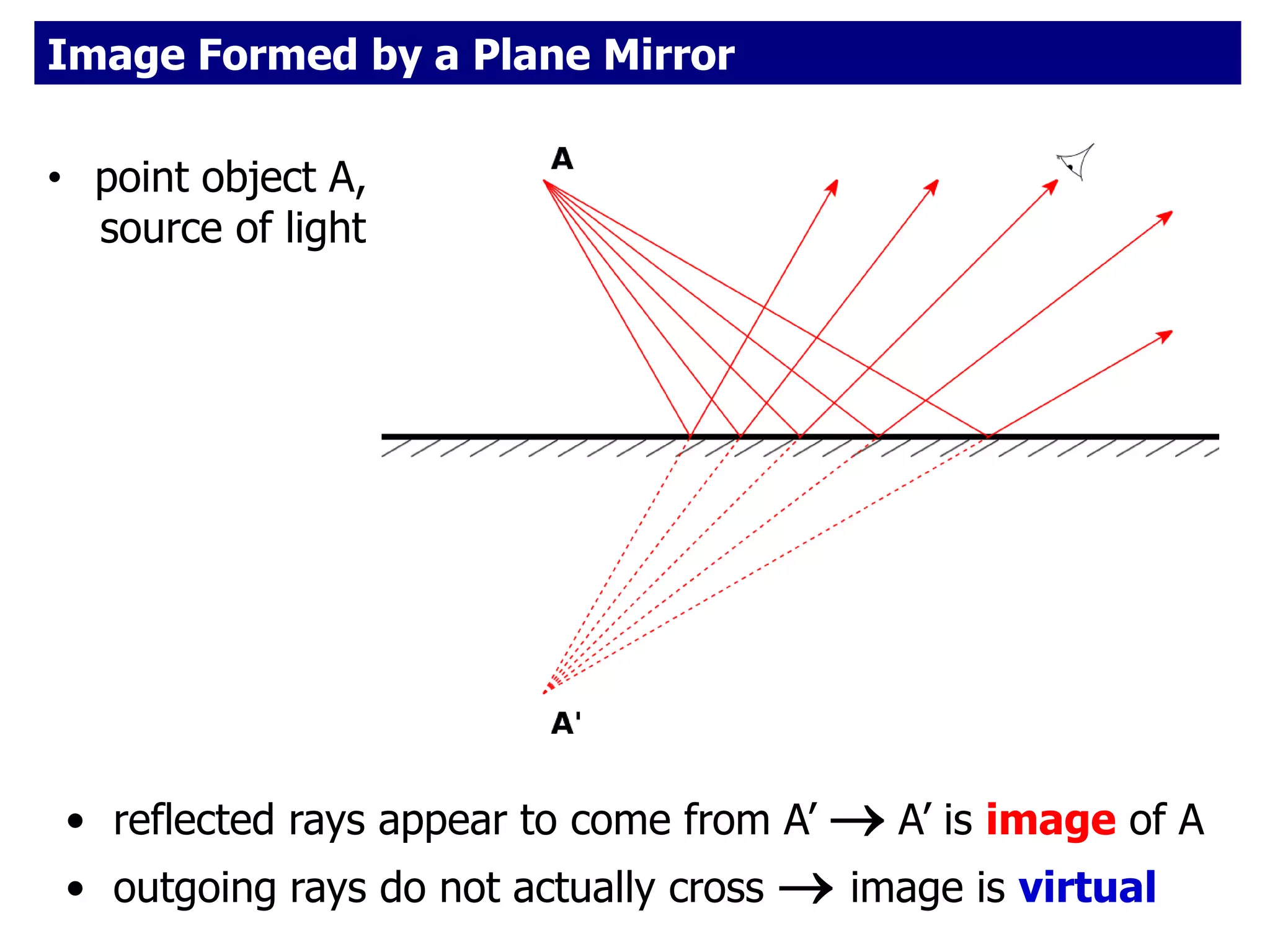
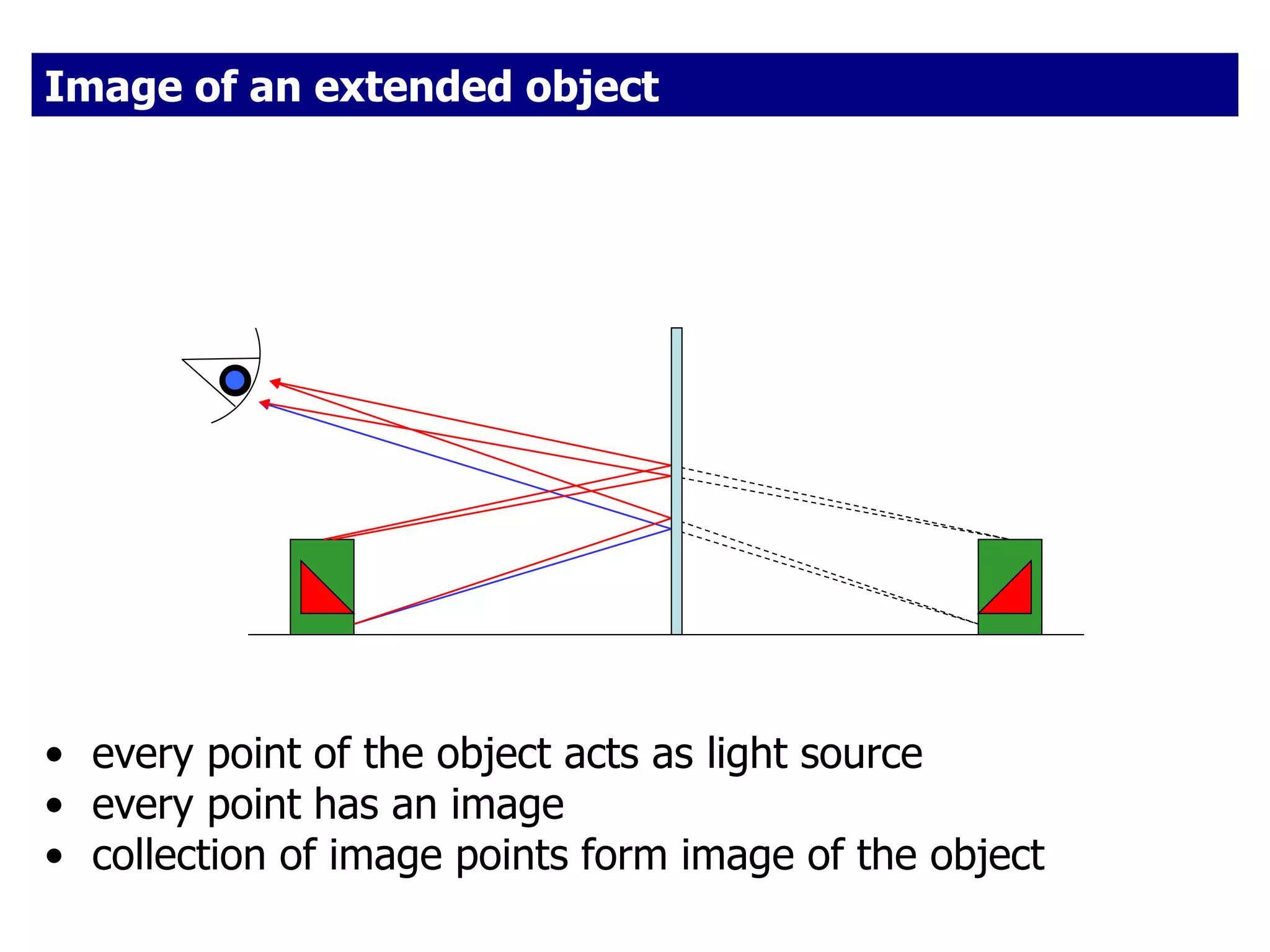
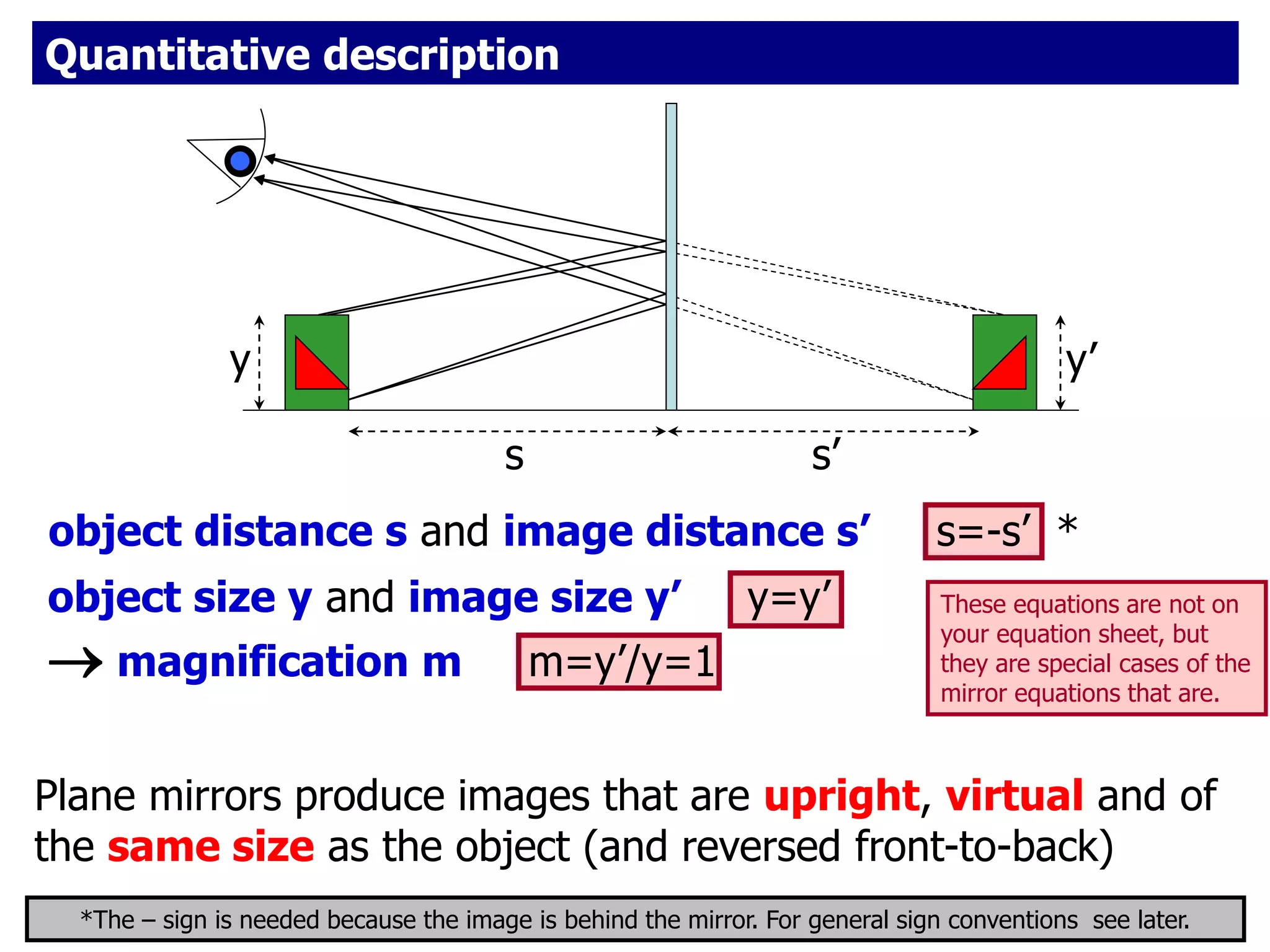
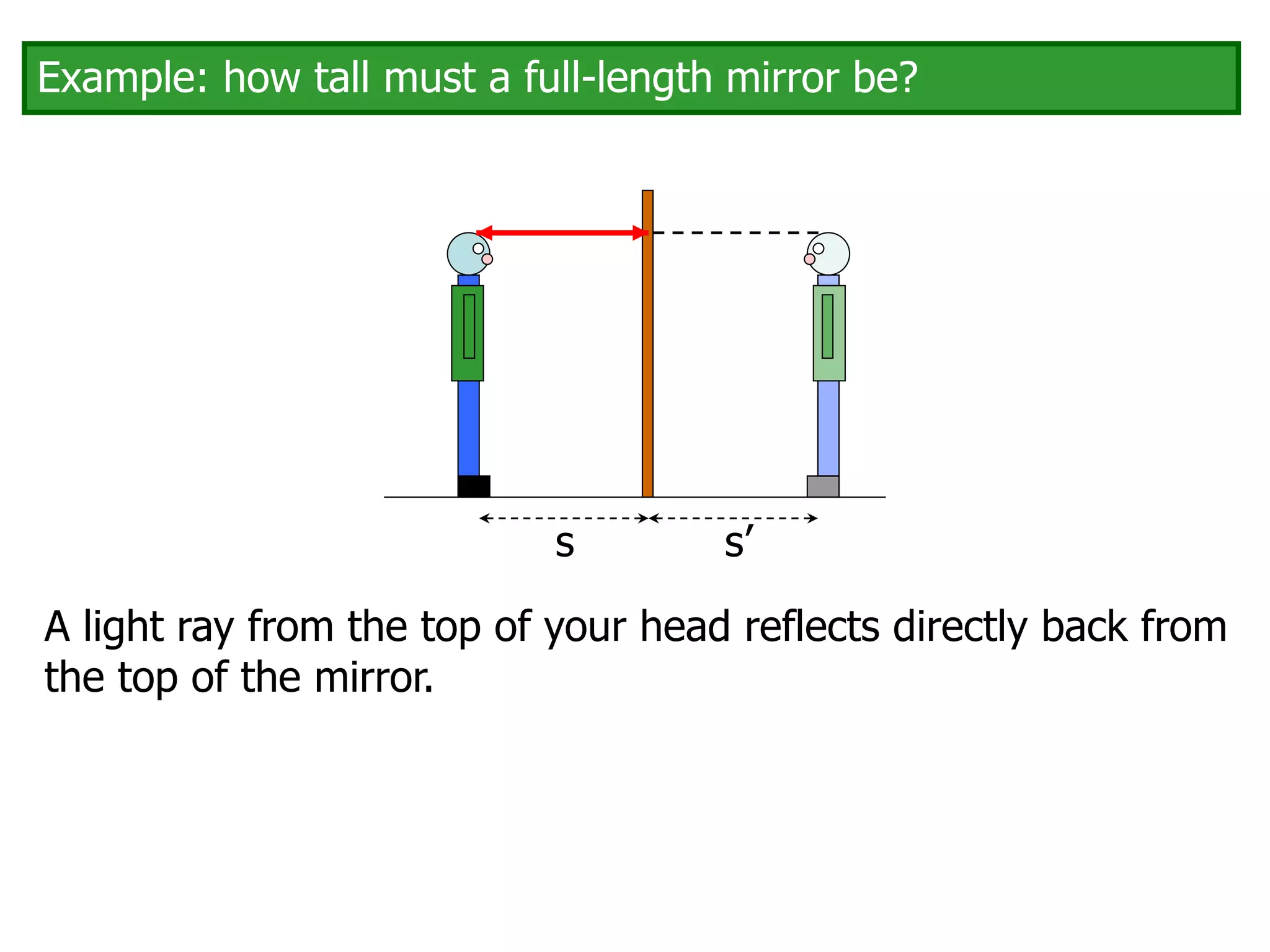
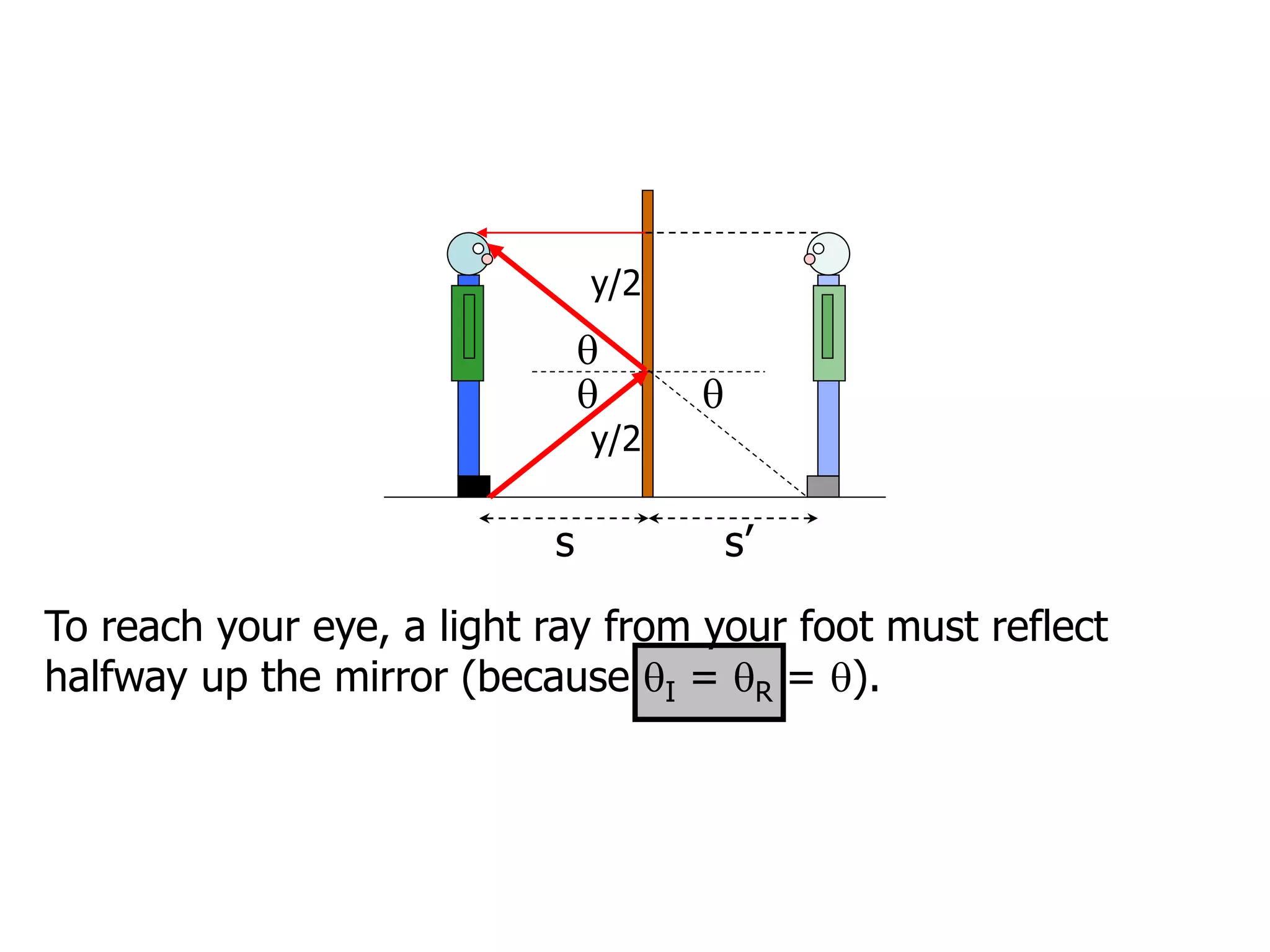
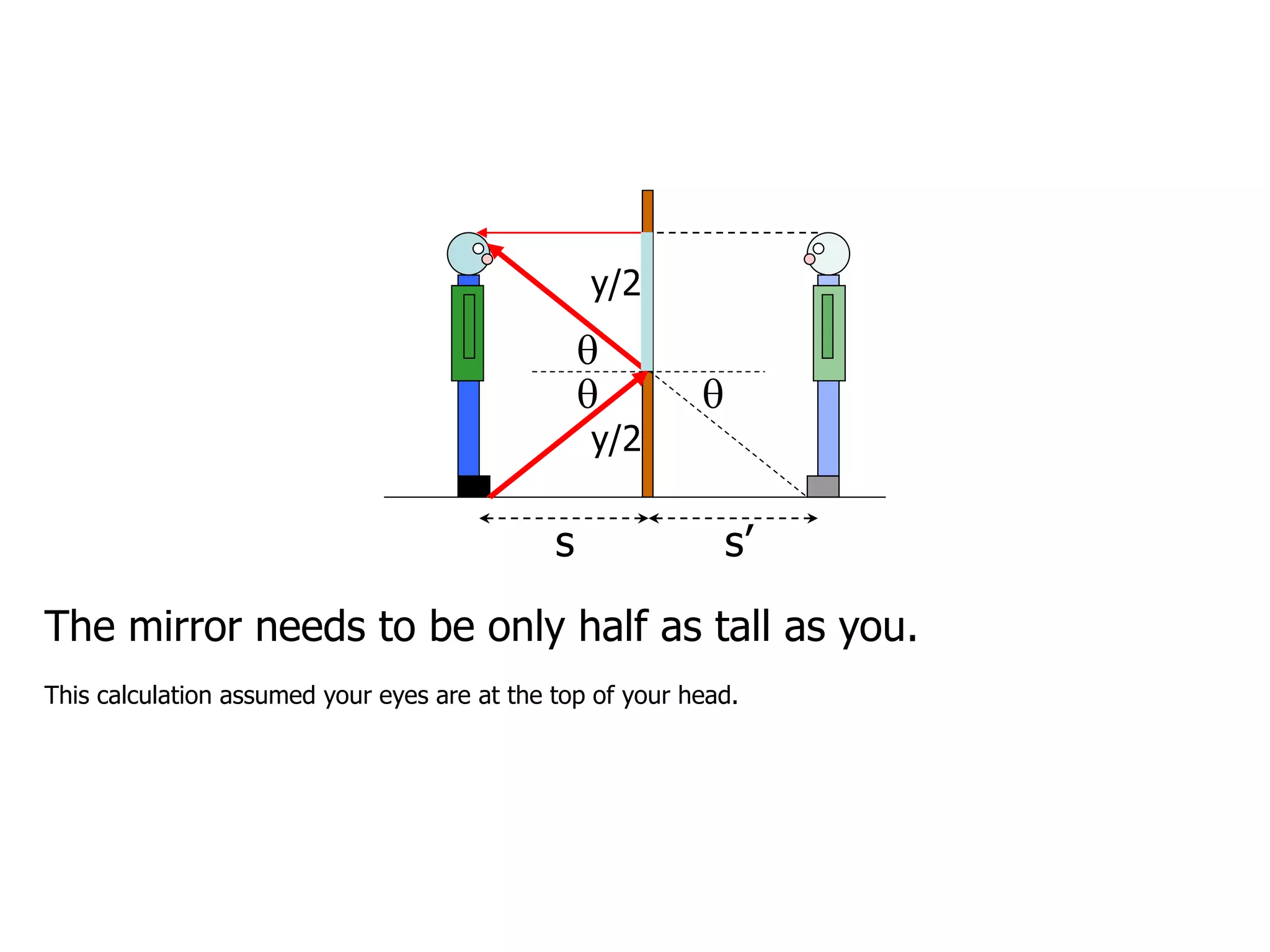
