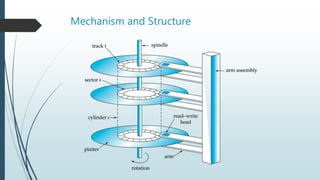
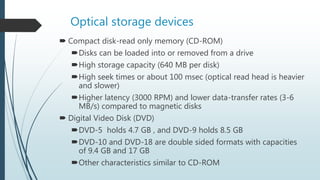
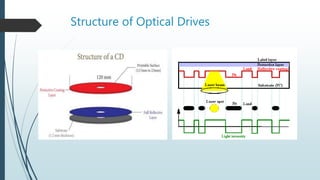
This document discusses different types of disk storage devices. It begins by defining disk storage as using magnetic, optical, or mechanical methods to record data on rotating disks. The first commercial disk storage device was the IBM 350 in 1956. Disk storage offers advantages like speed of access, control over data, lower cost per unit of data, and reliability compared to other storage methods. The document then describes different types of disk storage devices like hard disk drives, optical storage devices, magnetic tape drives, floppy disks, and portable hard disks. It explains the mechanisms, structures, and characteristics of each type.