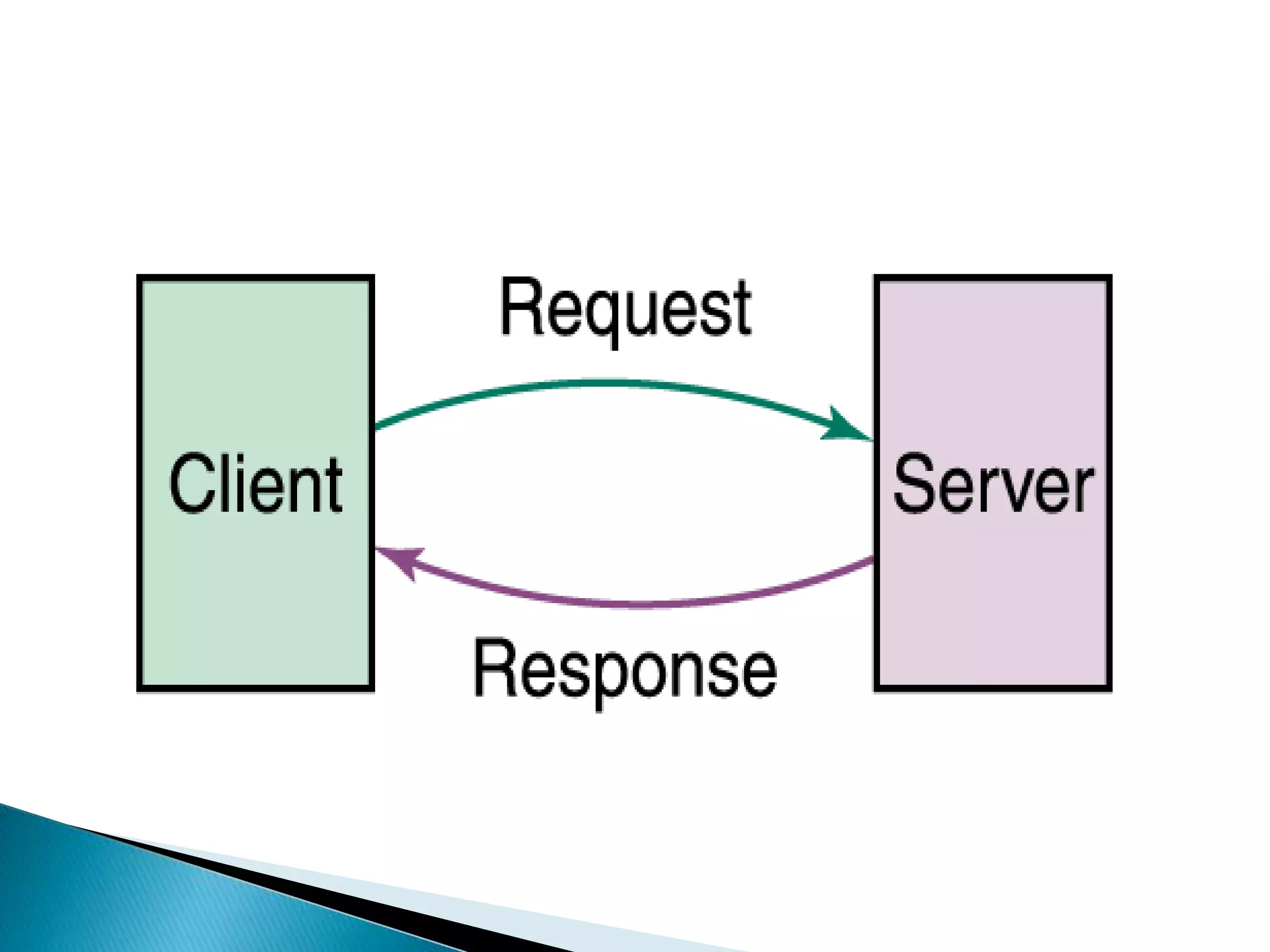
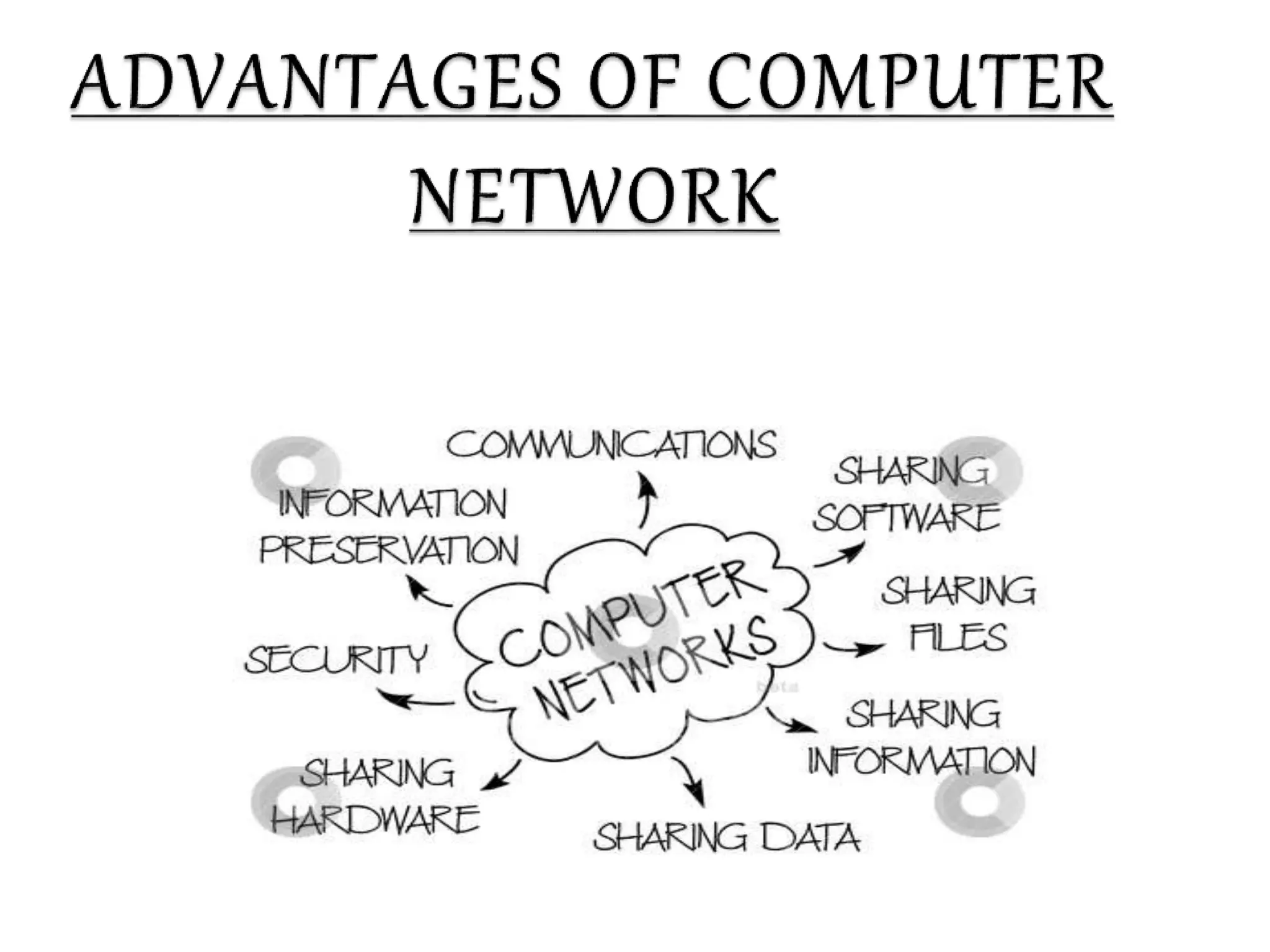
