The document discusses classical or crisp set theory. Some key points:
1) Classical set theory deals with sets that have definite membership - an element either fully belongs to a set or not. This is represented by true/false or yes/no.
2) A set is a well-defined collection of objects. The universal set is the overall context within which sets are defined.
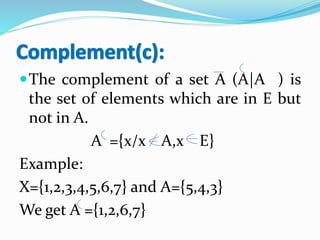
3) Set operations like union, intersection, complement and difference are used to combine or relate sets according to specific rules.
4) Properties like commutativity, associativity and distributivity define the logical behavior of sets under different operations.