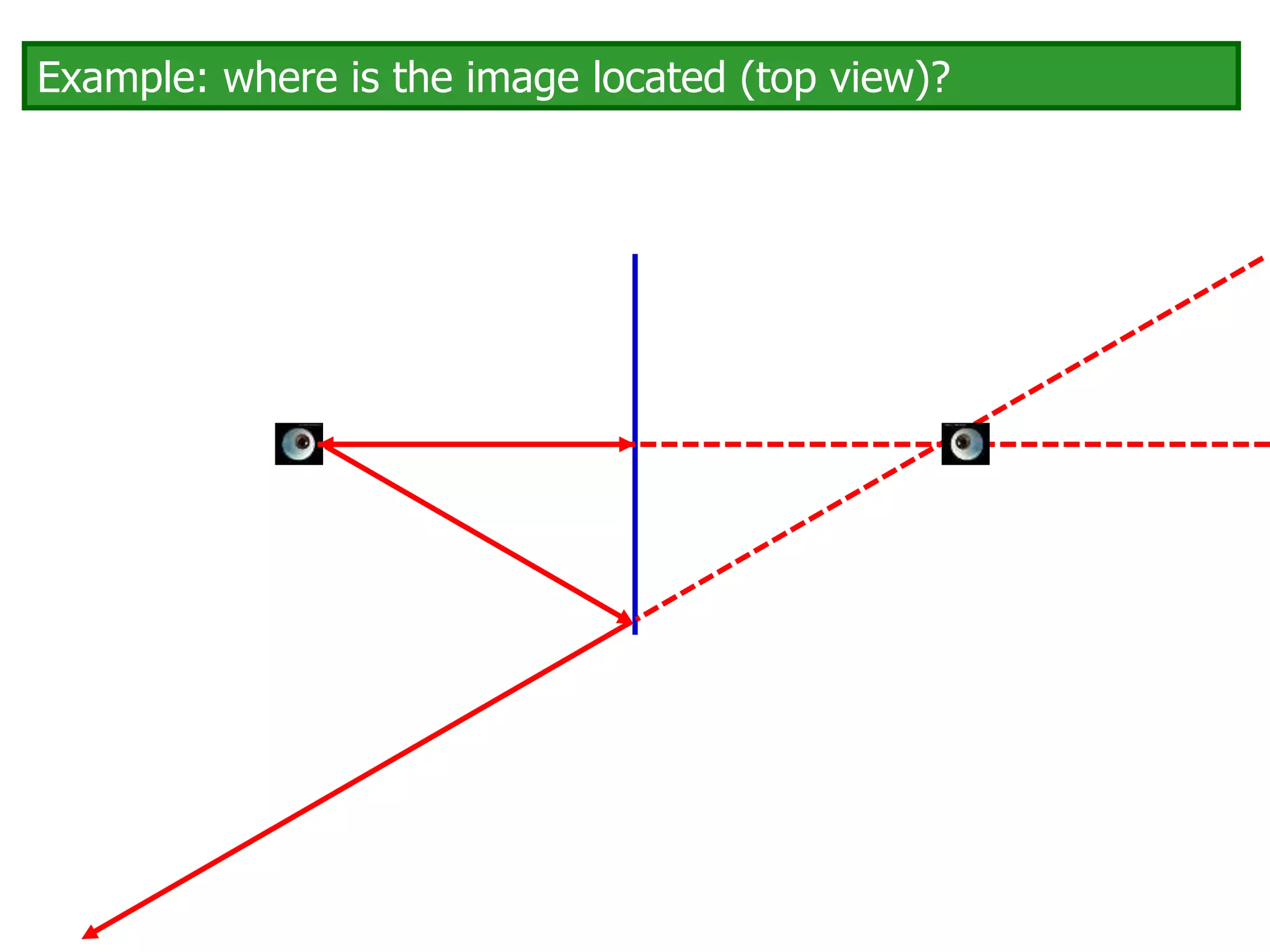
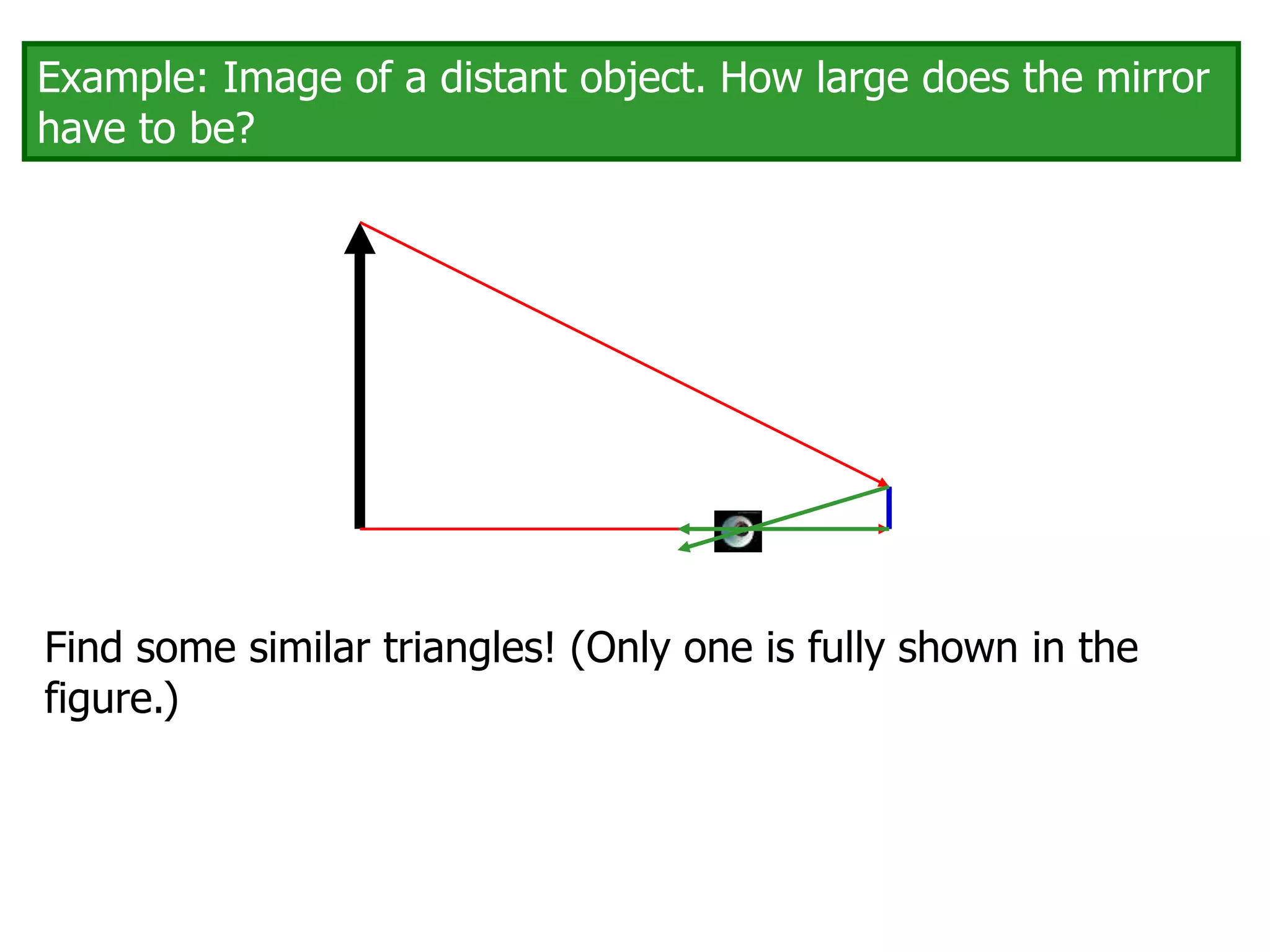
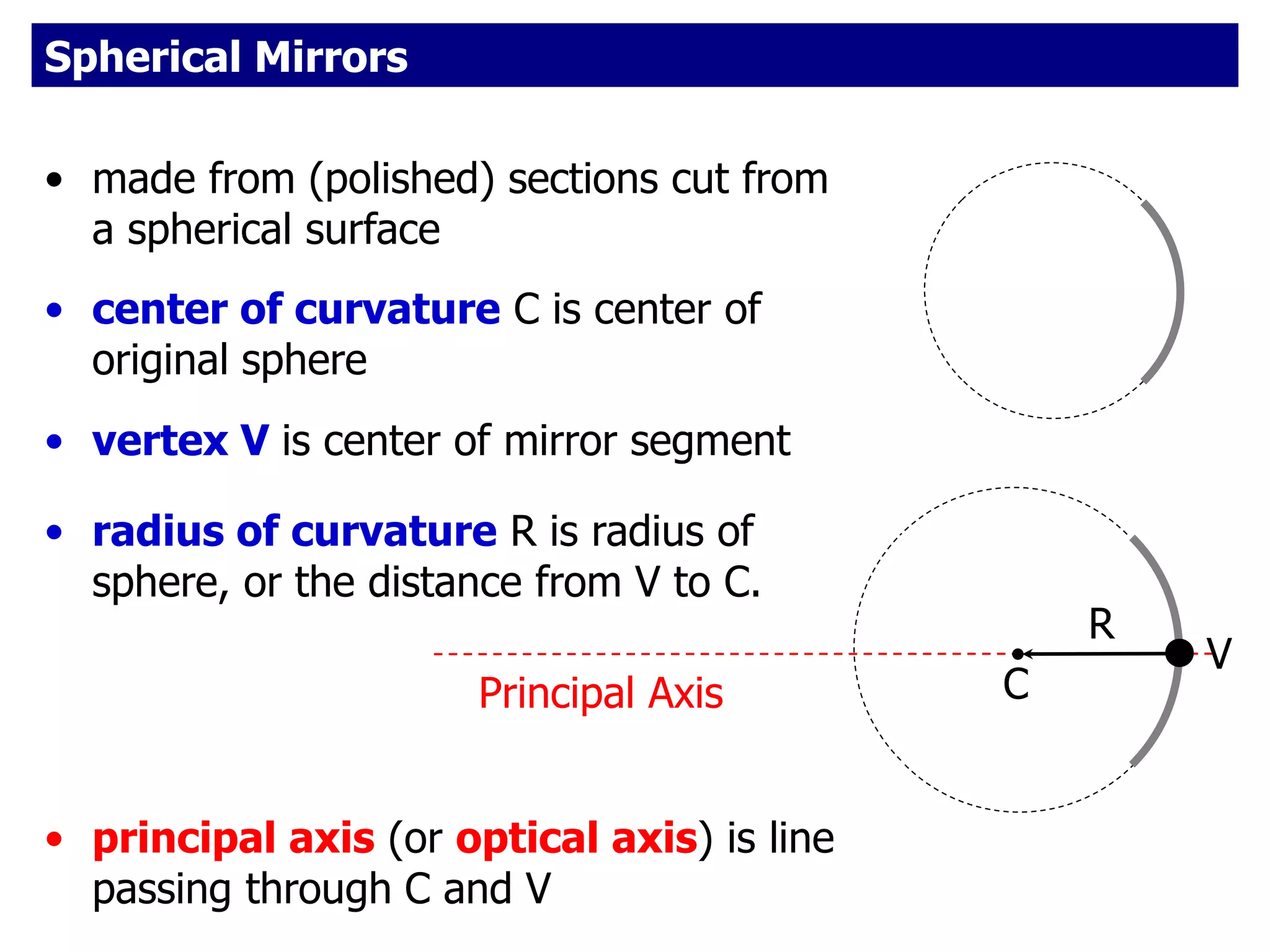
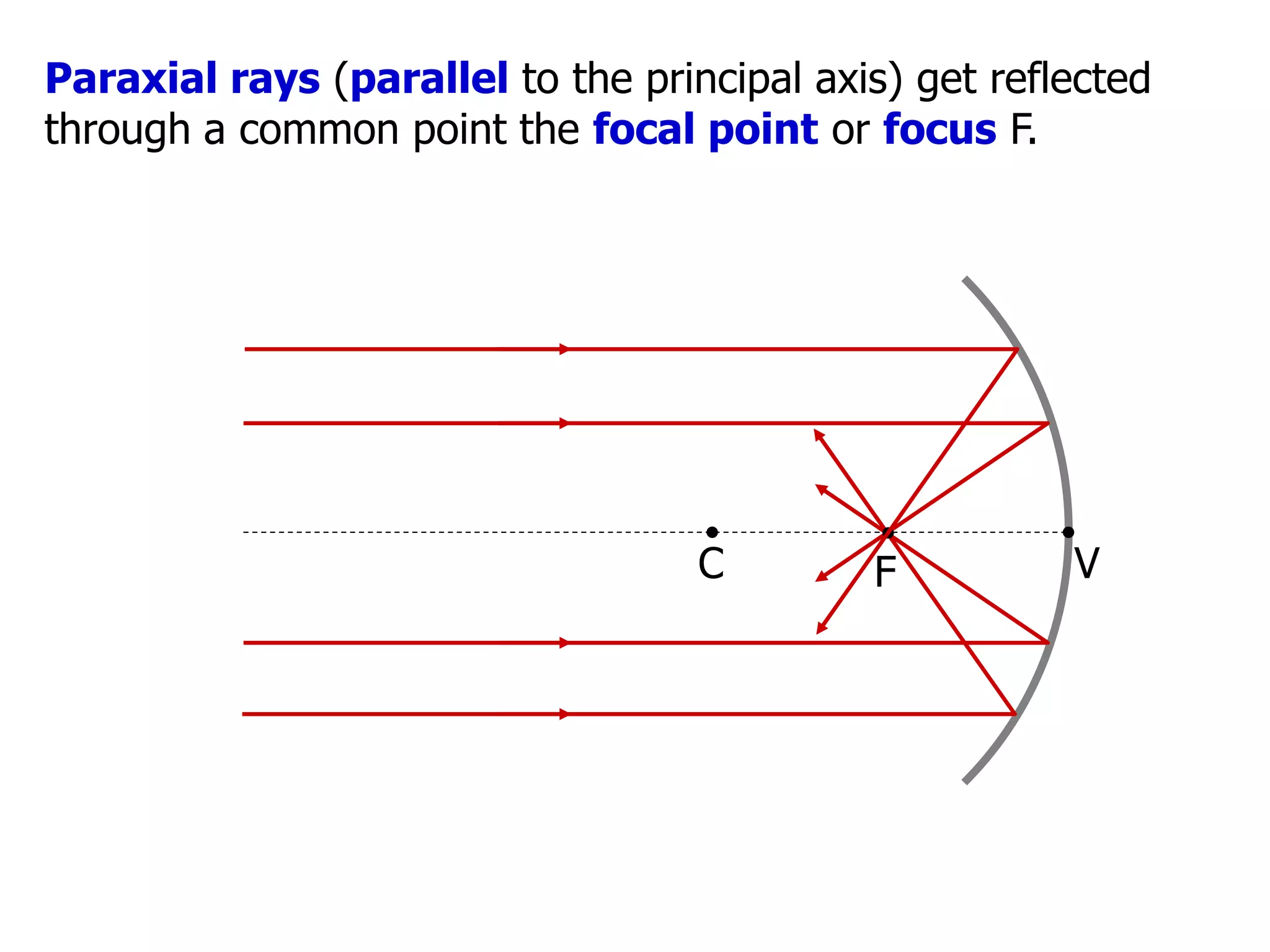
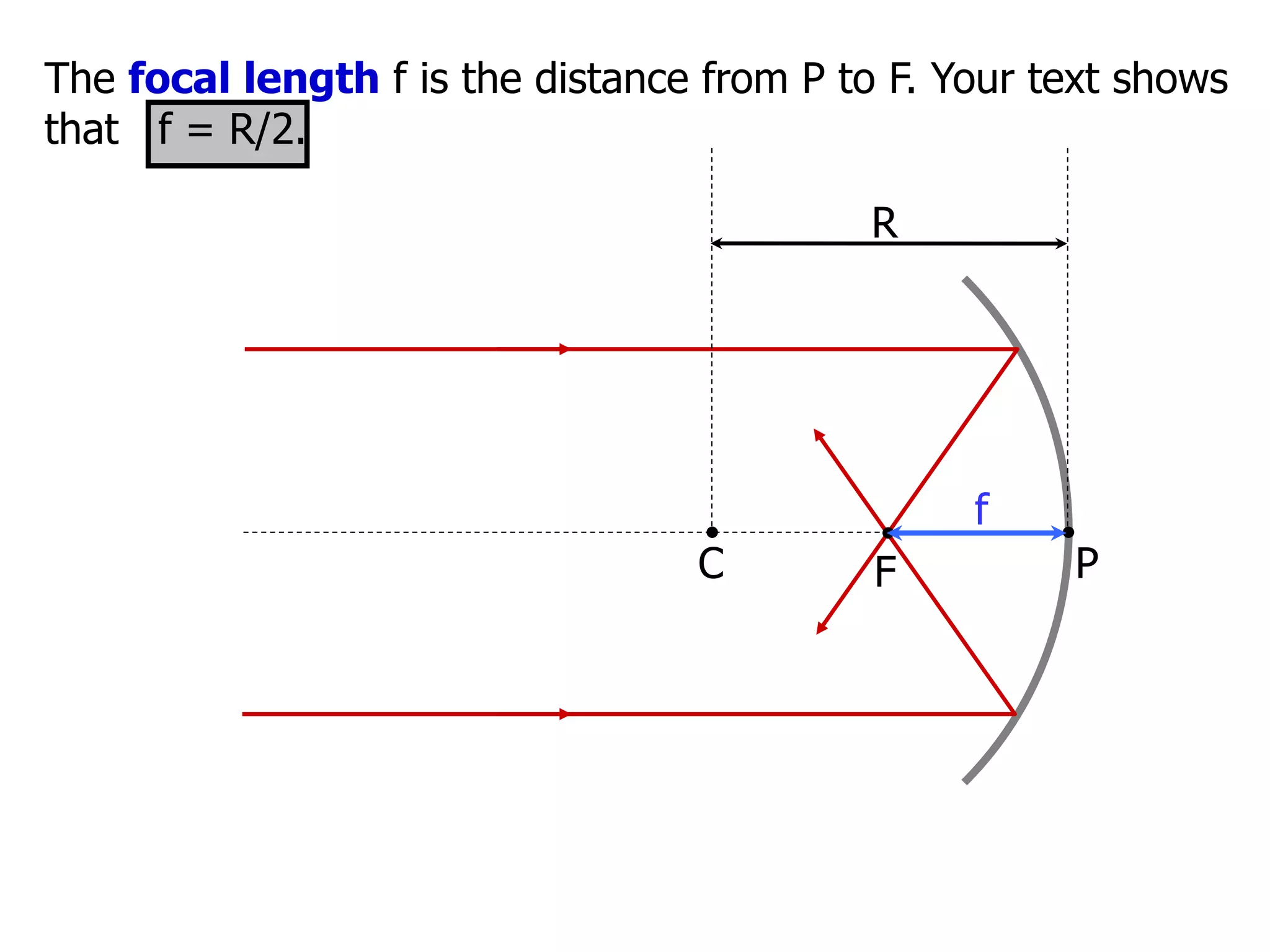
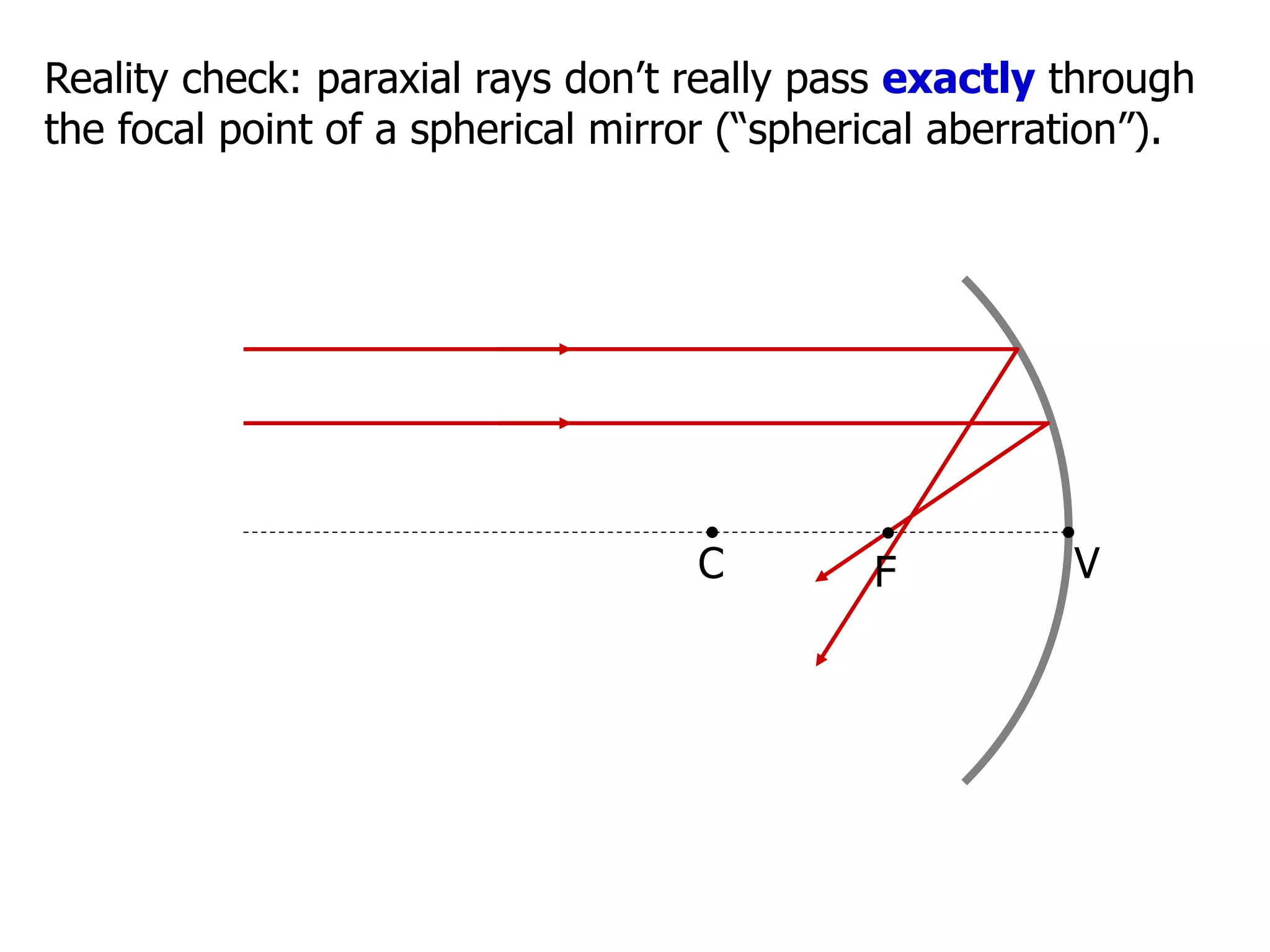
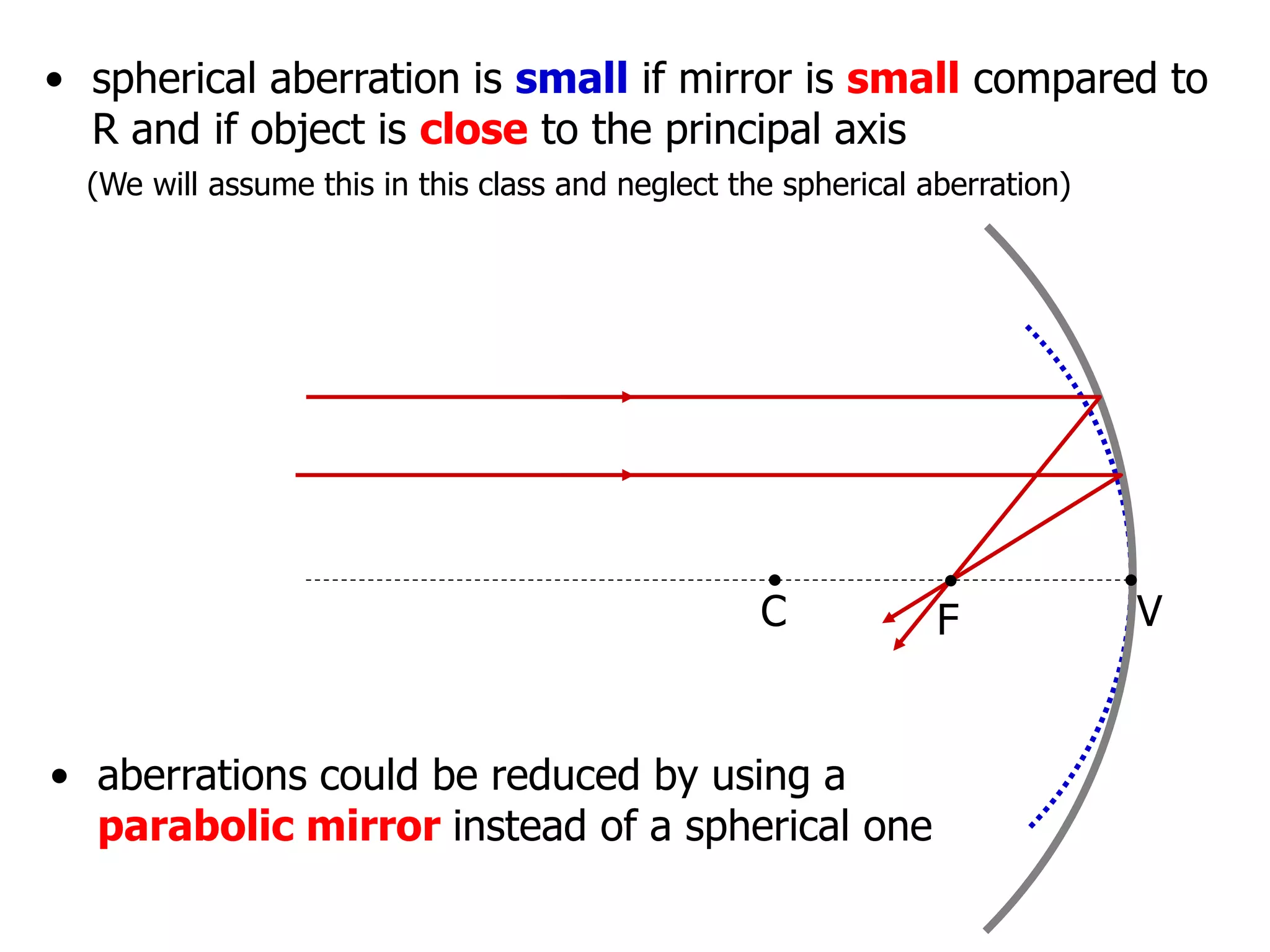