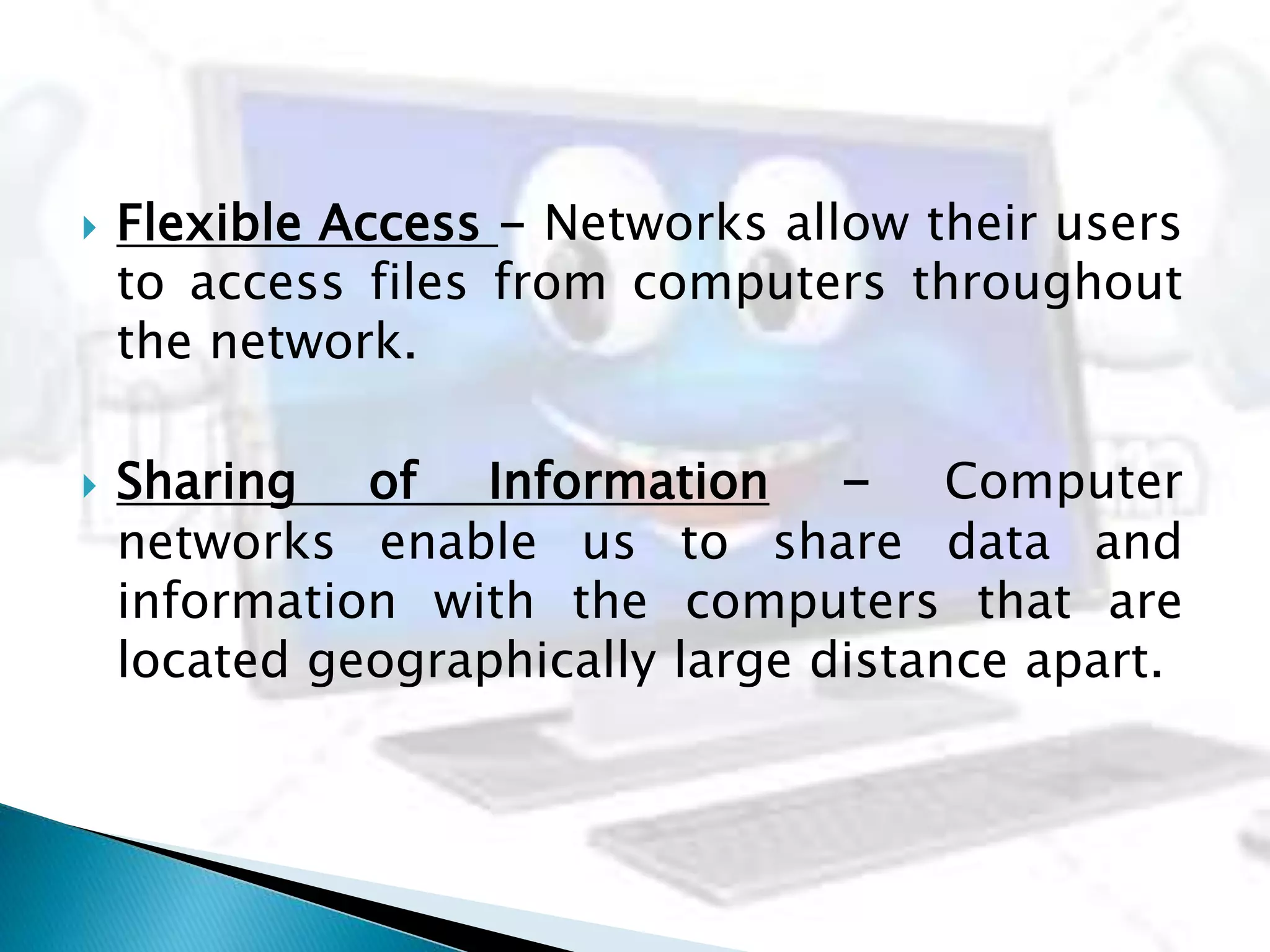
