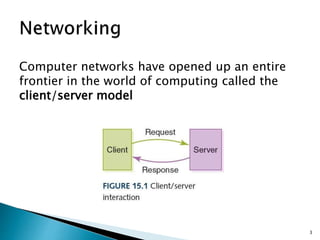
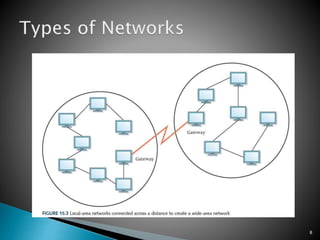
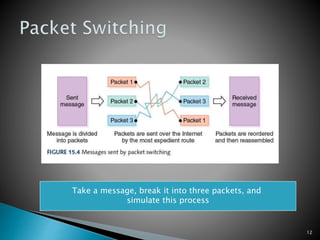
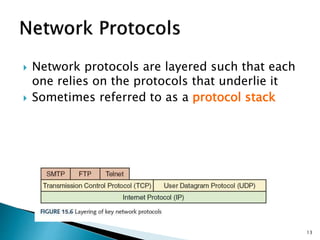
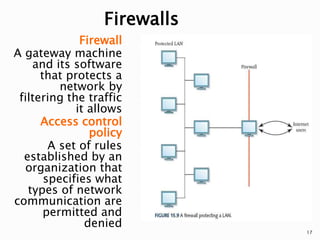
The document provides an overview of computer networks, detailing various types like local-area networks (LANs) and wide-area networks (WANs), as well as different topologies such as star and bus. It discusses network protocols including TCP/IP, packet switching, and common technologies for internet connectivity such as DSL and cable modems. Additionally, the document touches on the importance of firewalls and access control policies for network security.