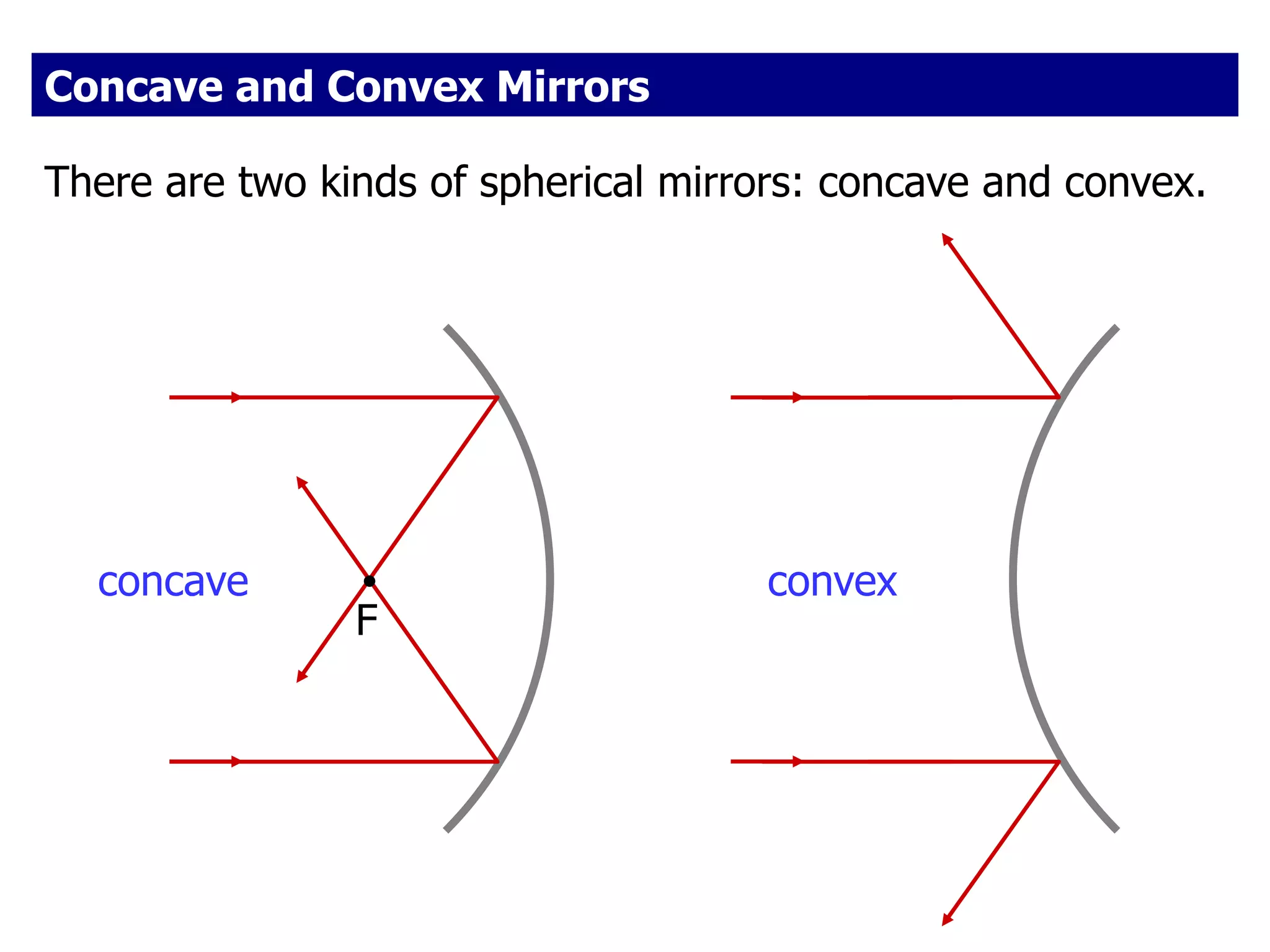
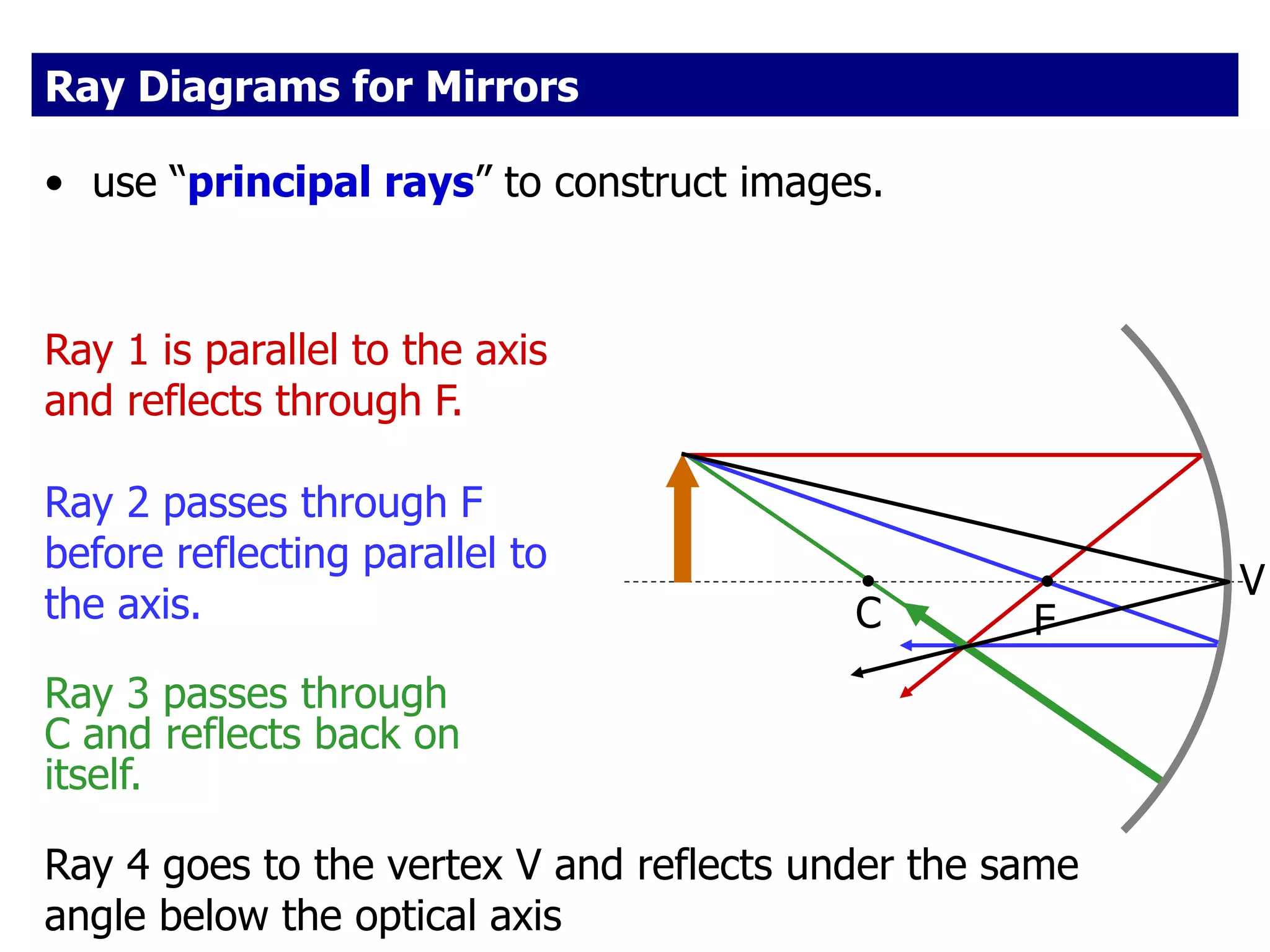
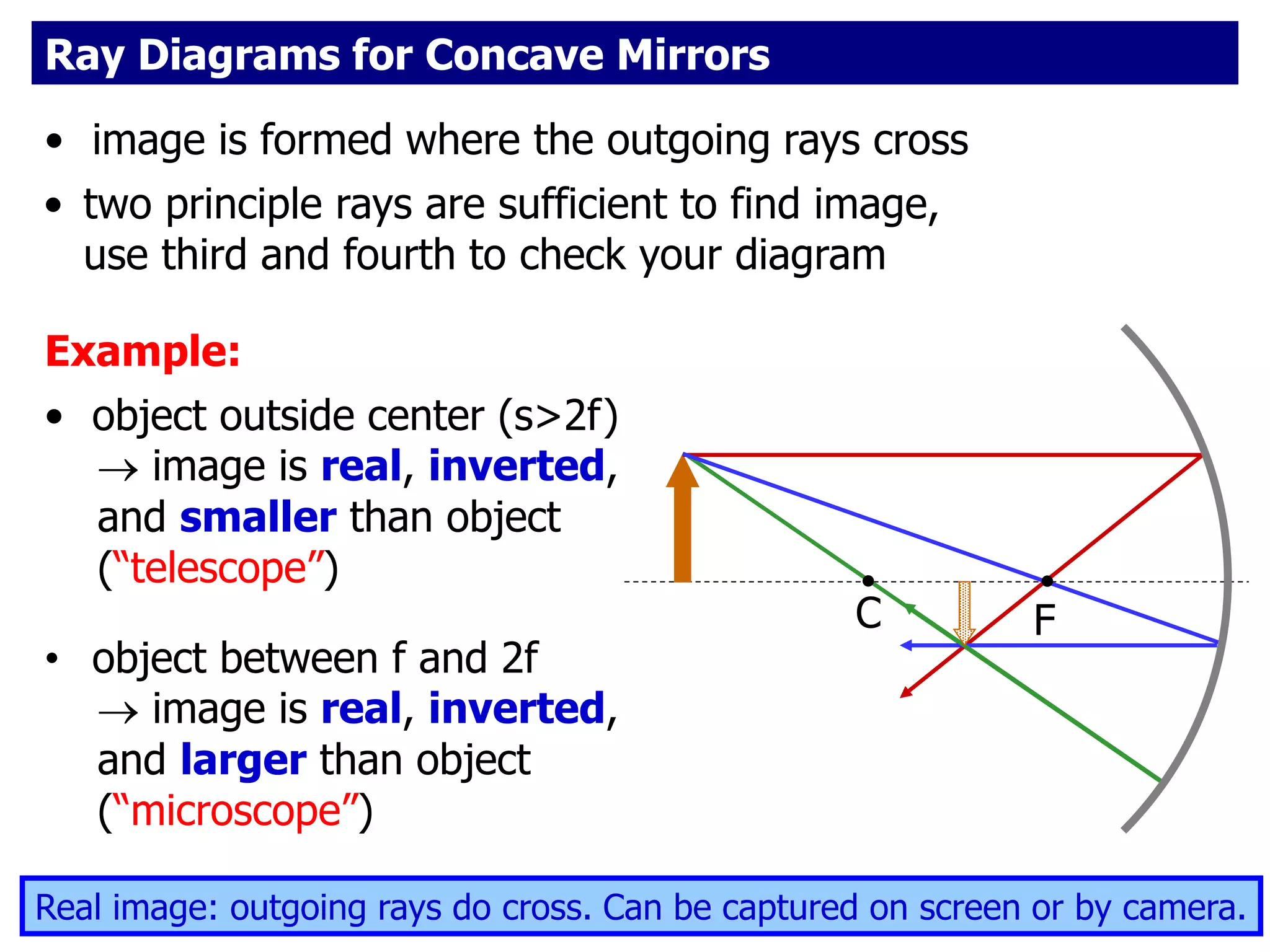
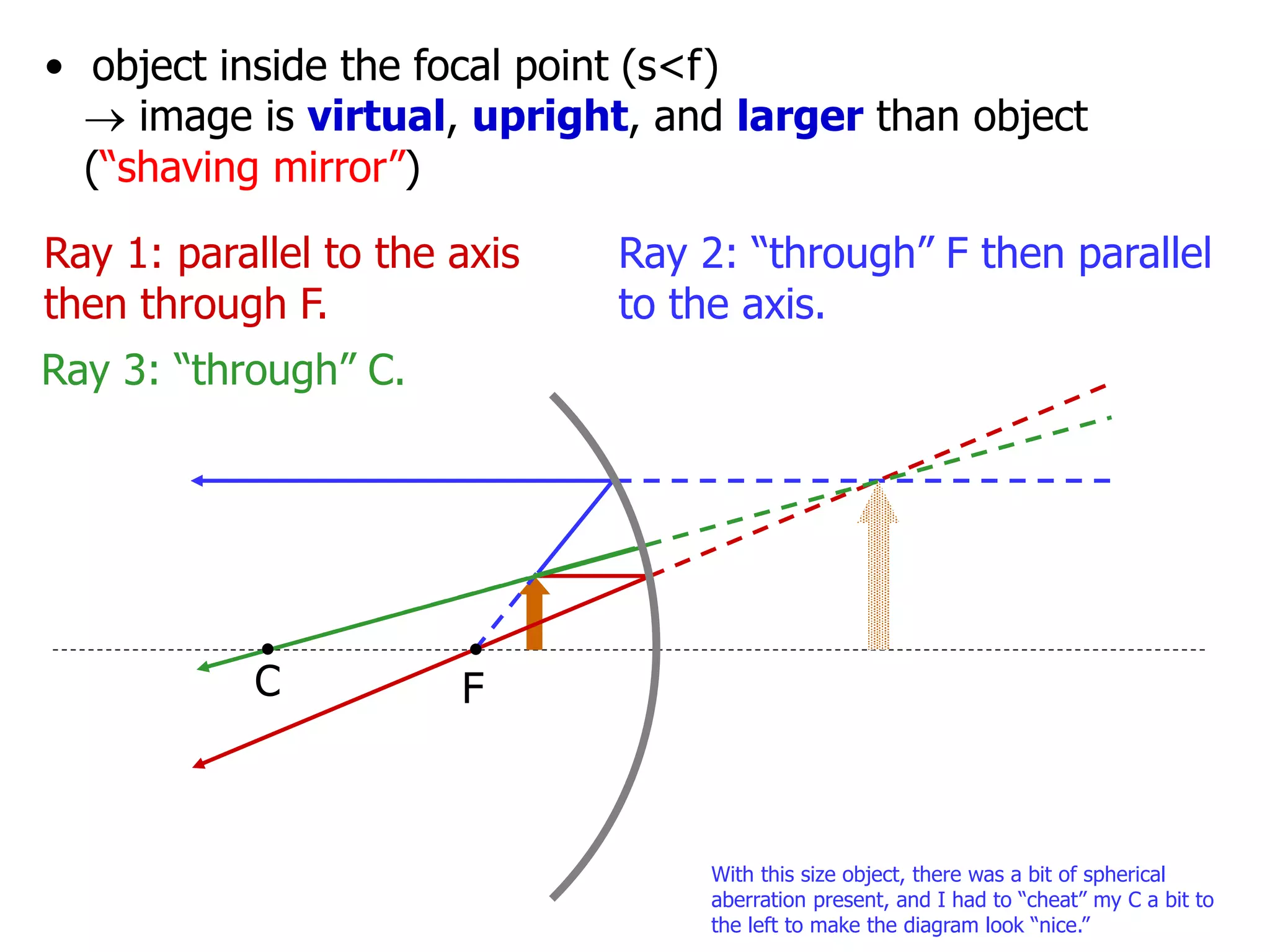
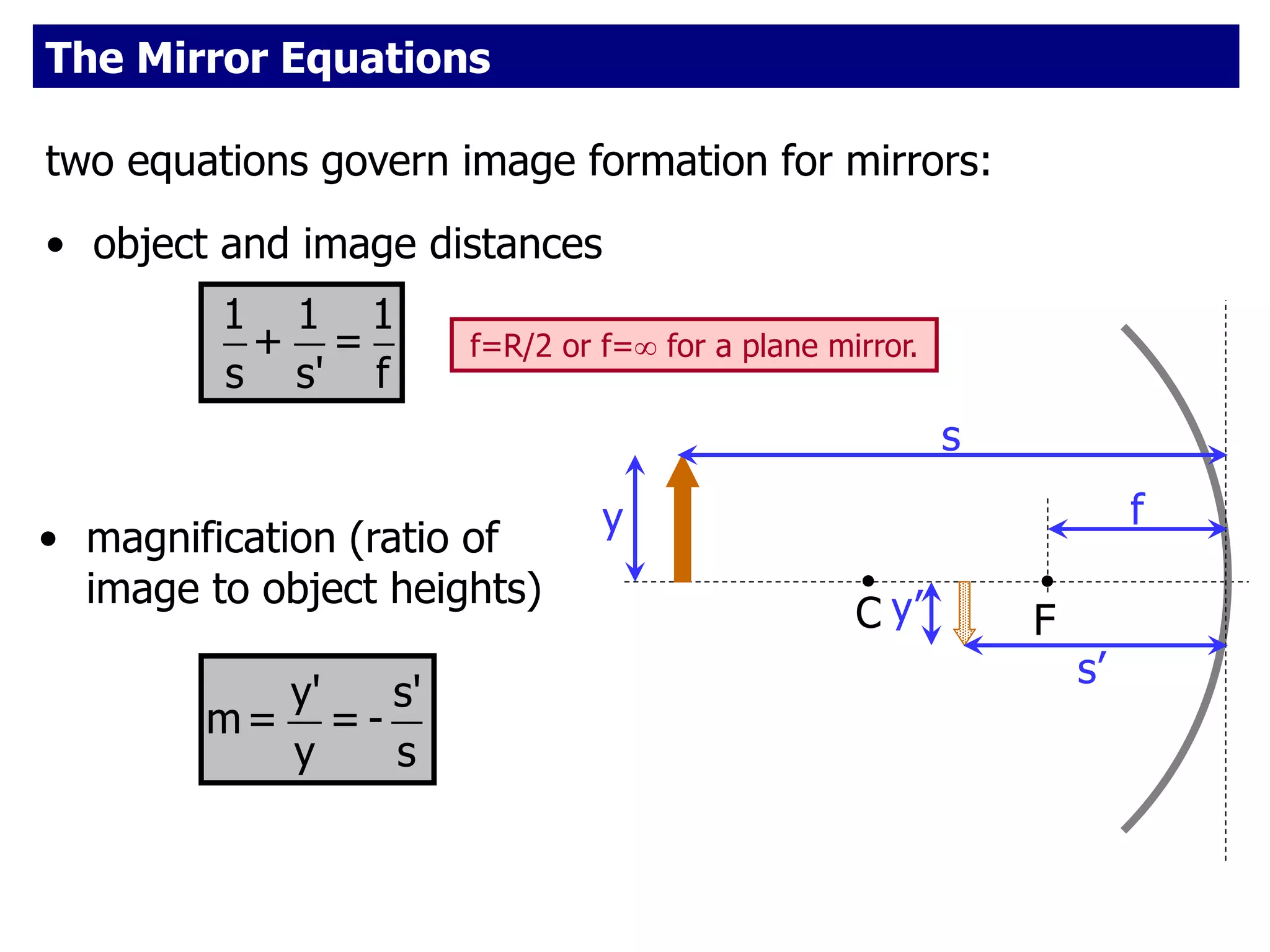
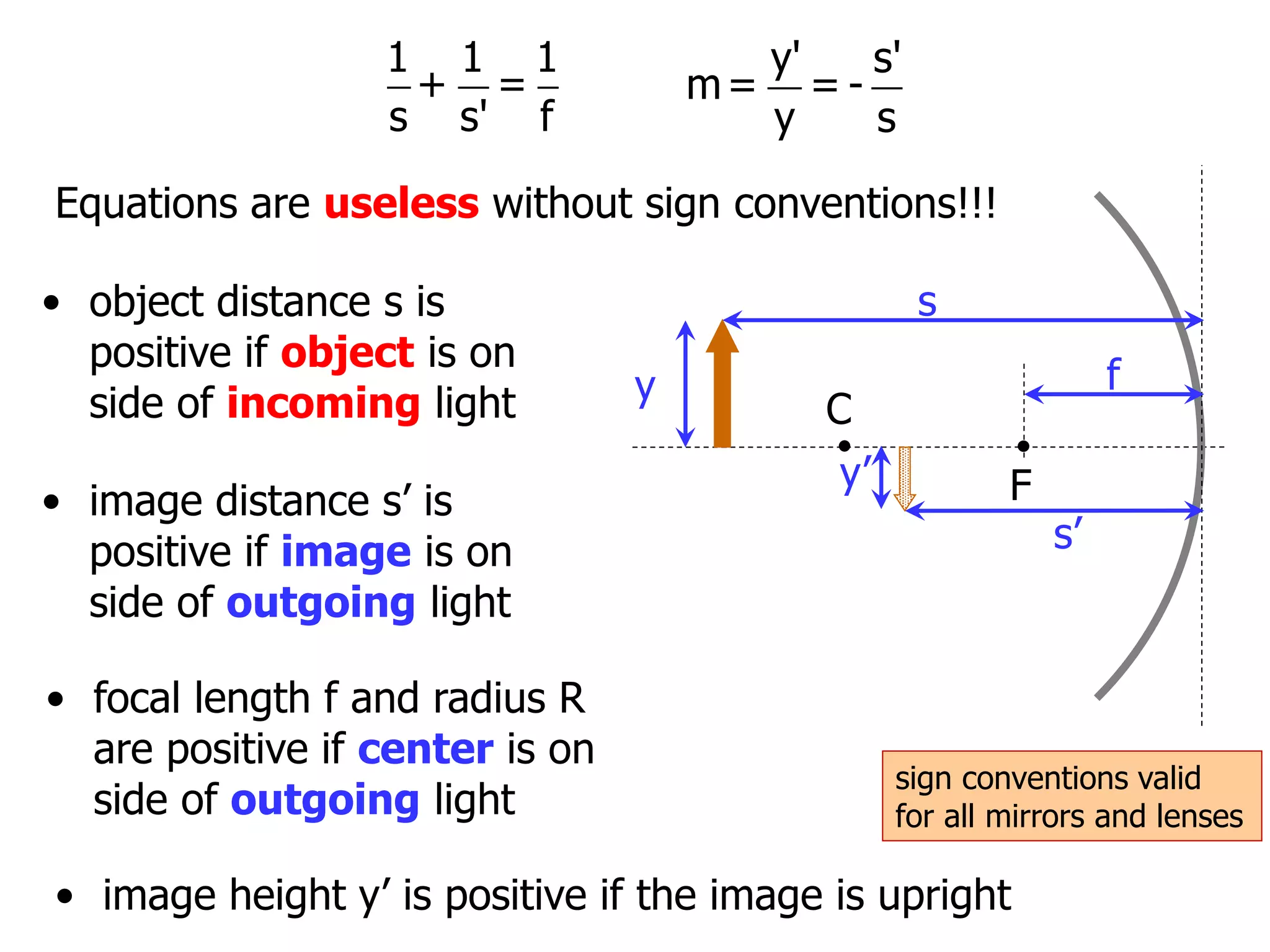
