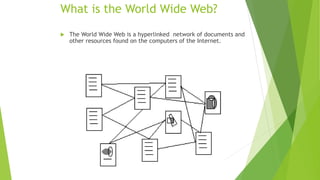
The document provides an introduction to computers and basic computer concepts. It defines a computer as an electronic device that can store, process, and retrieve data. It then describes the basic components of a computer system including input, output, and storage devices. It also explains the functions of the central processing unit and memory. Finally, it discusses the history of computers from the abacus to modern computer generations and characteristics of computers like speed, accuracy, and reliability.