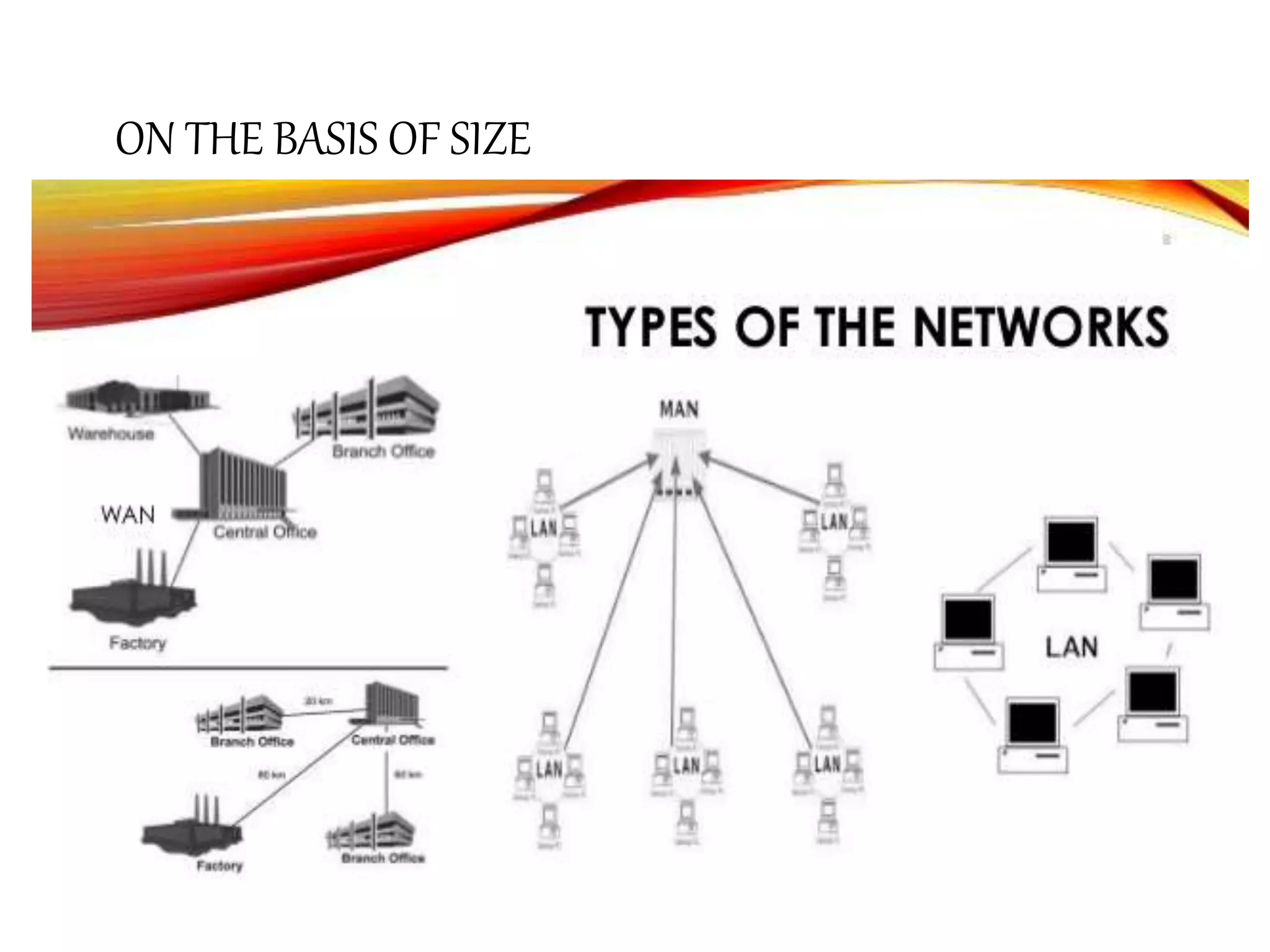
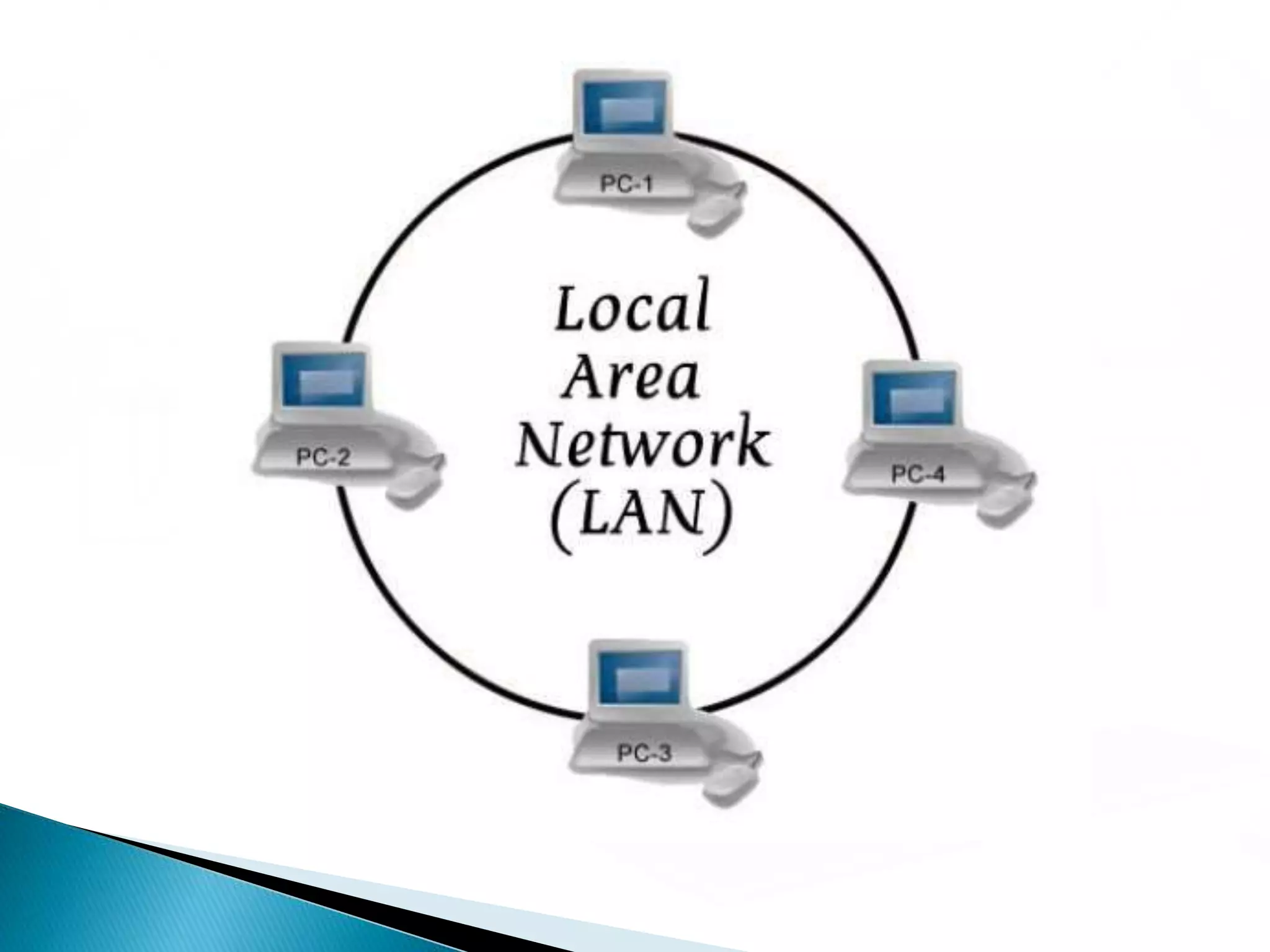