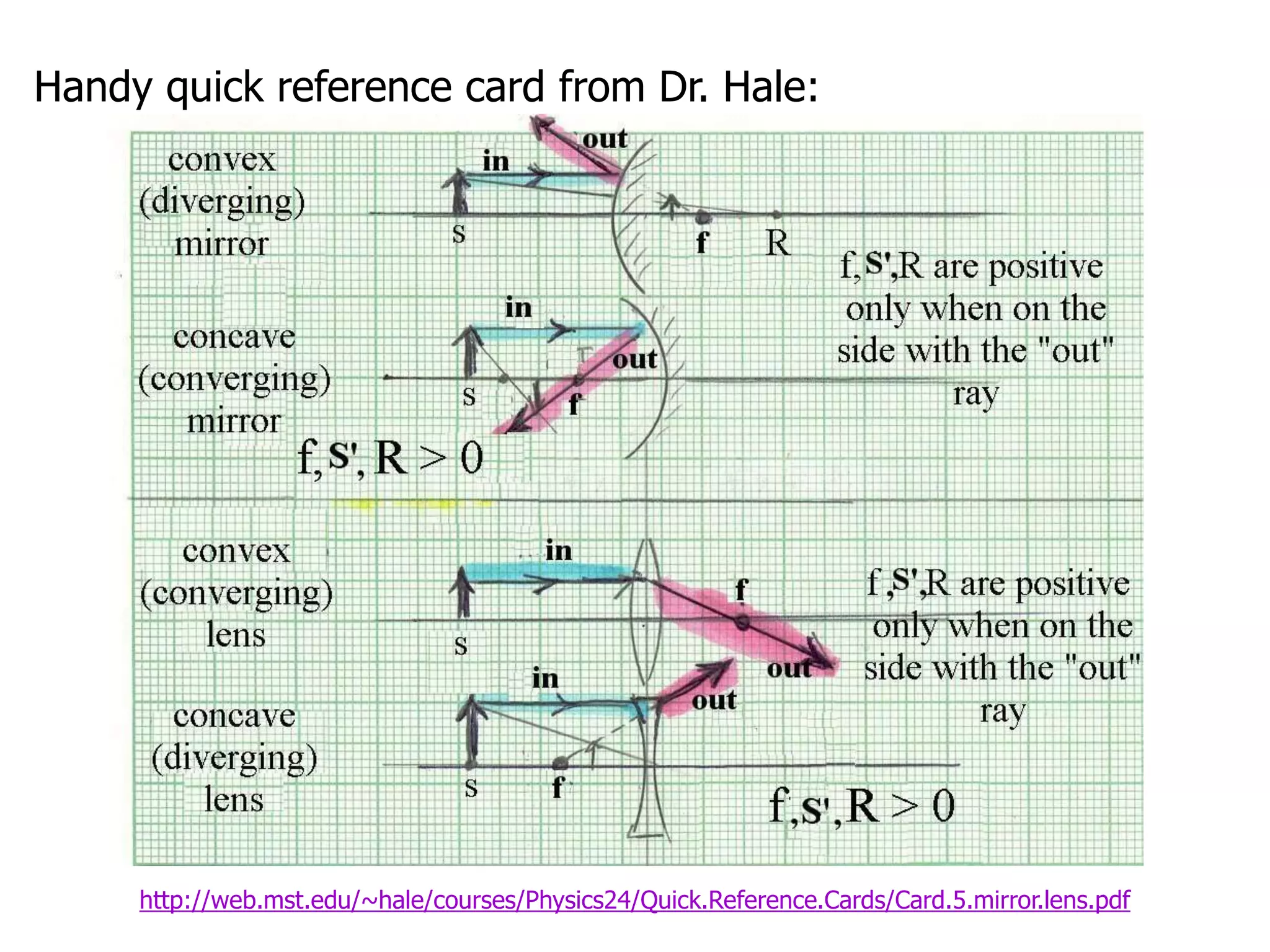
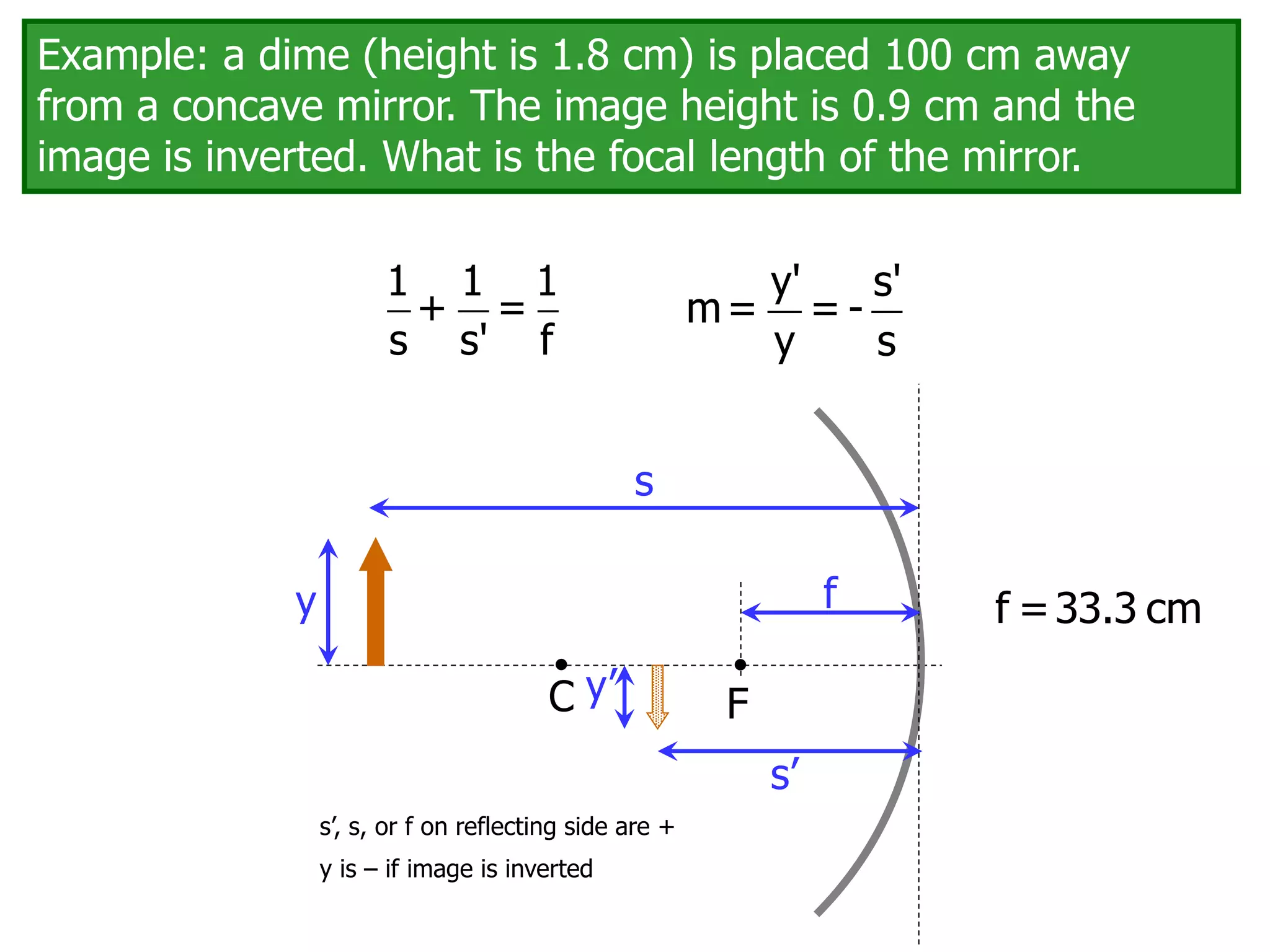
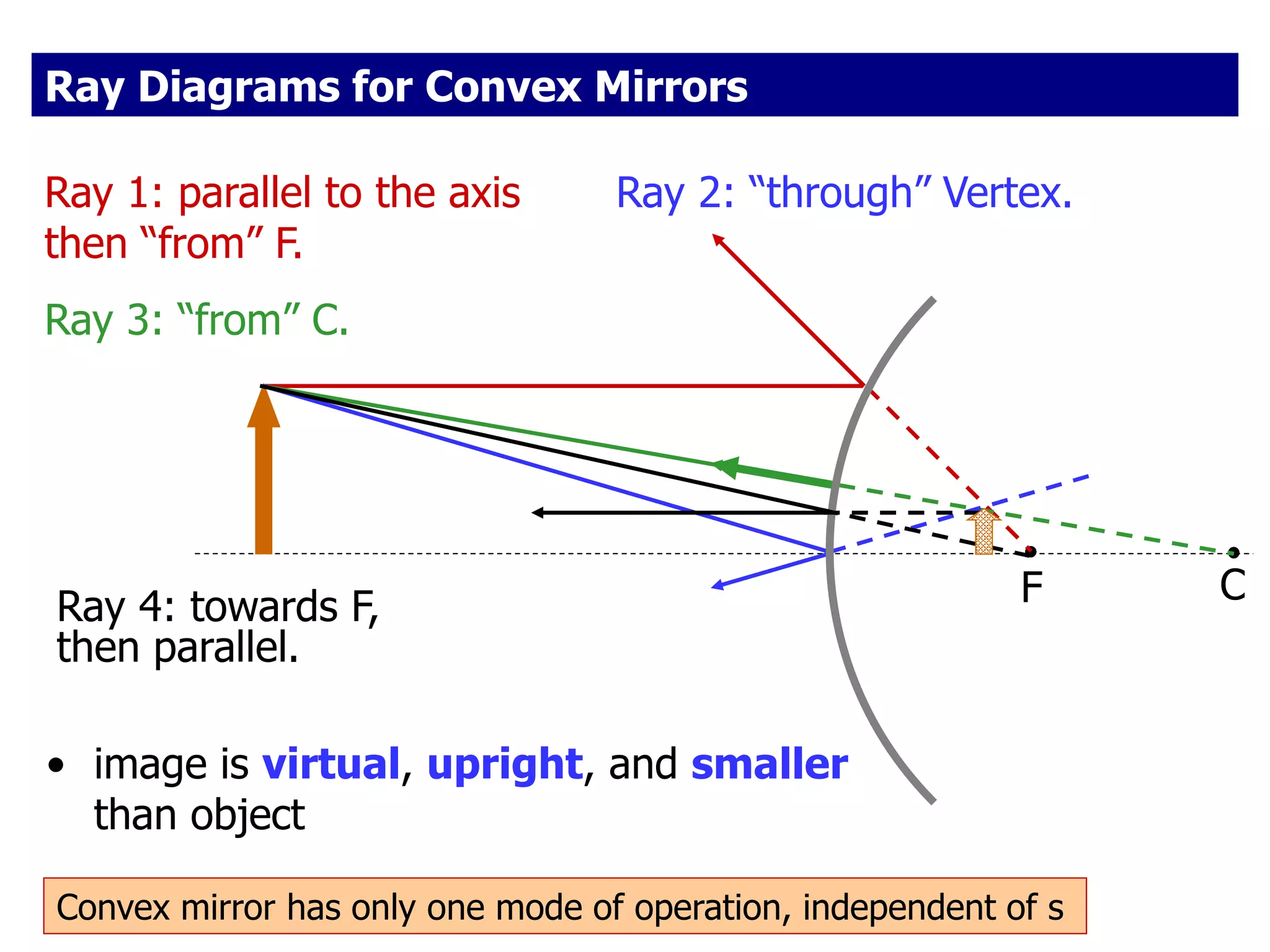
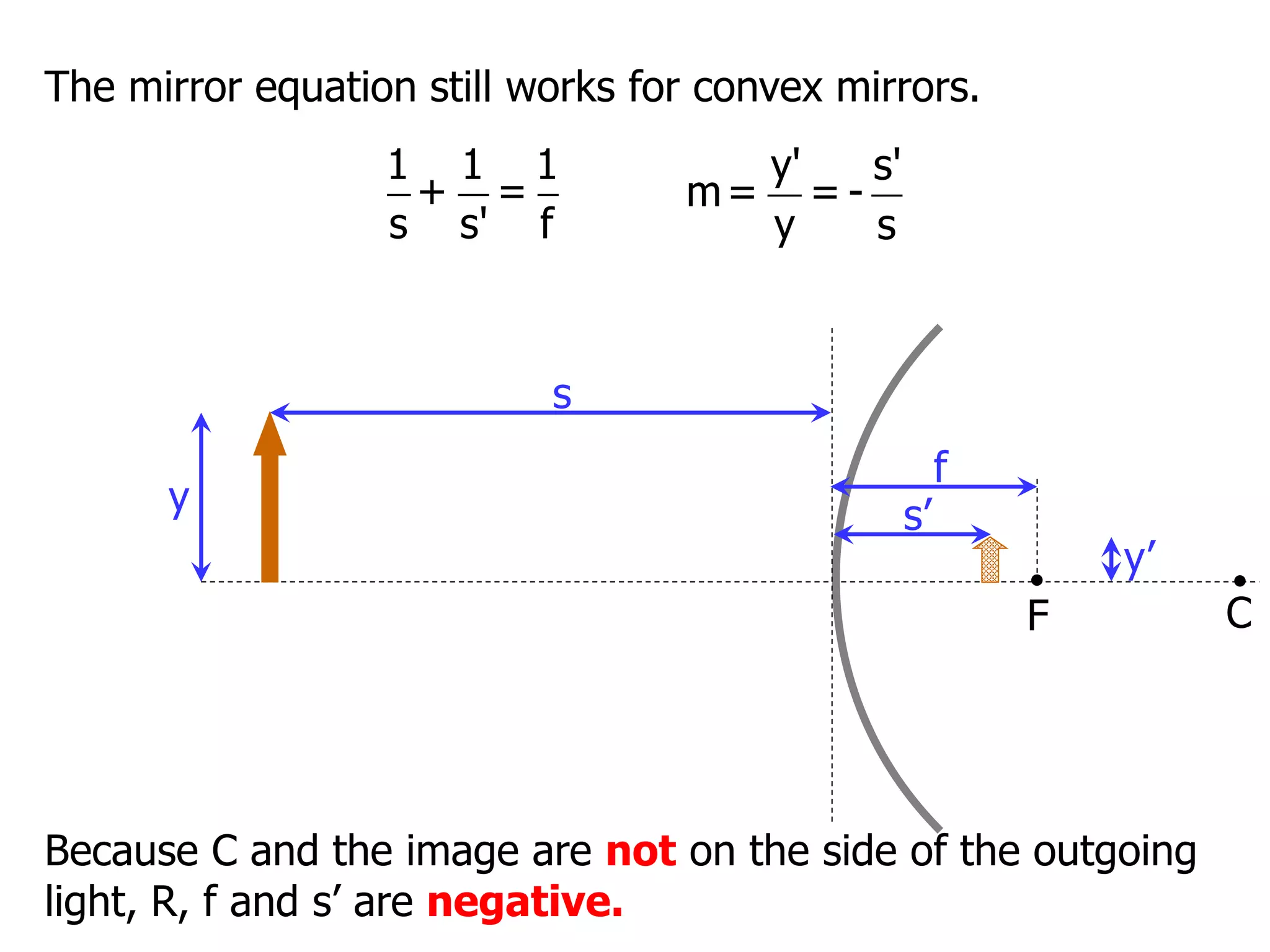
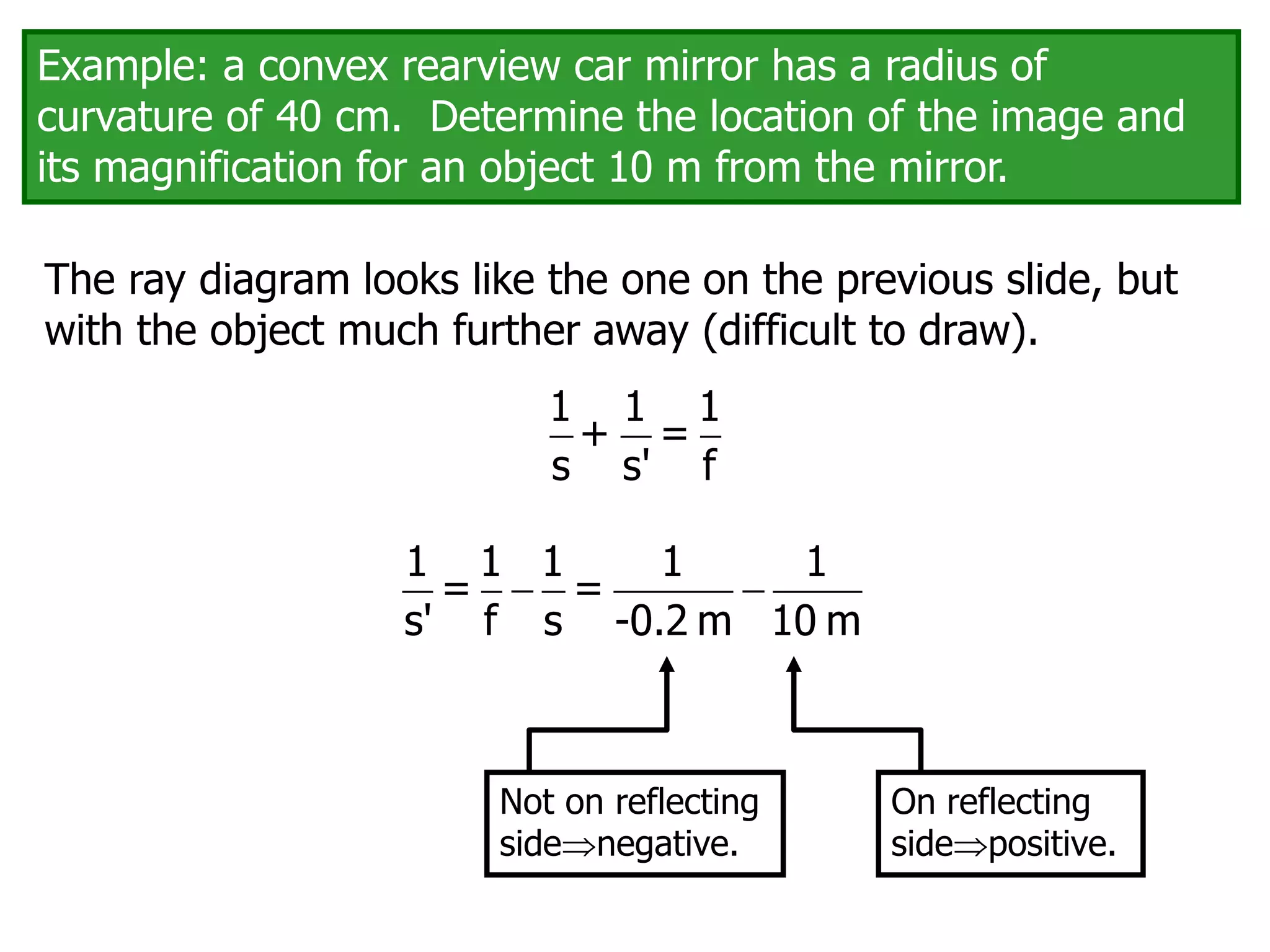
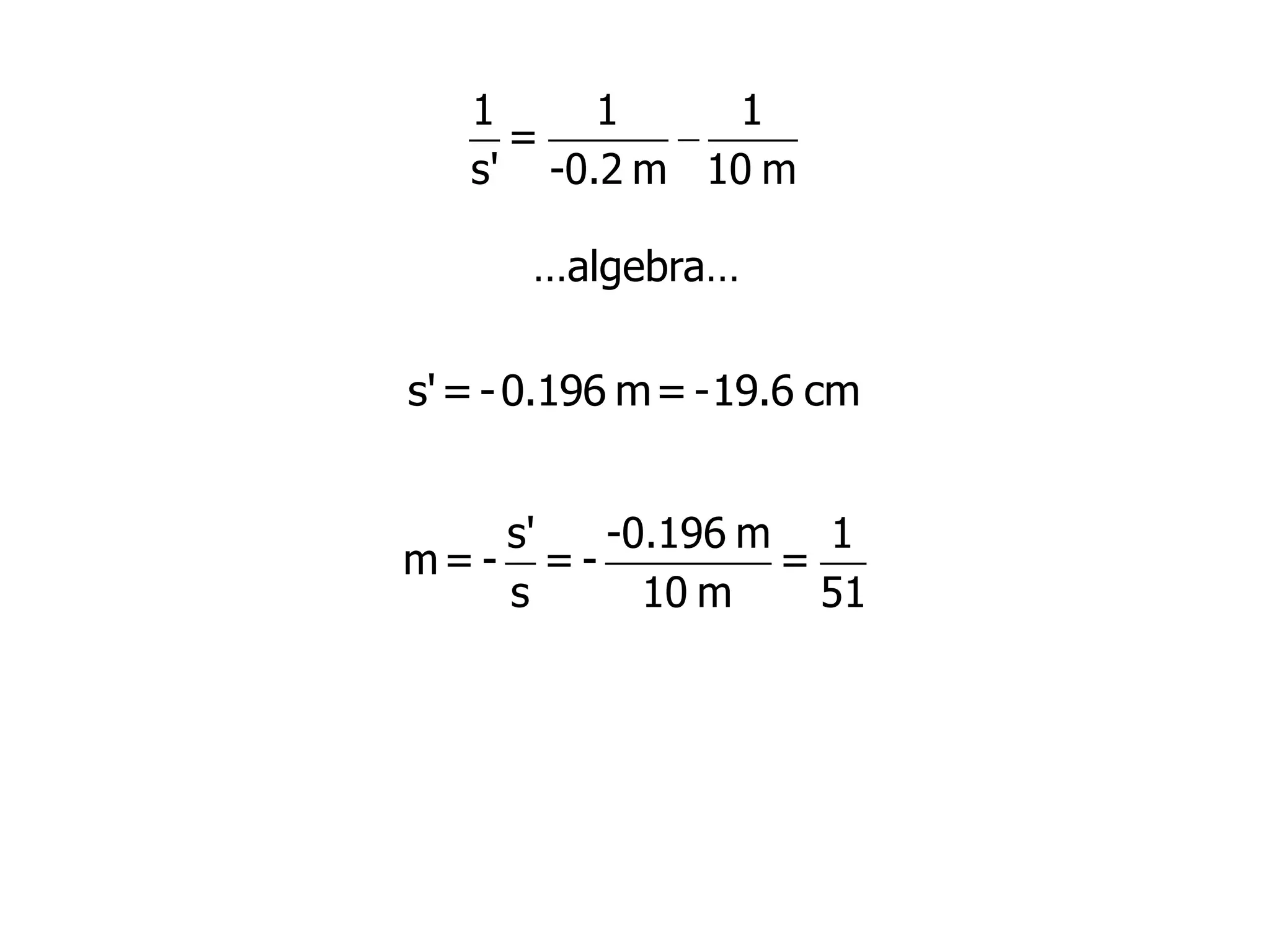
