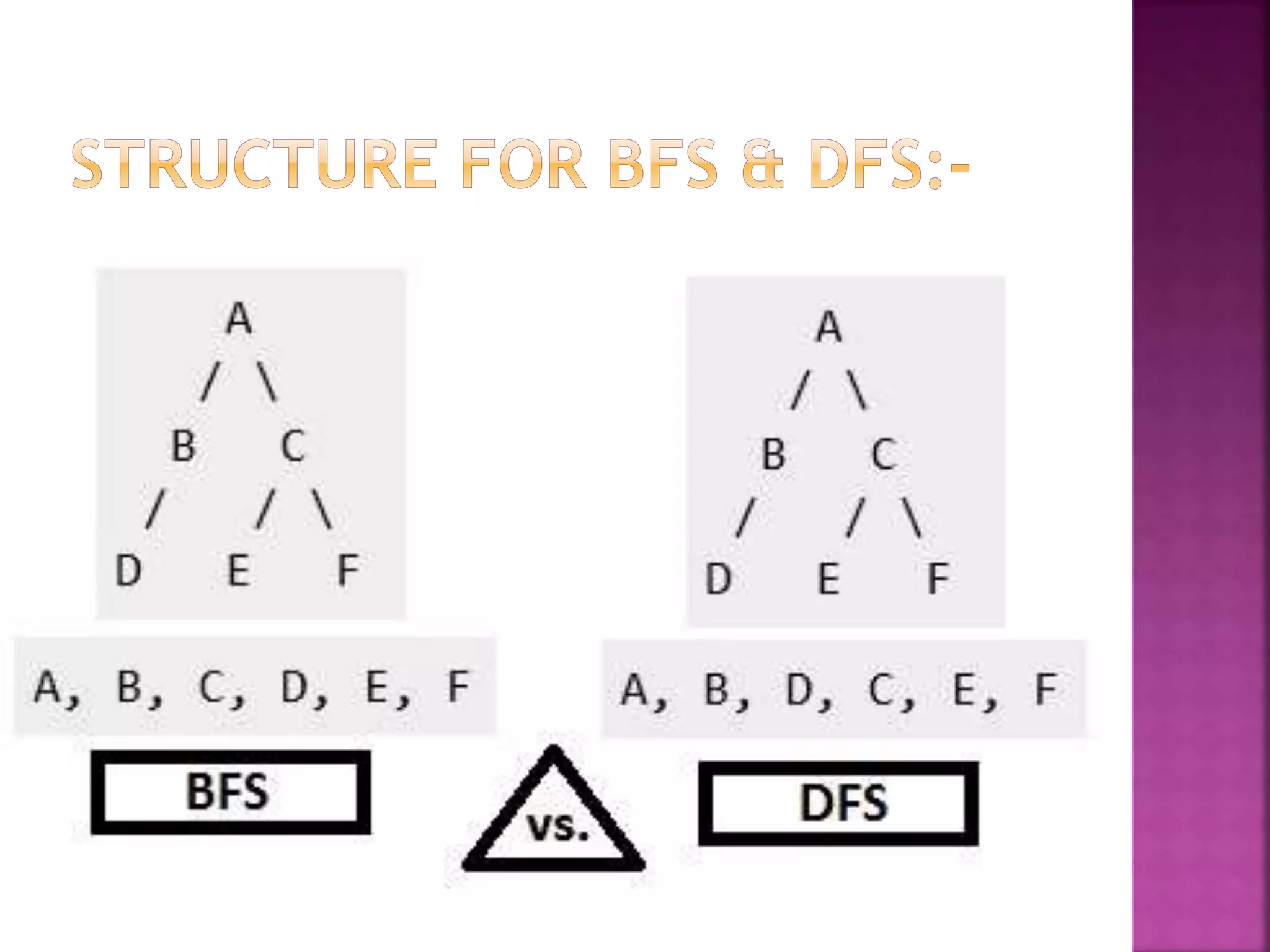
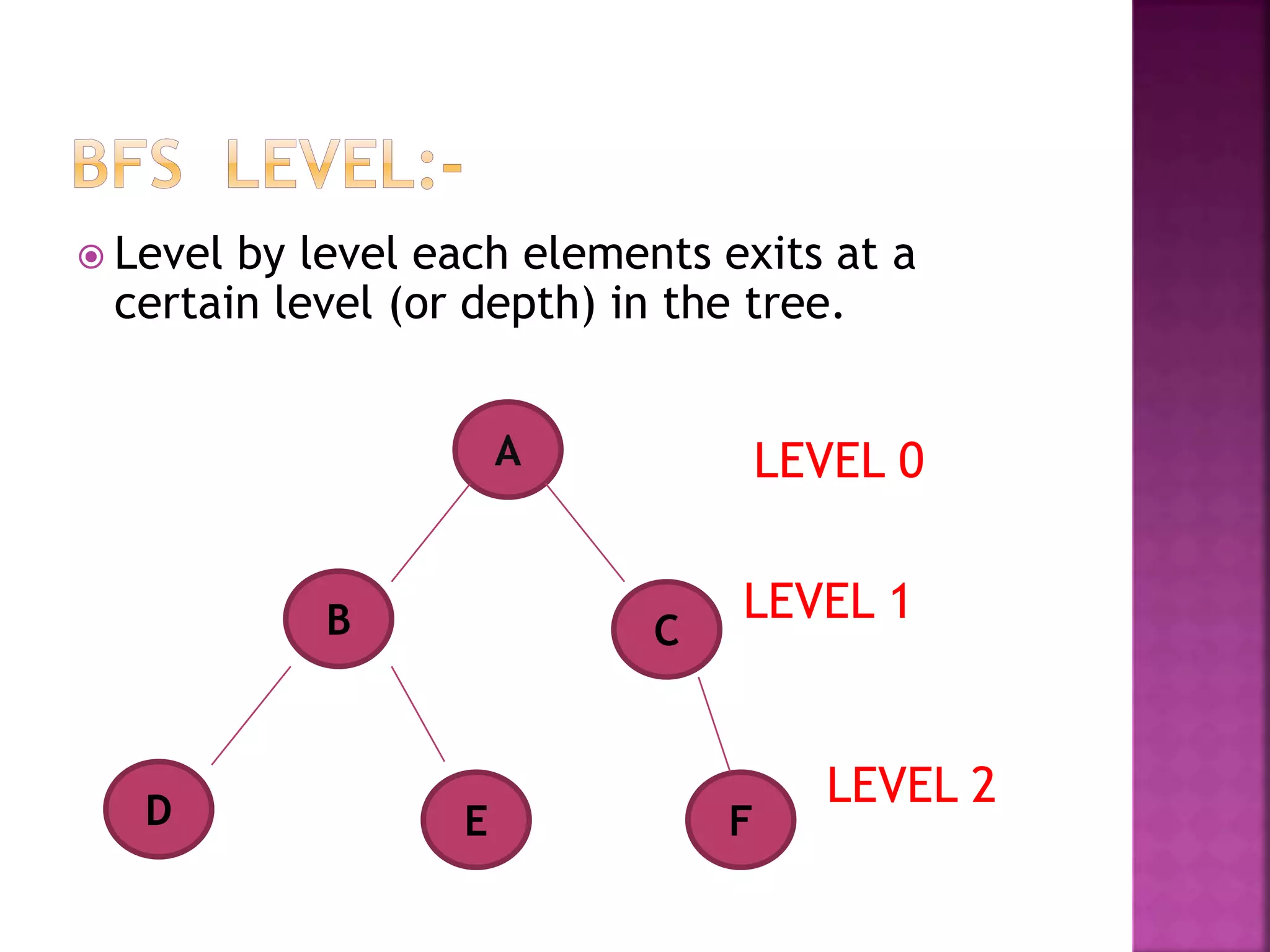
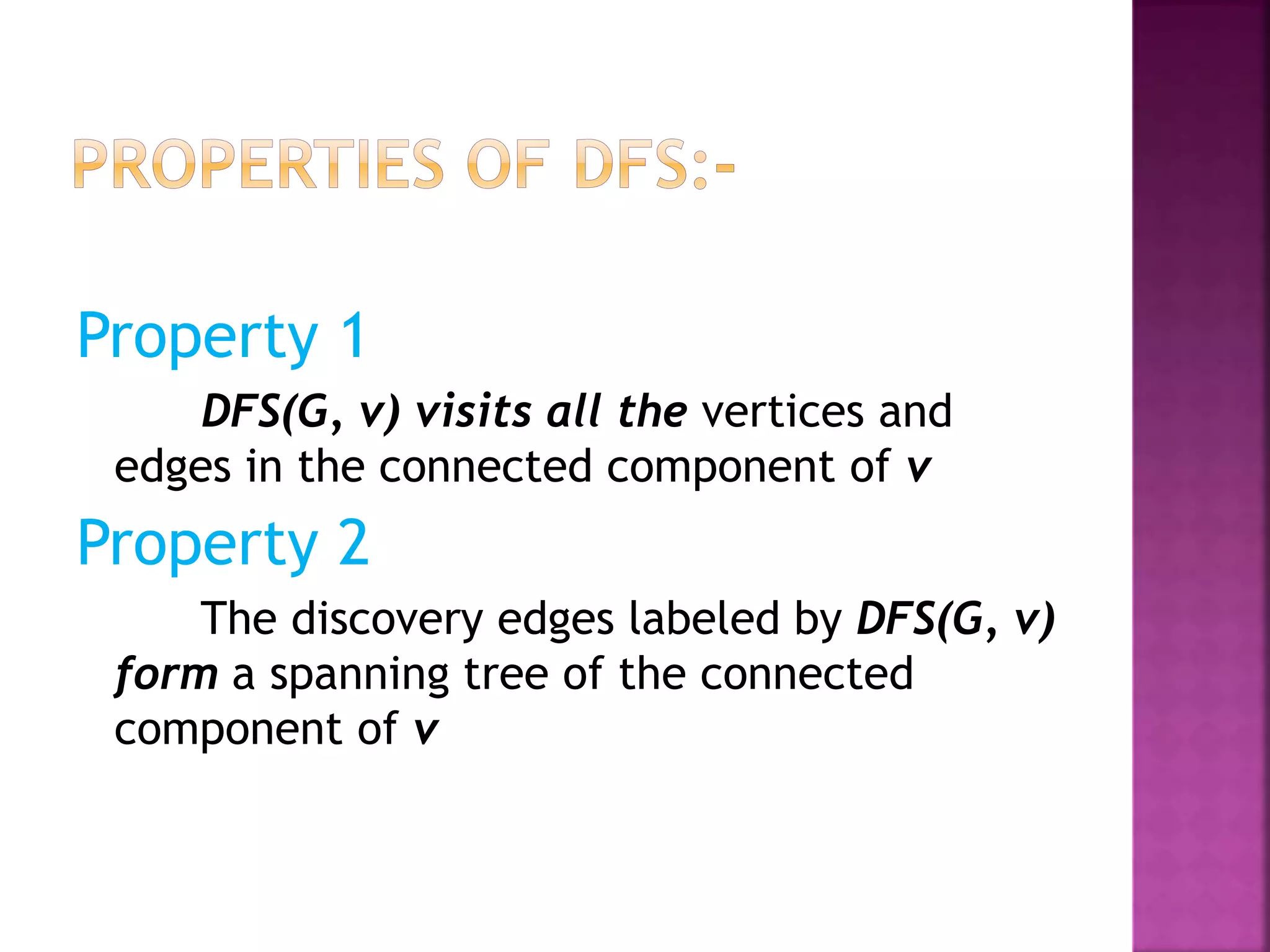
Breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS) are two standard graph traversal algorithms. BFS explores nodes level-by-level starting from the root node, using a queue data structure. In contrast, DFS prioritizes exploring nodes to the deepest levels first, using a stack data structure. Both algorithms are useful for problems like finding the shortest path in a graph and determining connected components. BFS and DFS can be used to generate spanning trees and forests that connect all nodes within each component of the graph.