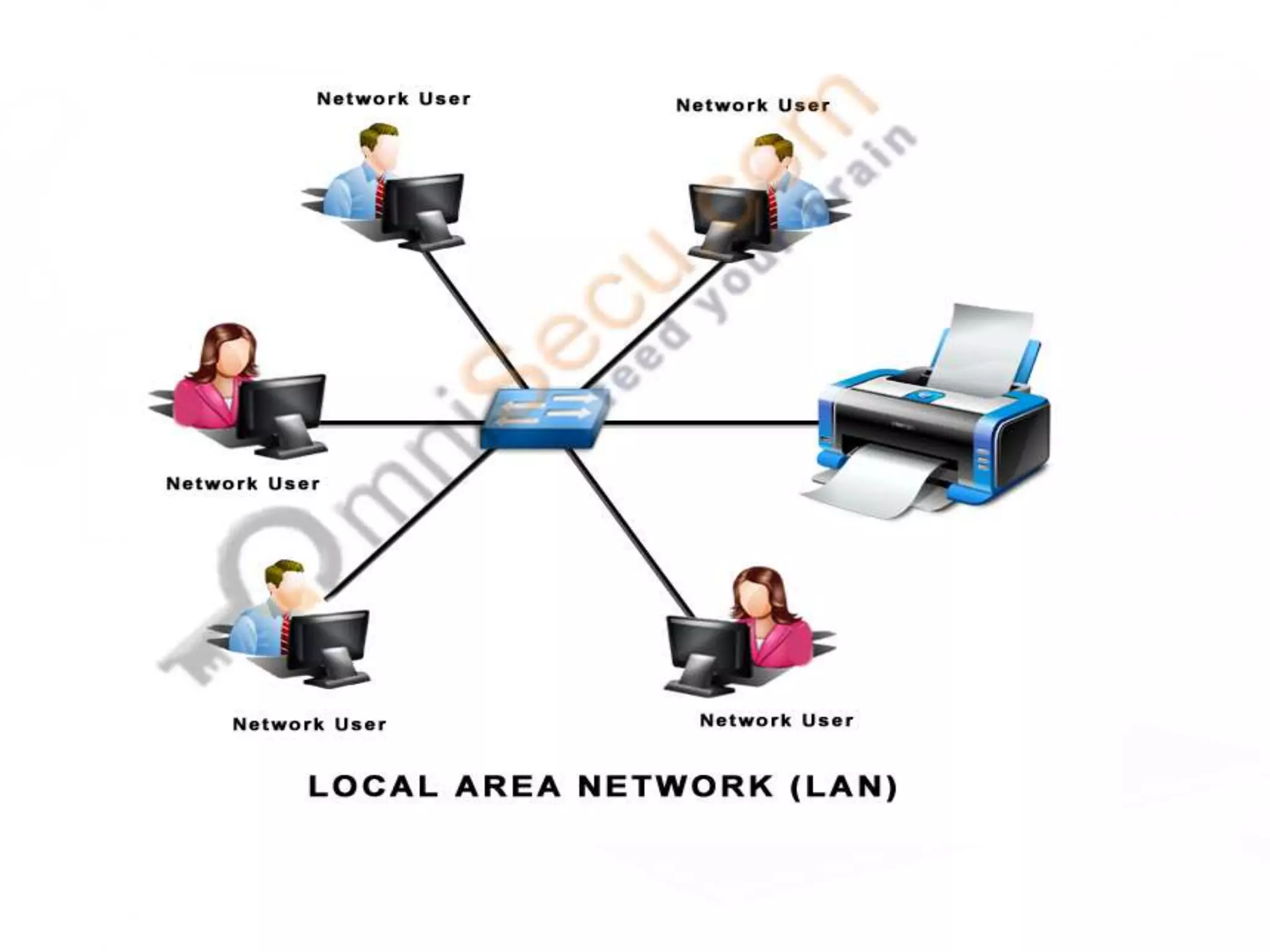