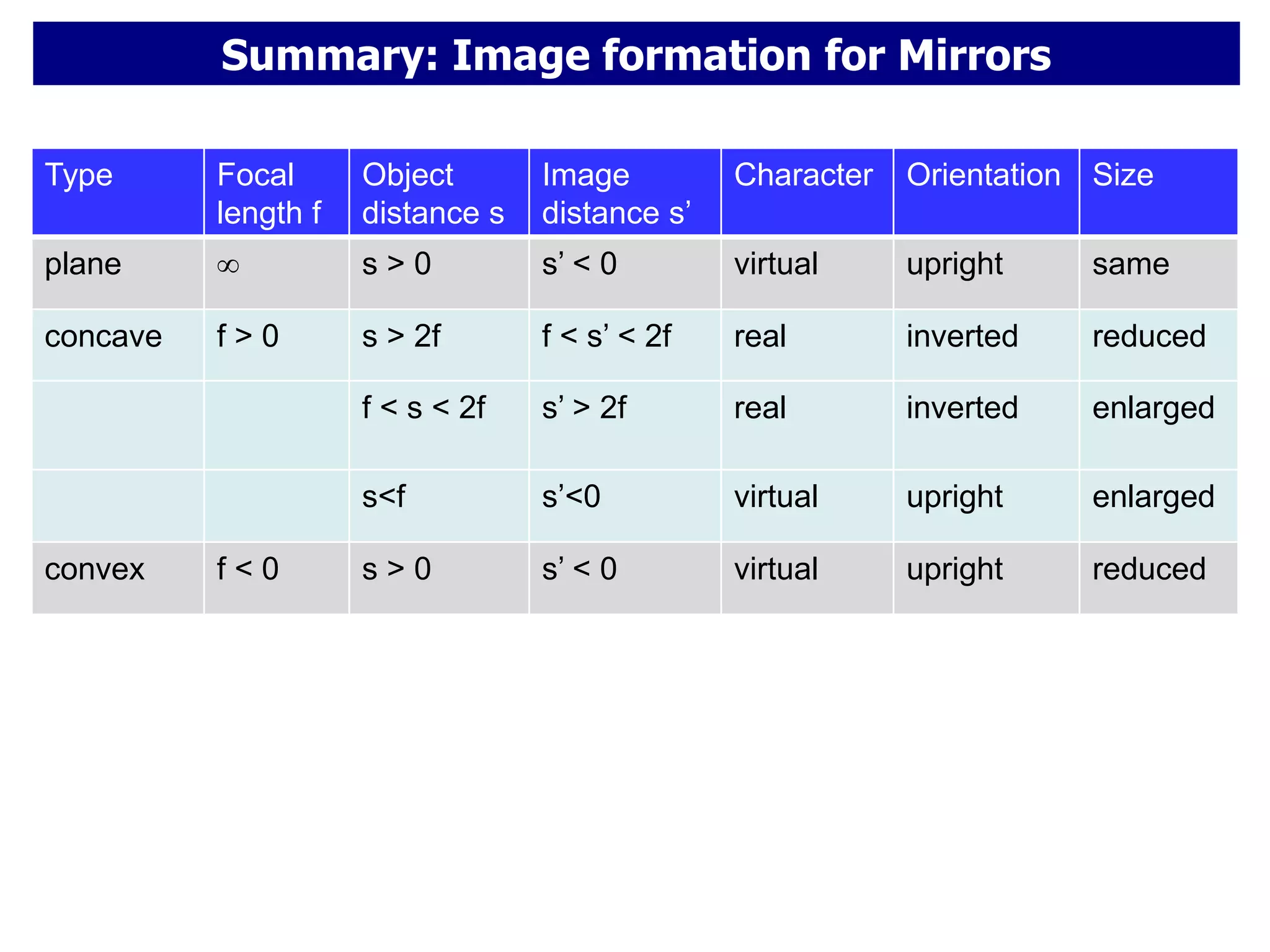
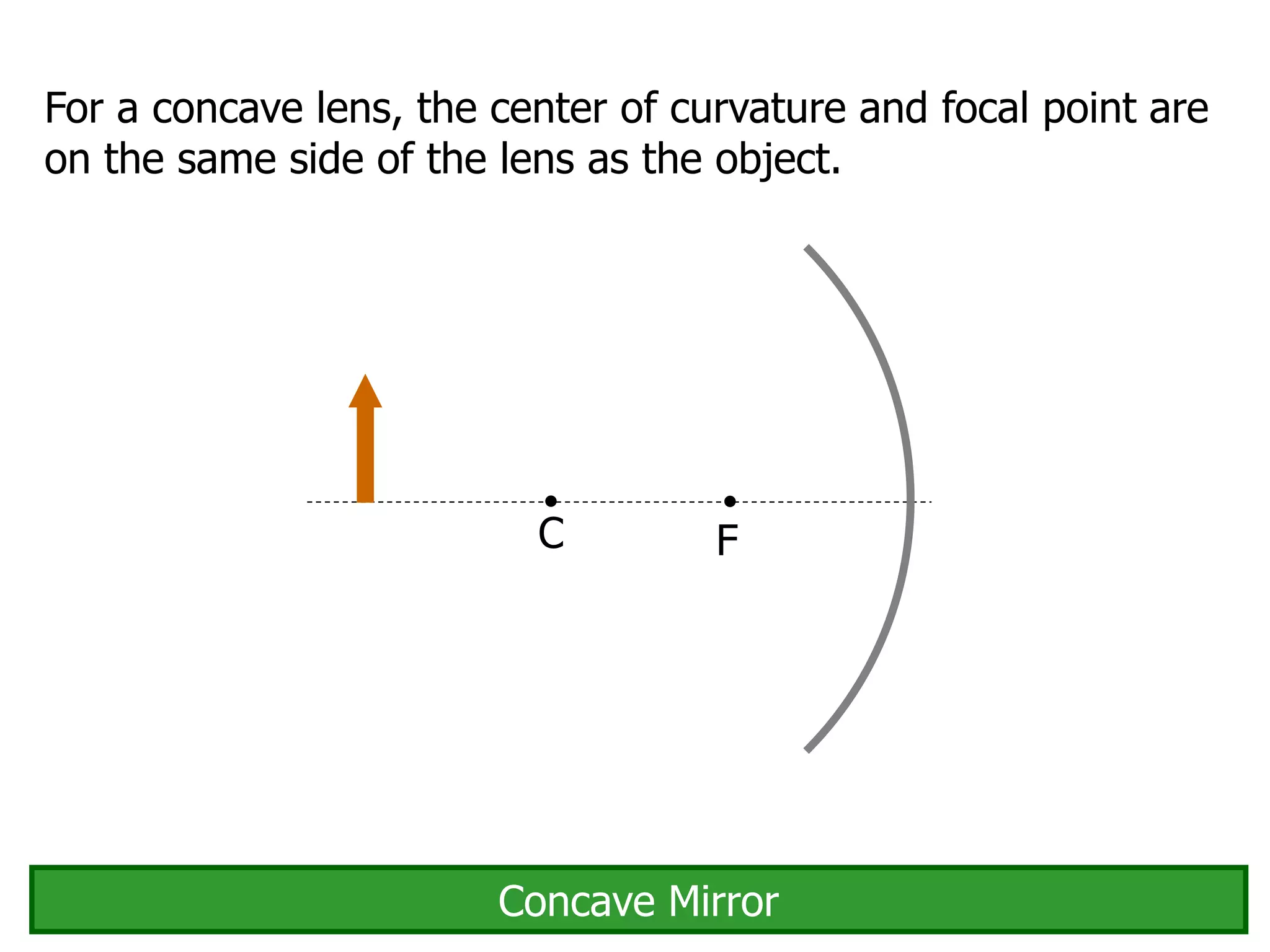
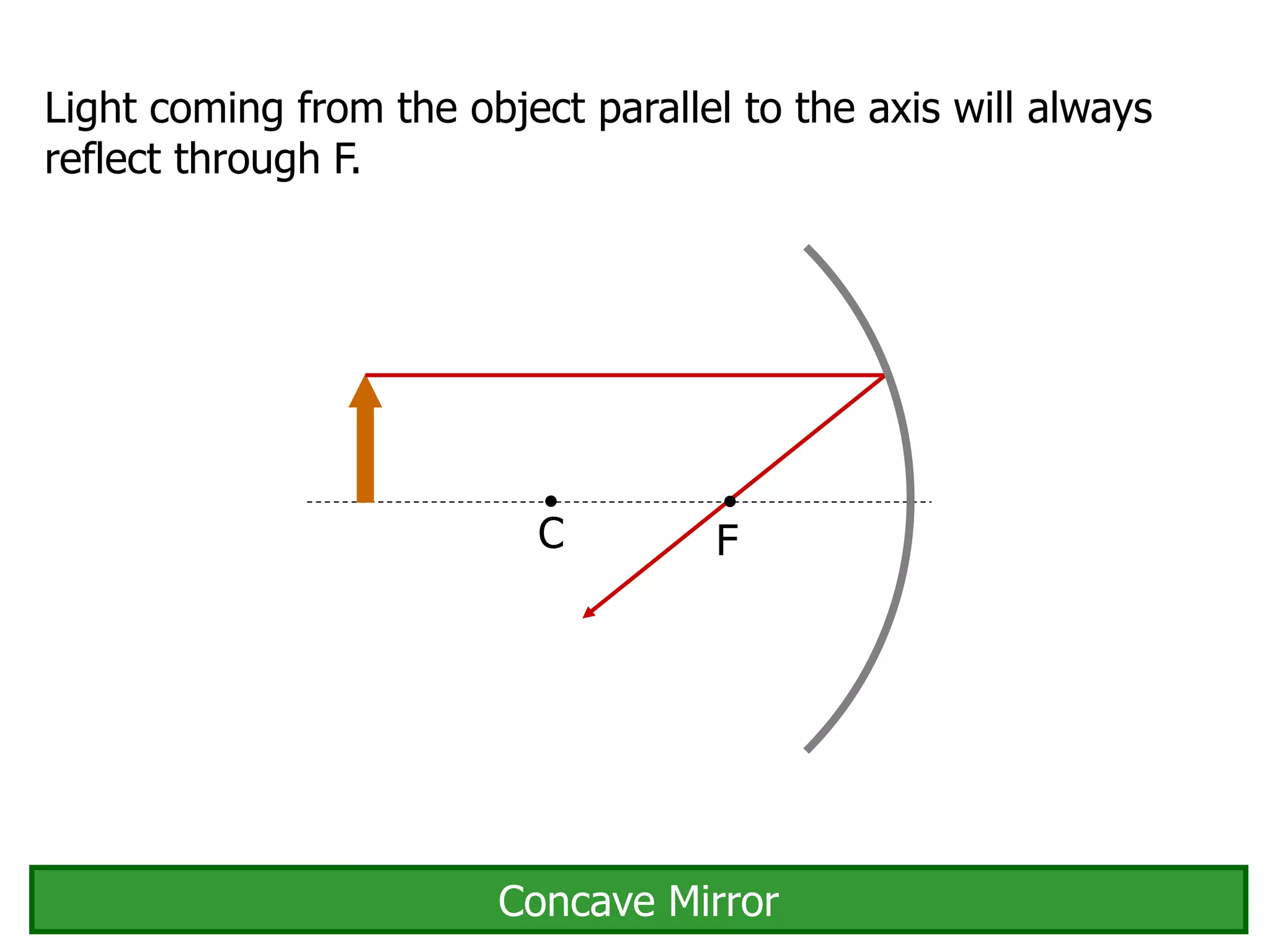
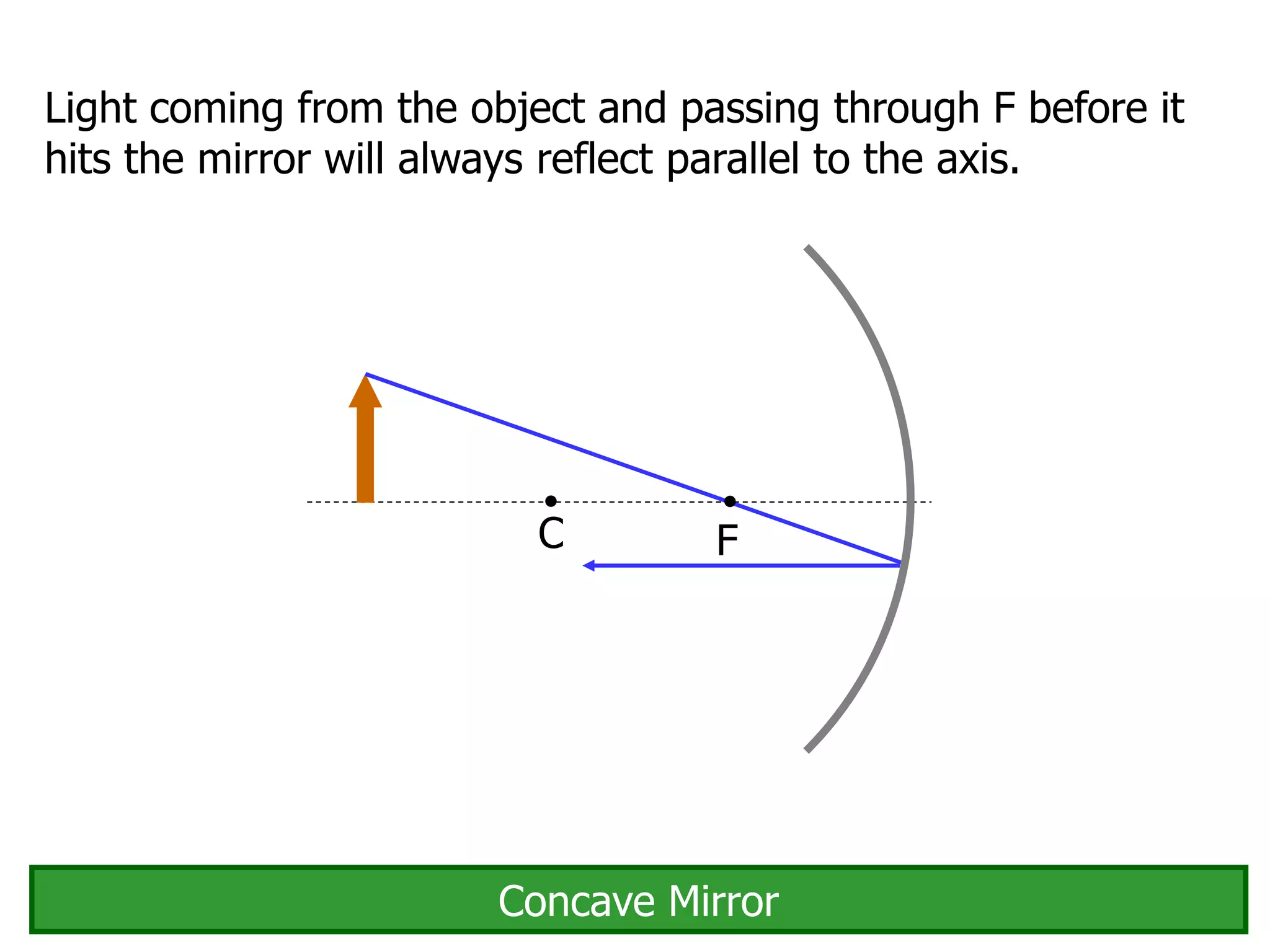
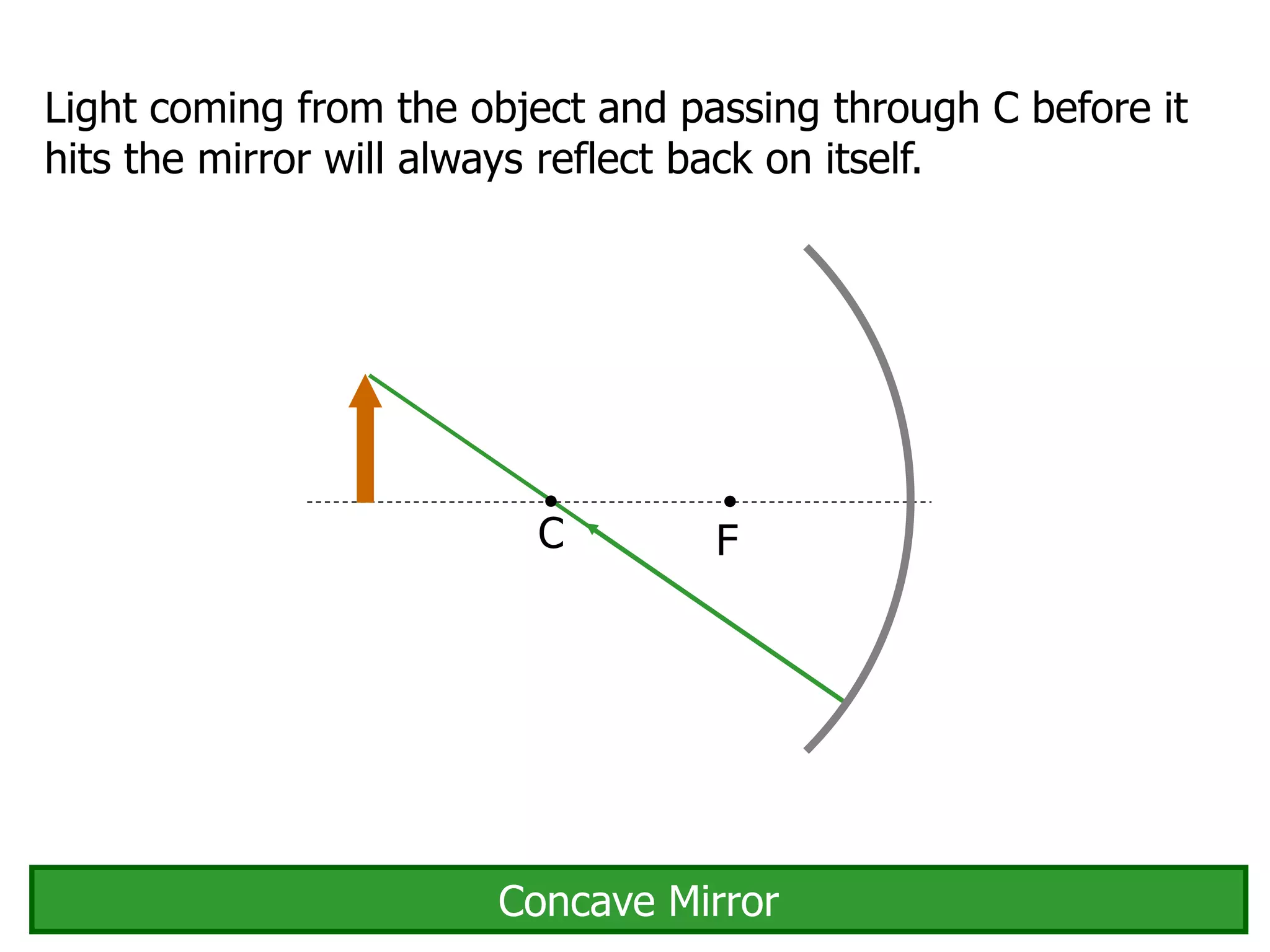
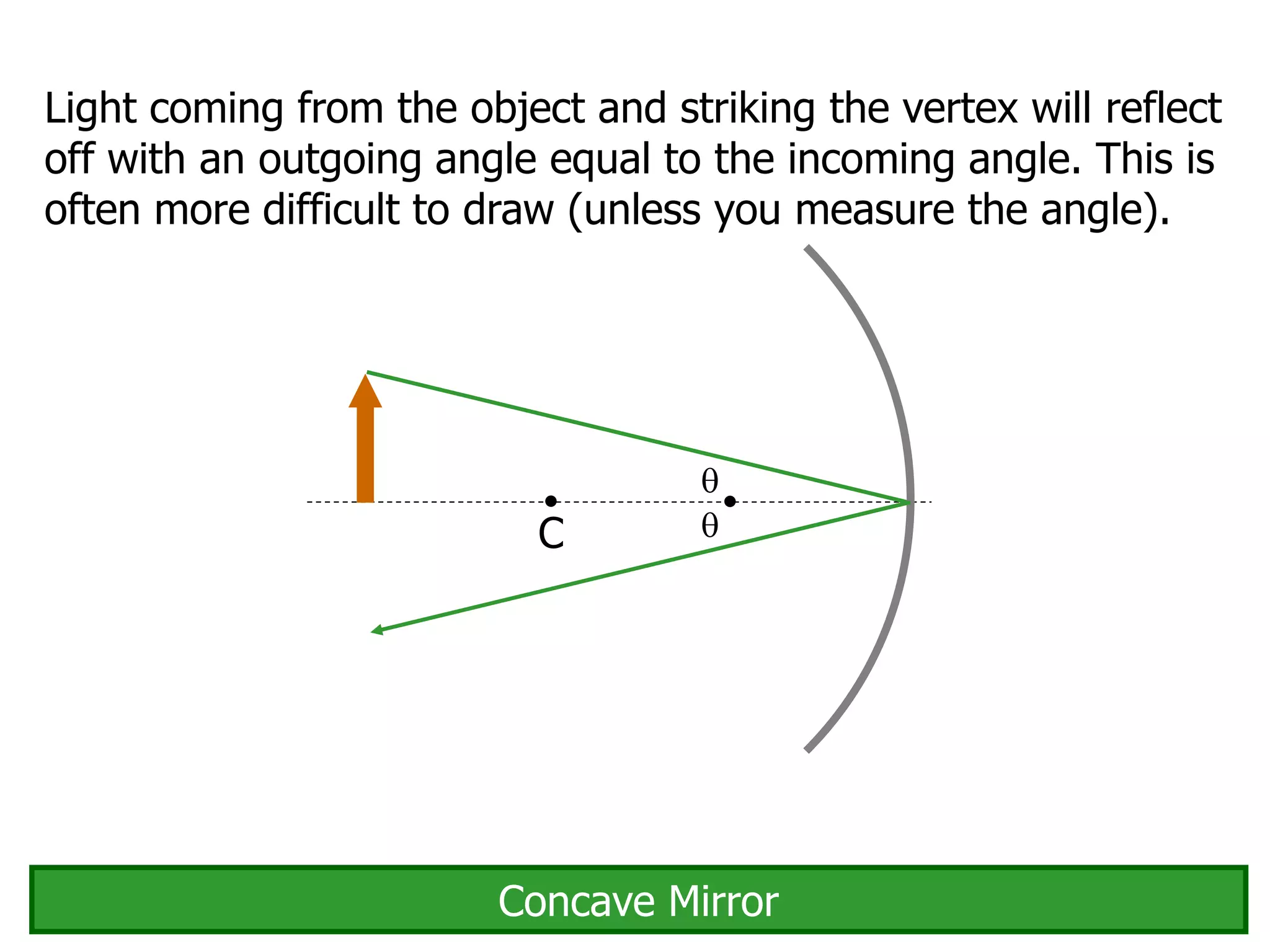
