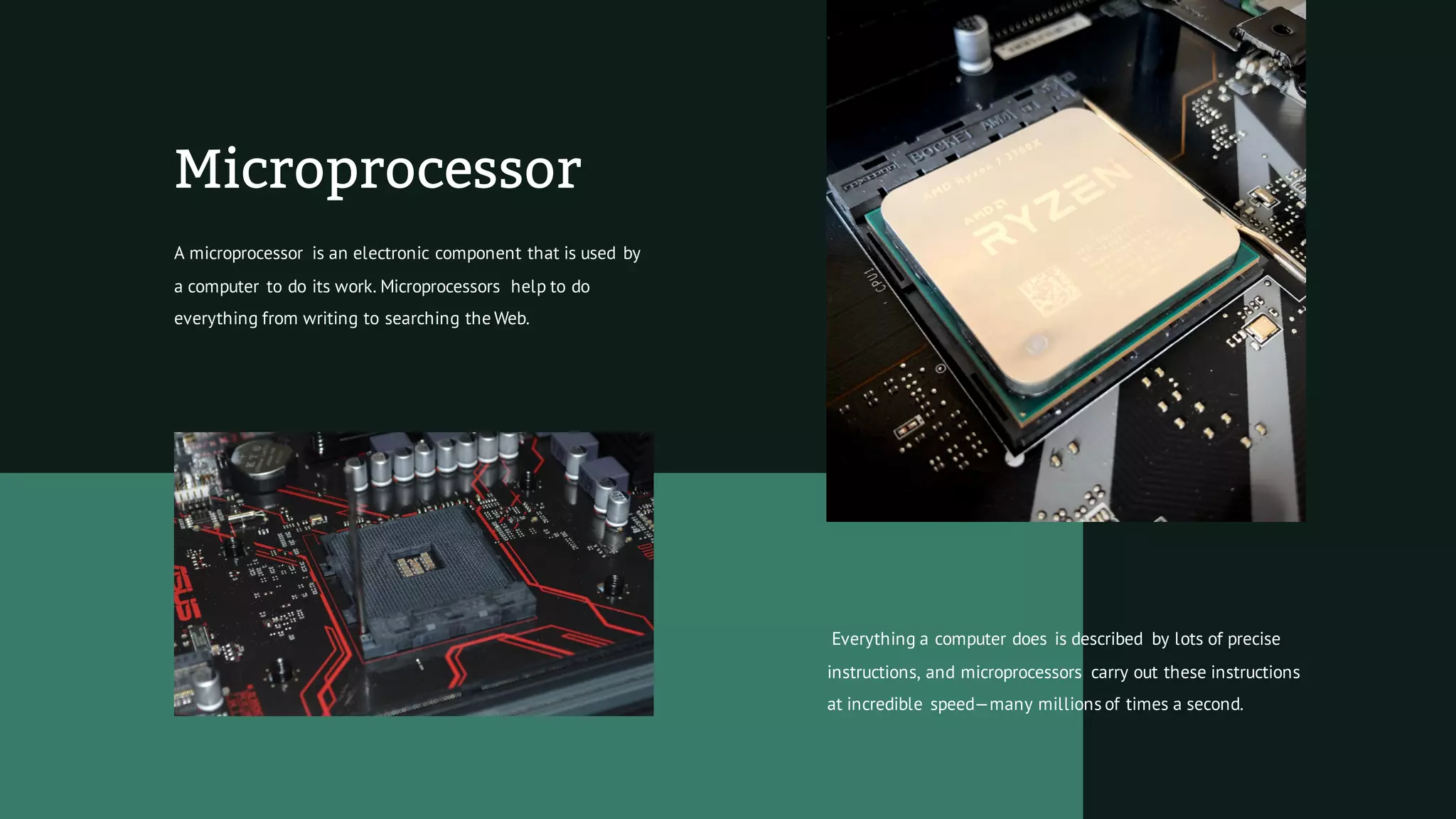
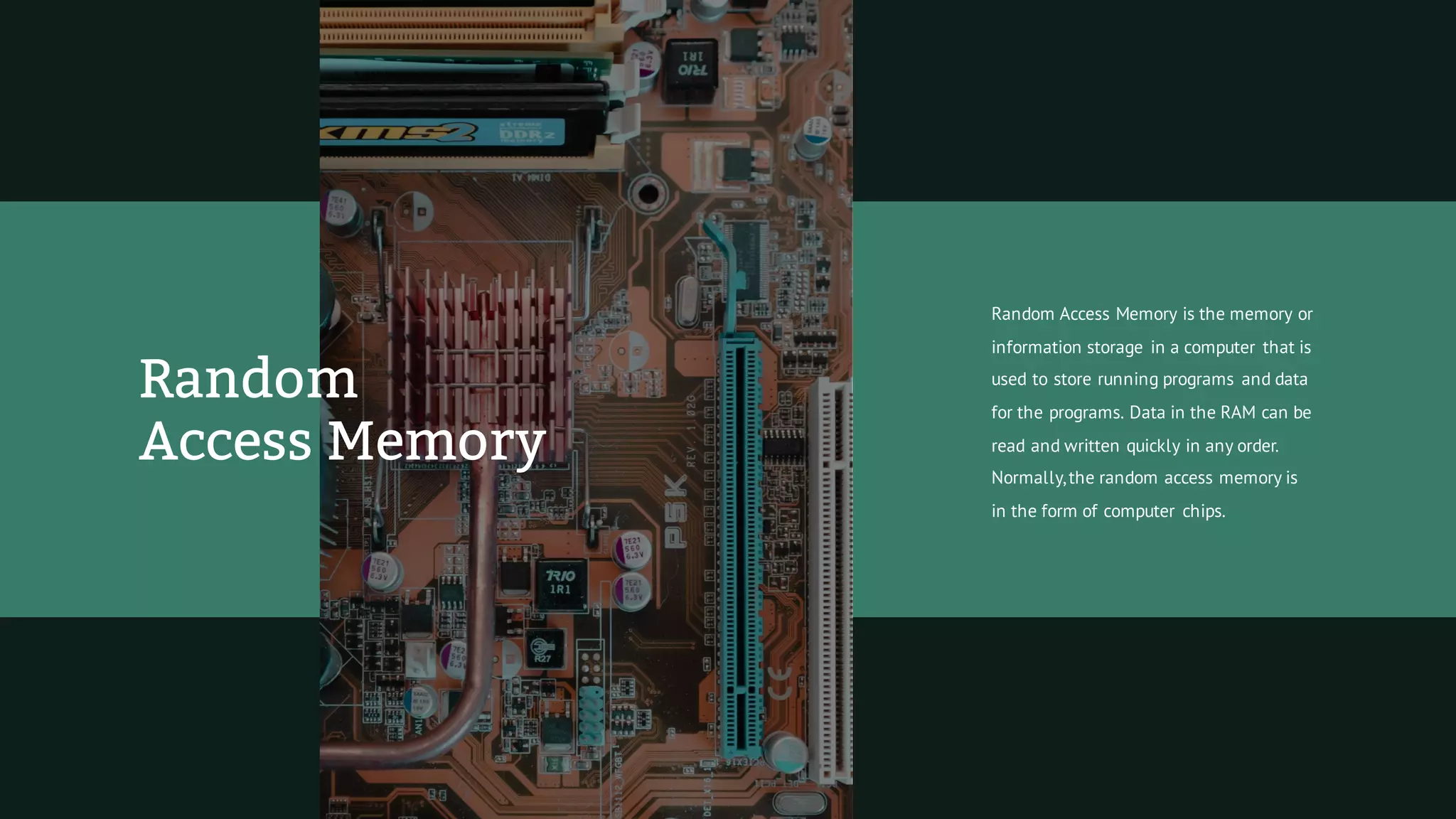
This document provides information about computers and their basic components. It defines what a computer is as a machine that takes in information, processes it, and produces new information. It describes the different types of computers like desktop PCs, laptops, mainframes, and supercomputers. It explains how computers work by storing data and instructions as binary digits. It also outlines some common hardware components inside computers like the central processing unit (CPU), microprocessor, random access memory (RAM), and hard disk drive.