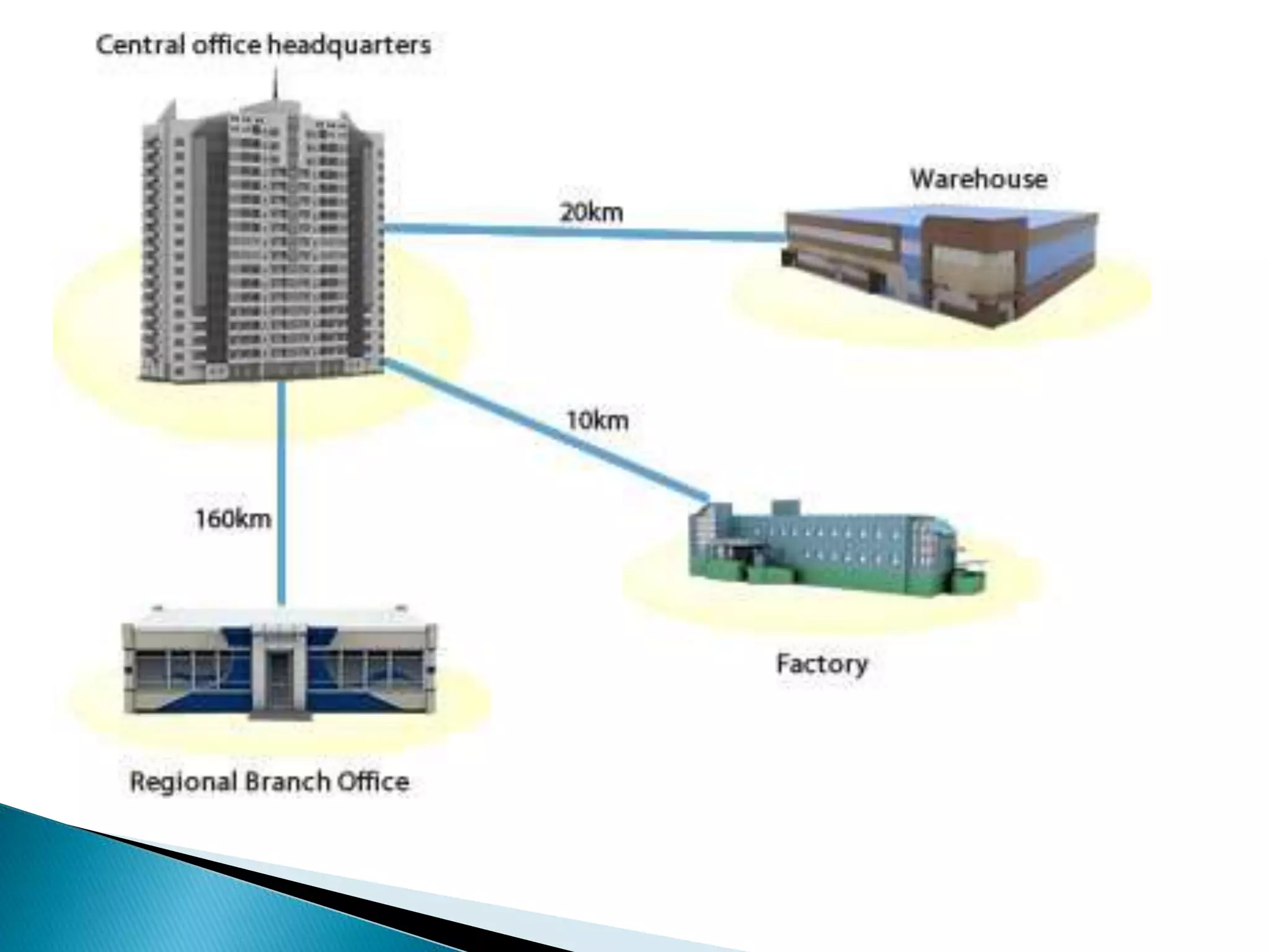
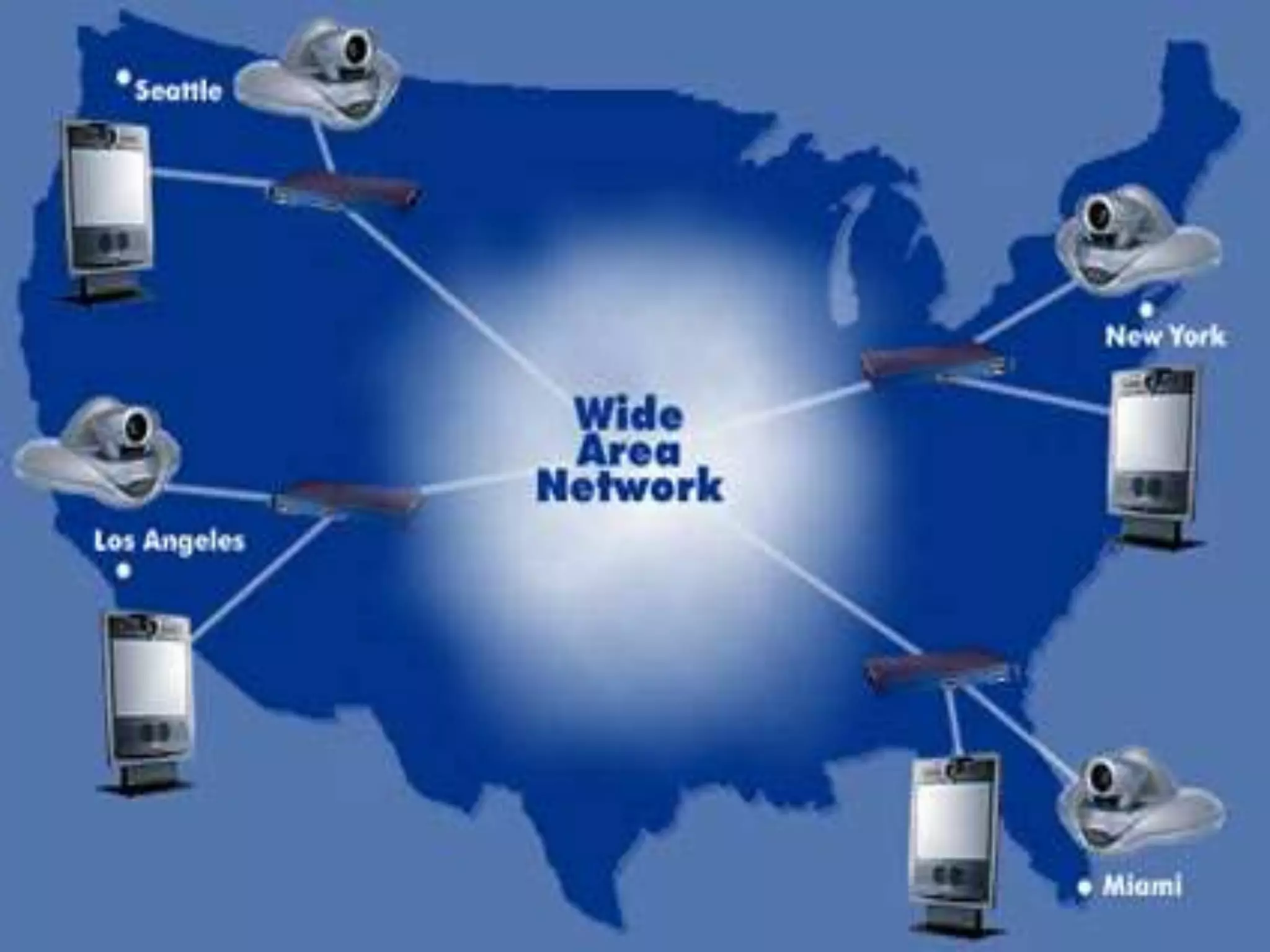