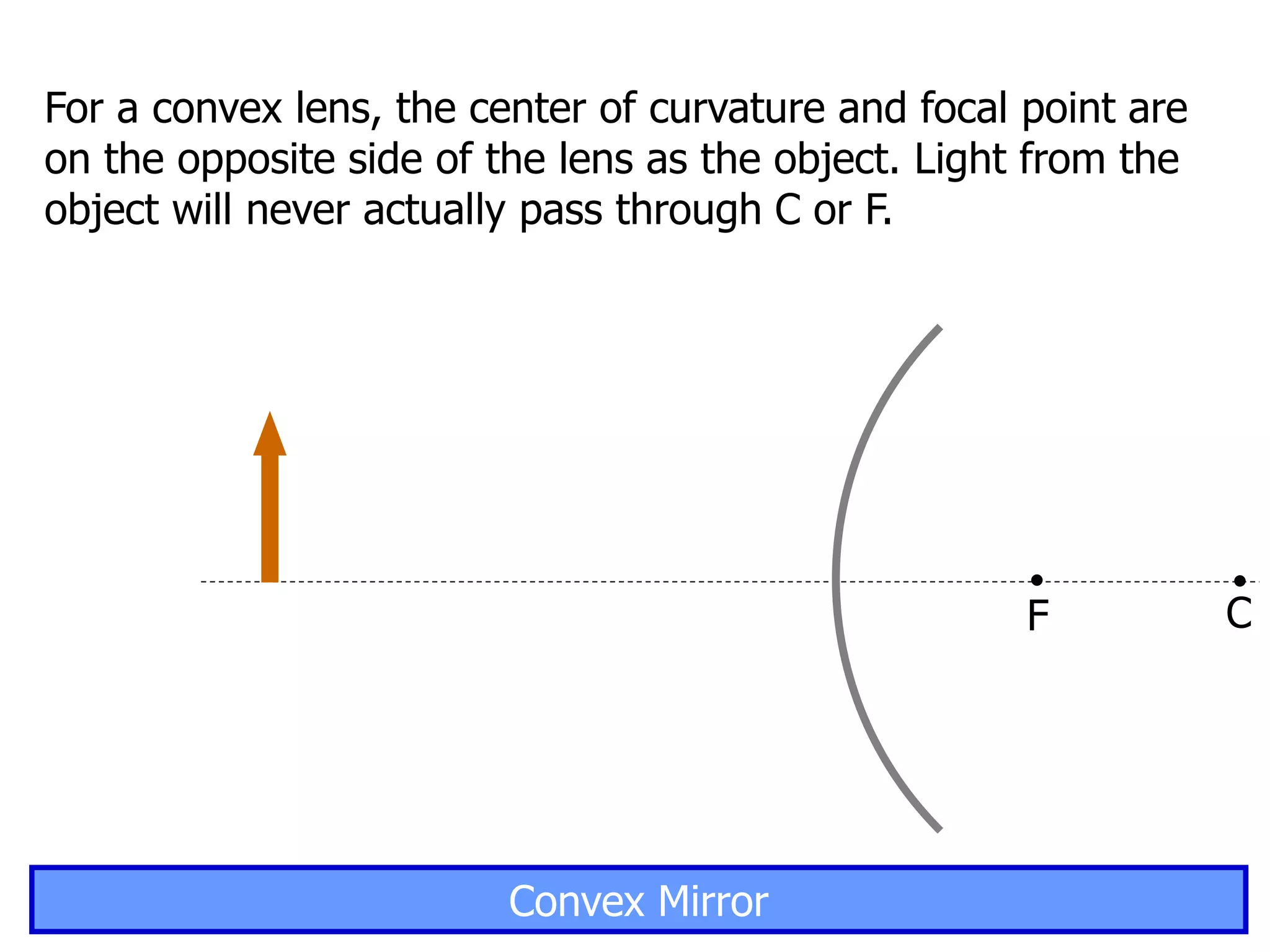
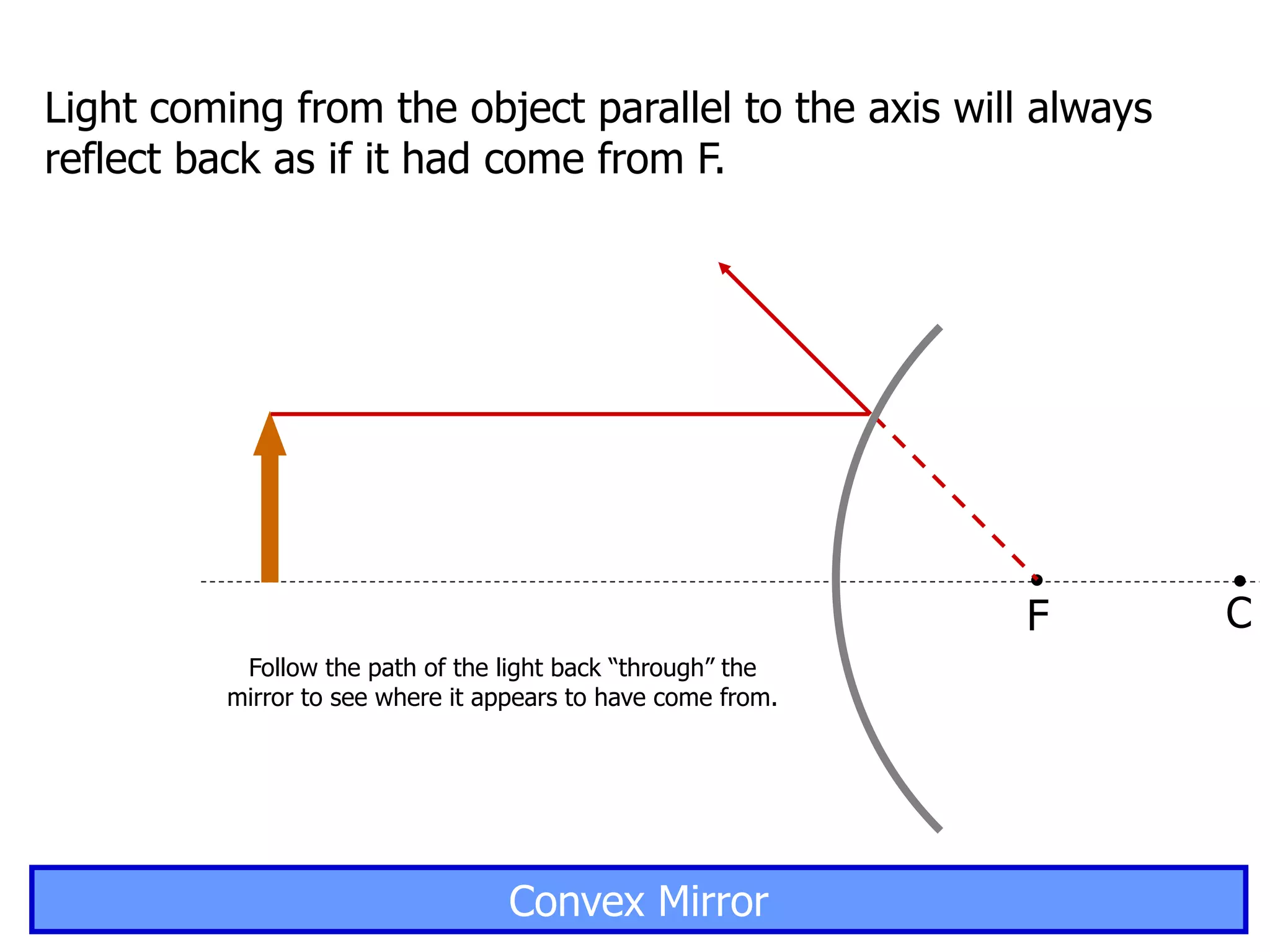
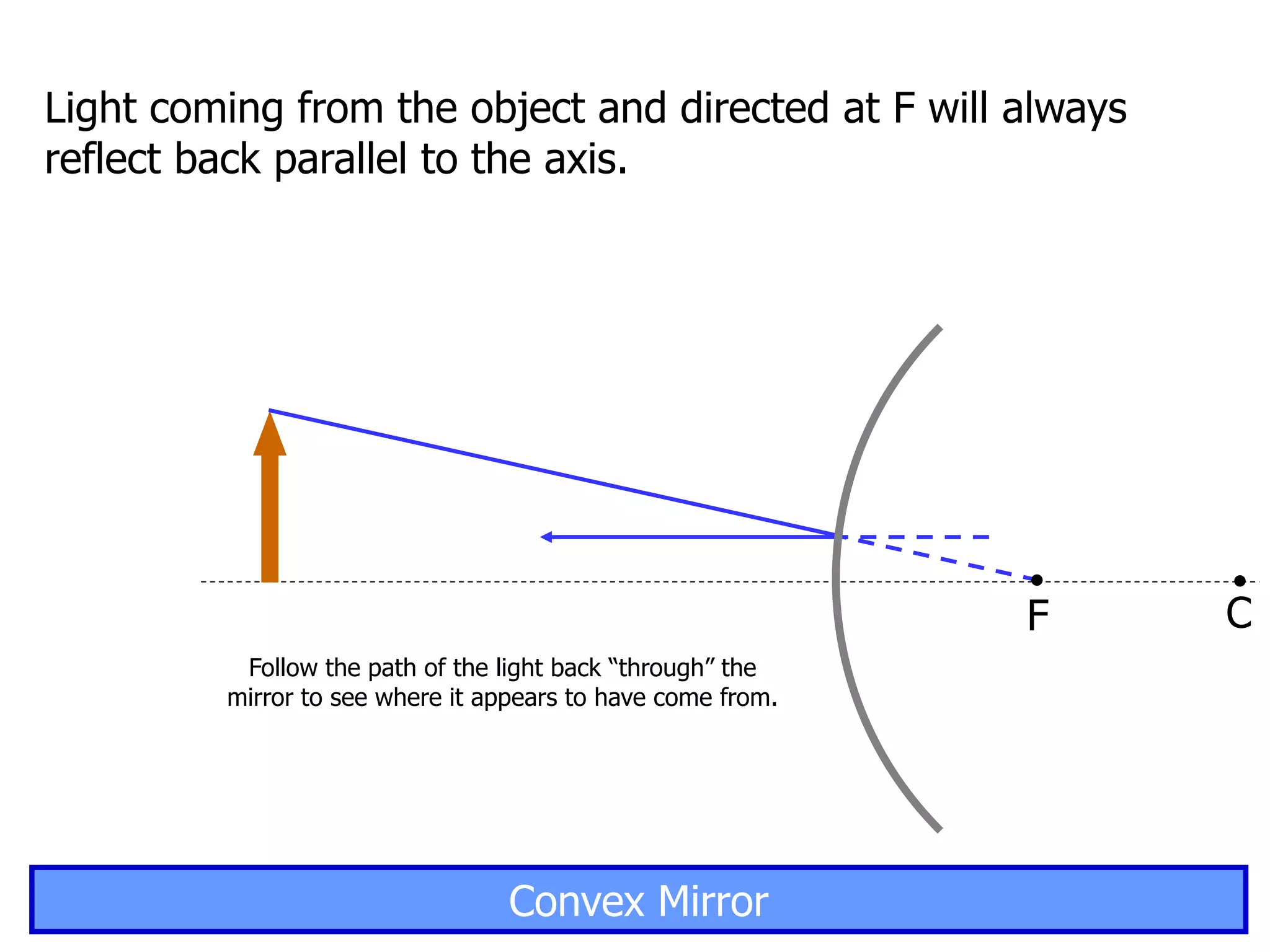
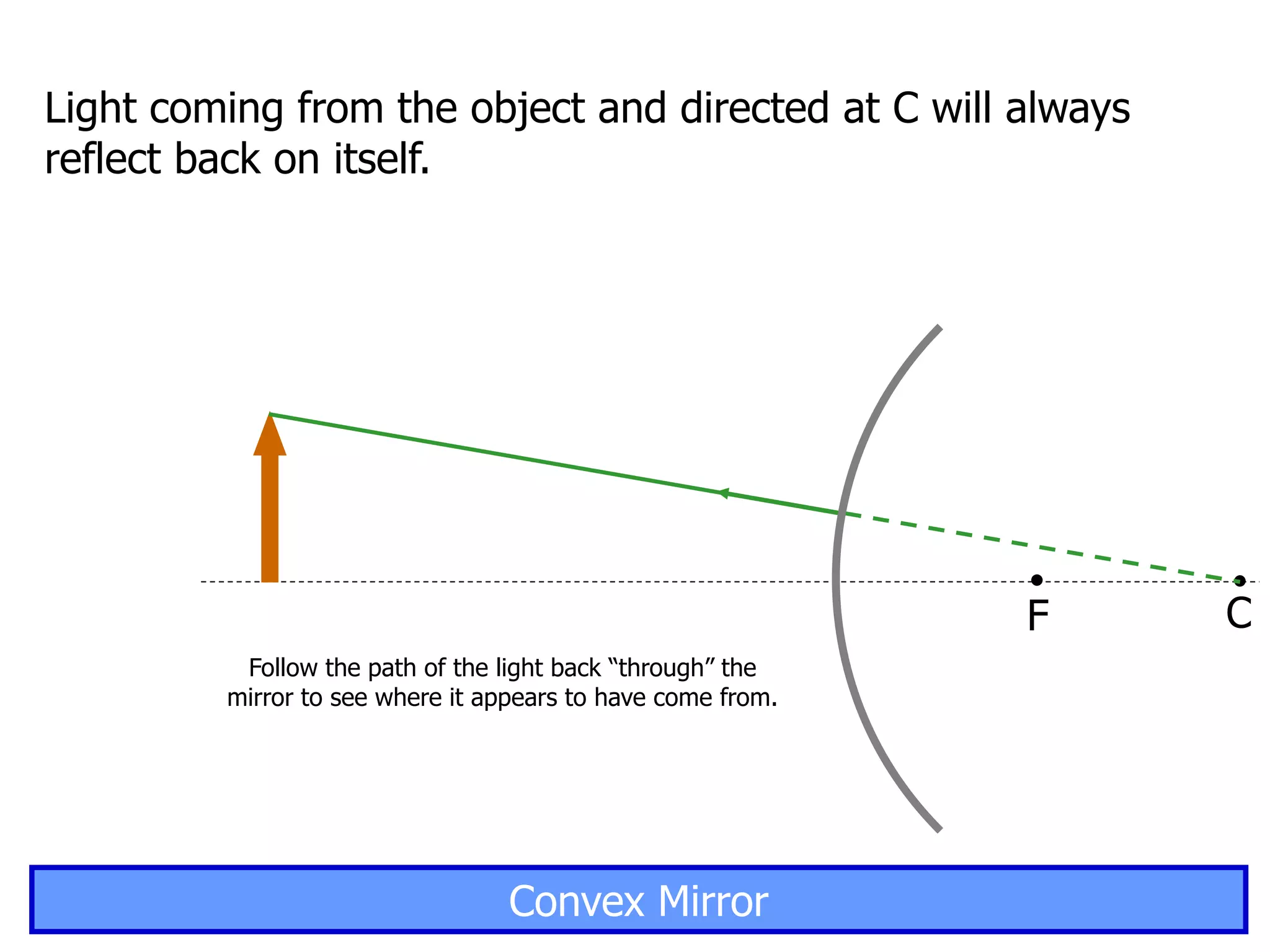
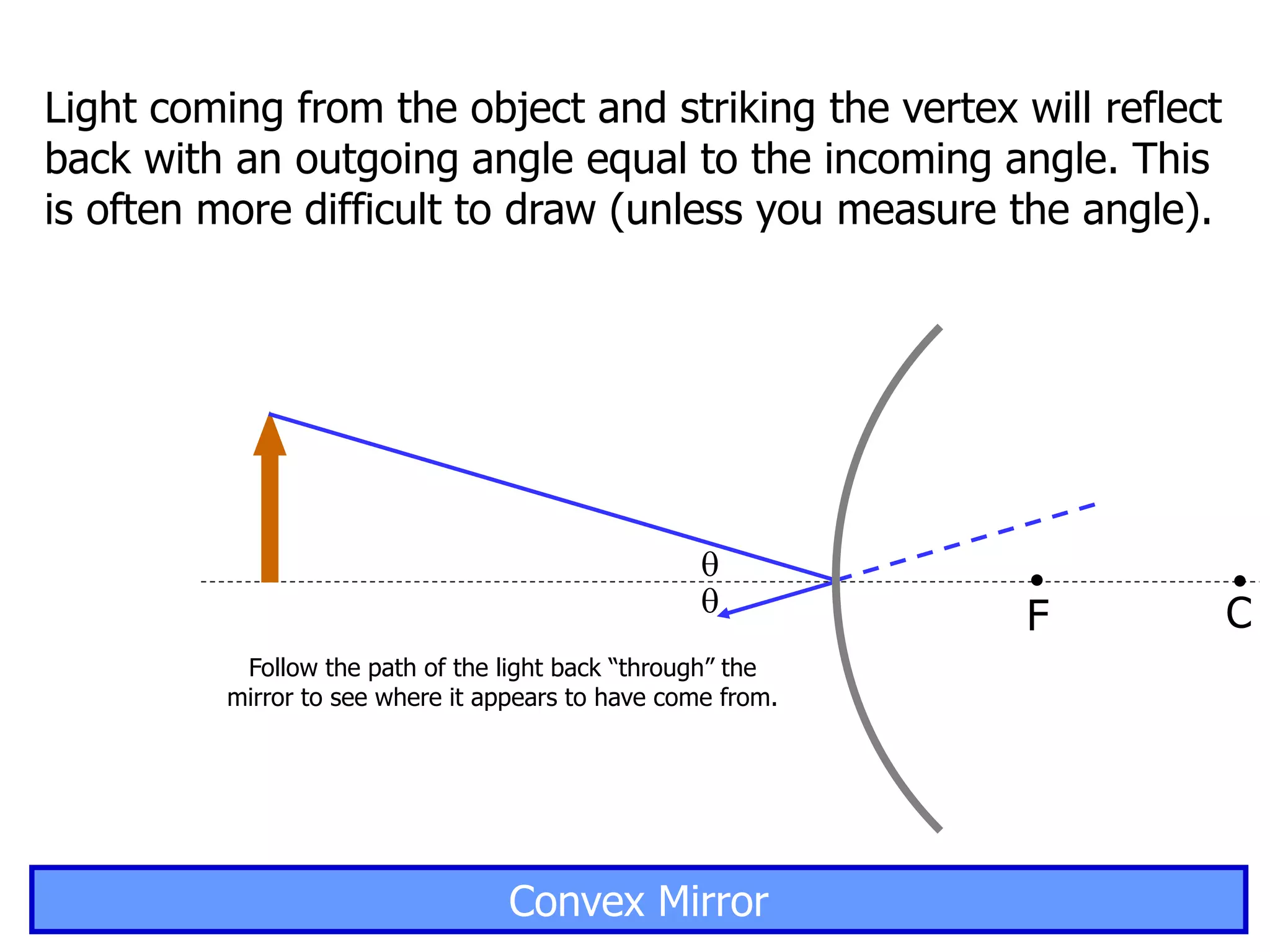
Today's lesson covers image formation using plane mirrors, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors. Students must learn to draw ray diagrams and solve the mirror equations to determine the characteristics of images such as orientation, size, and location. Ray diagrams use two or more principle rays to locate the image. The mirror equations describe the relationships between object and image distances and focal length. Images formed by concave mirrors can be real or virtual depending on the object position, while convex mirrors always form virtual upright images.