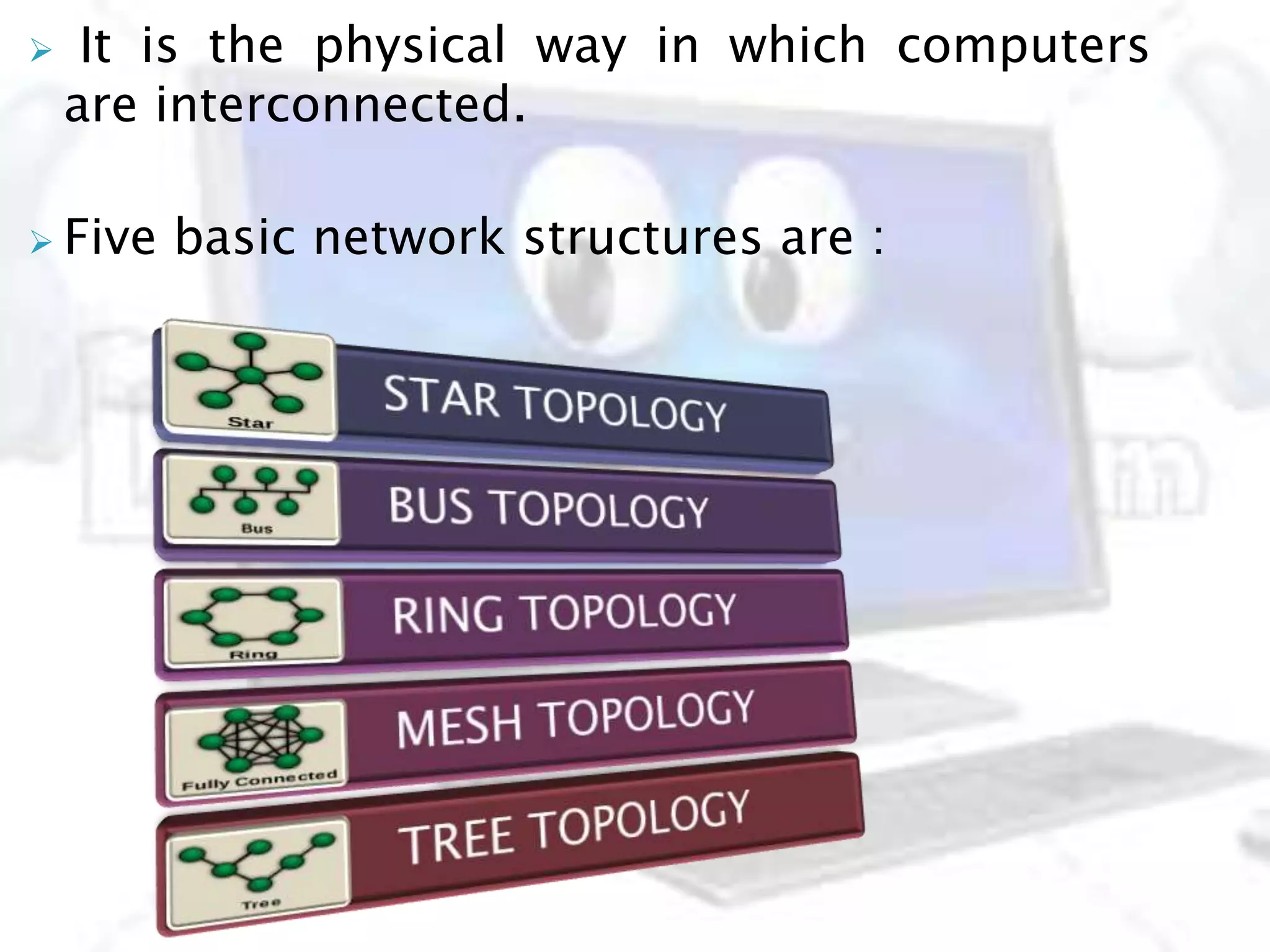
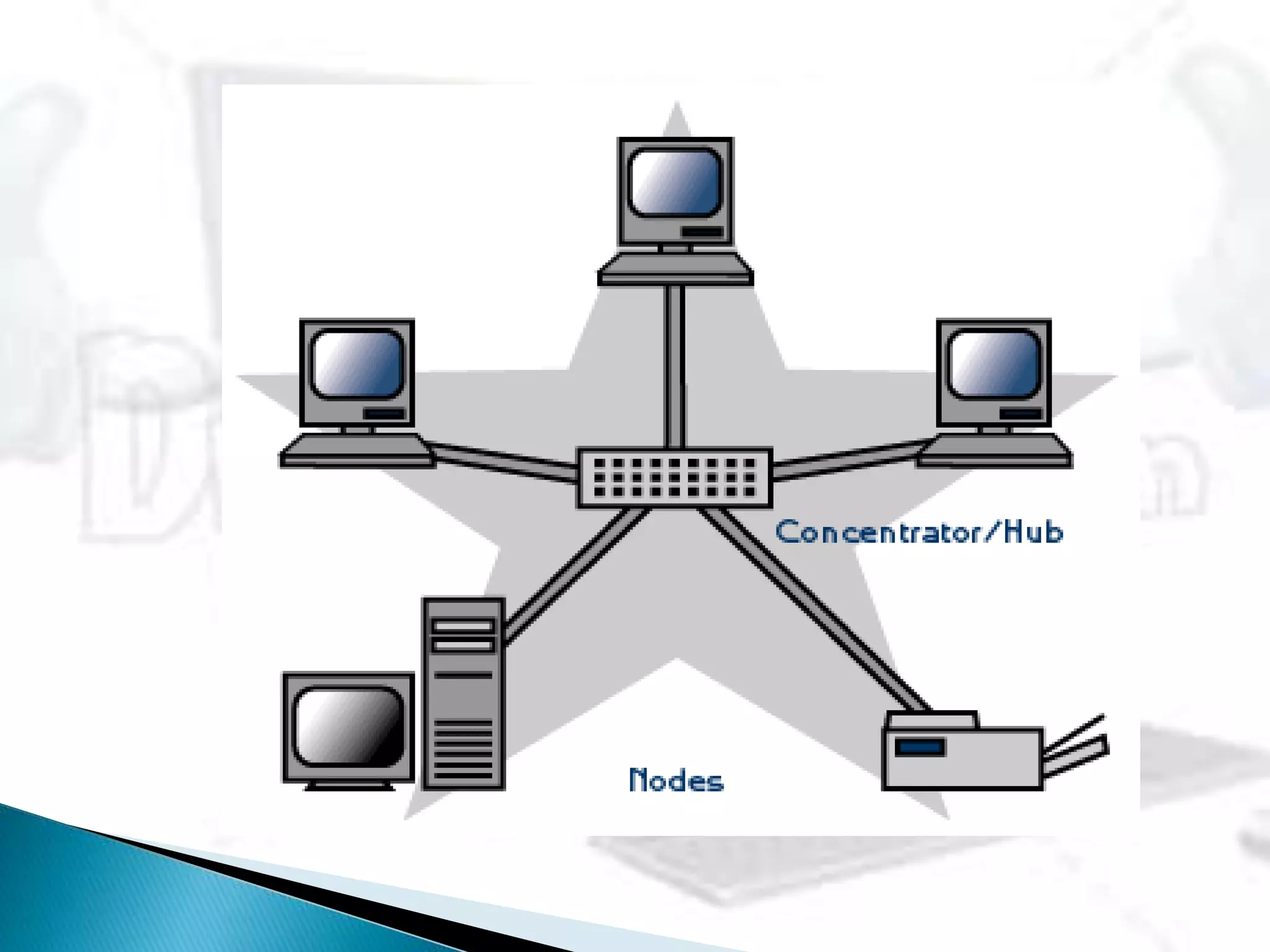
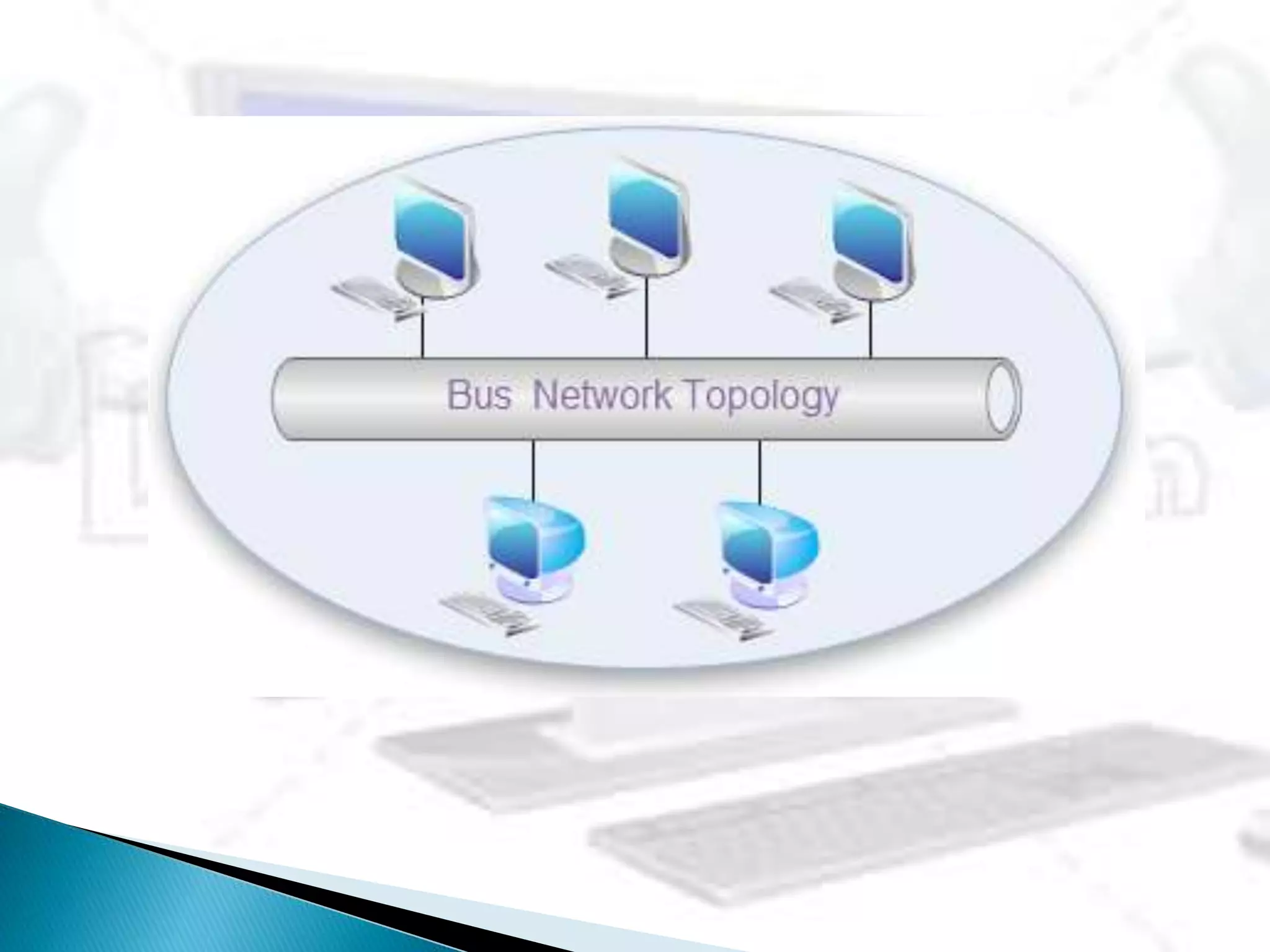
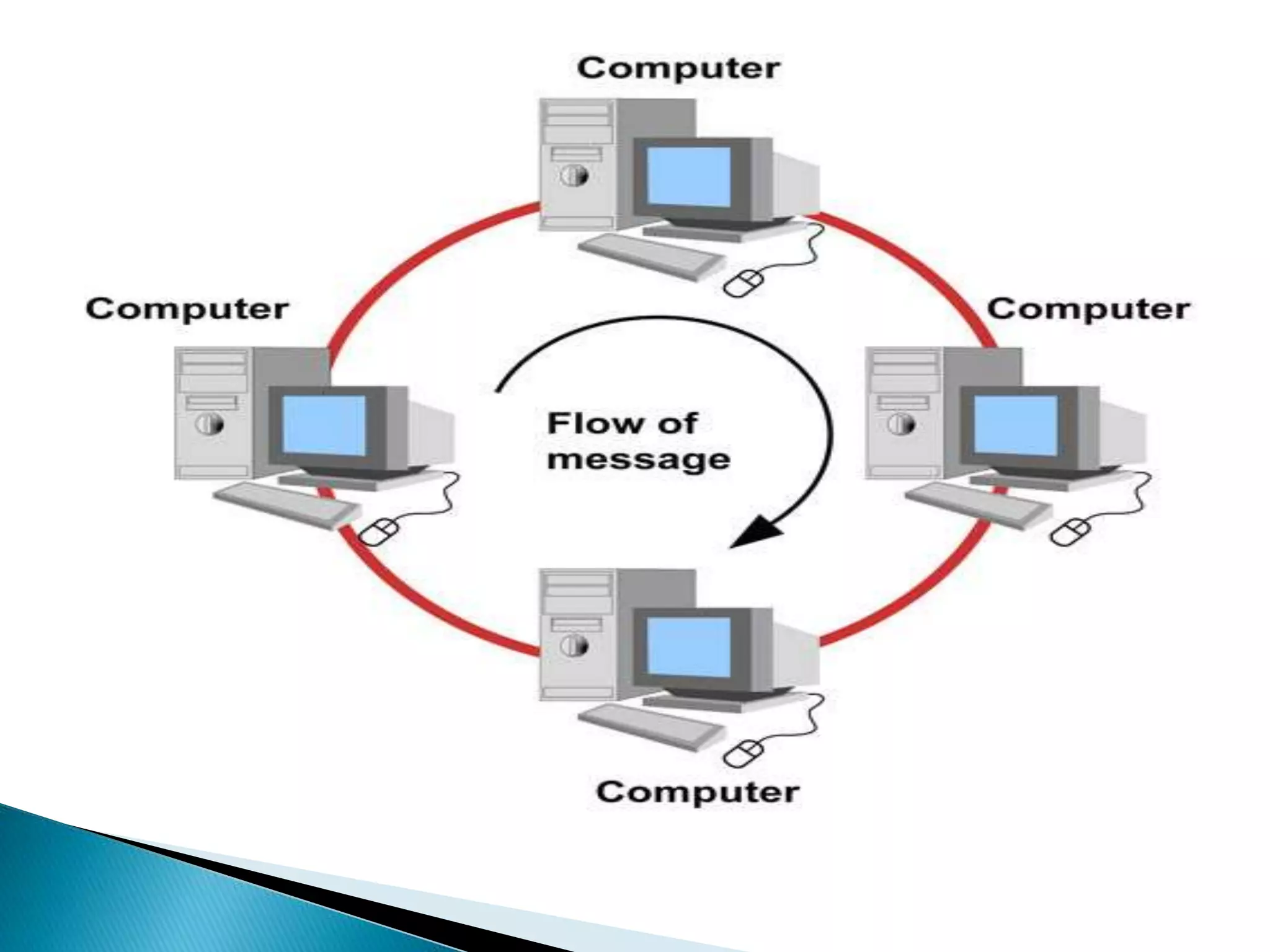
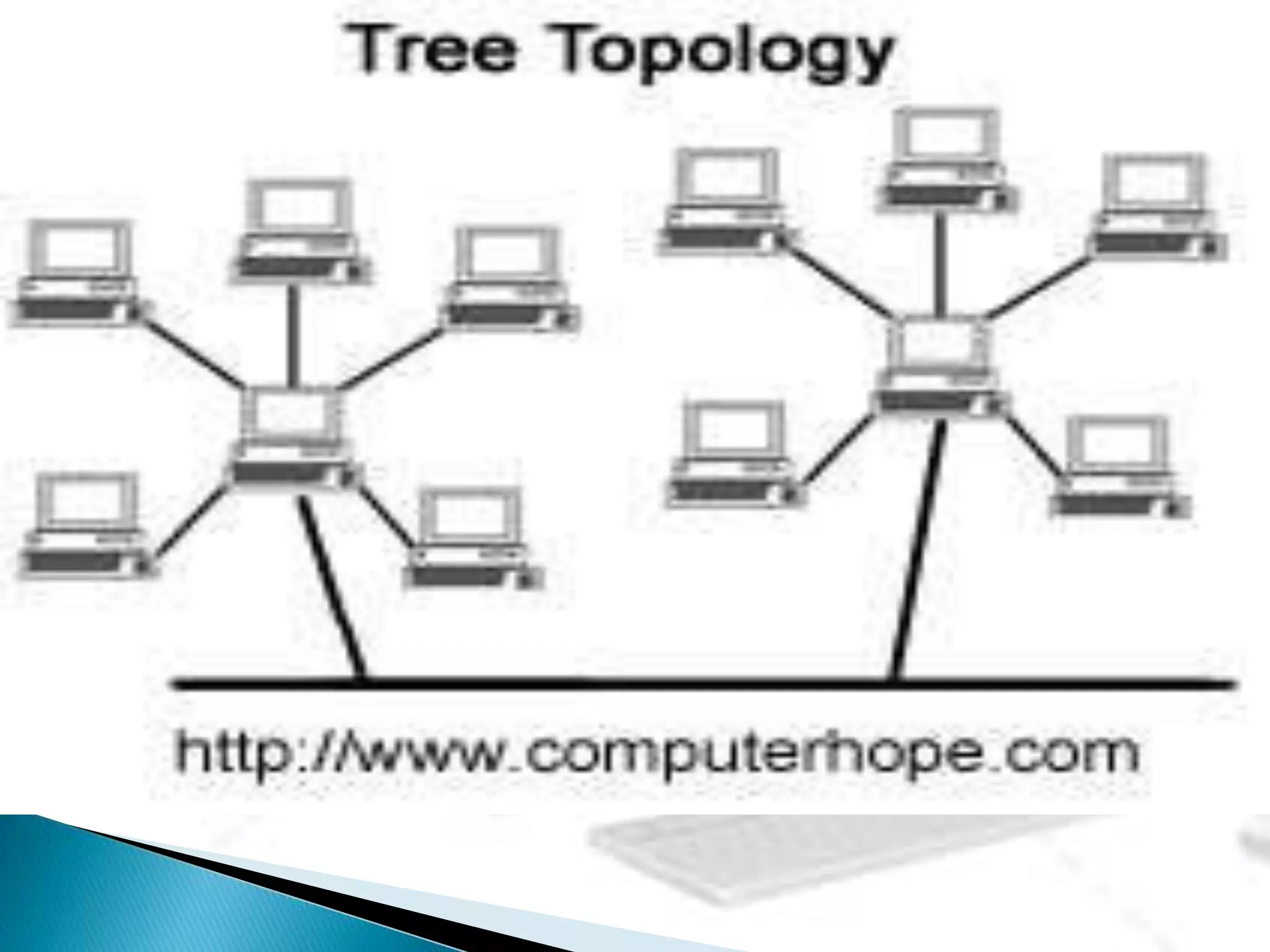
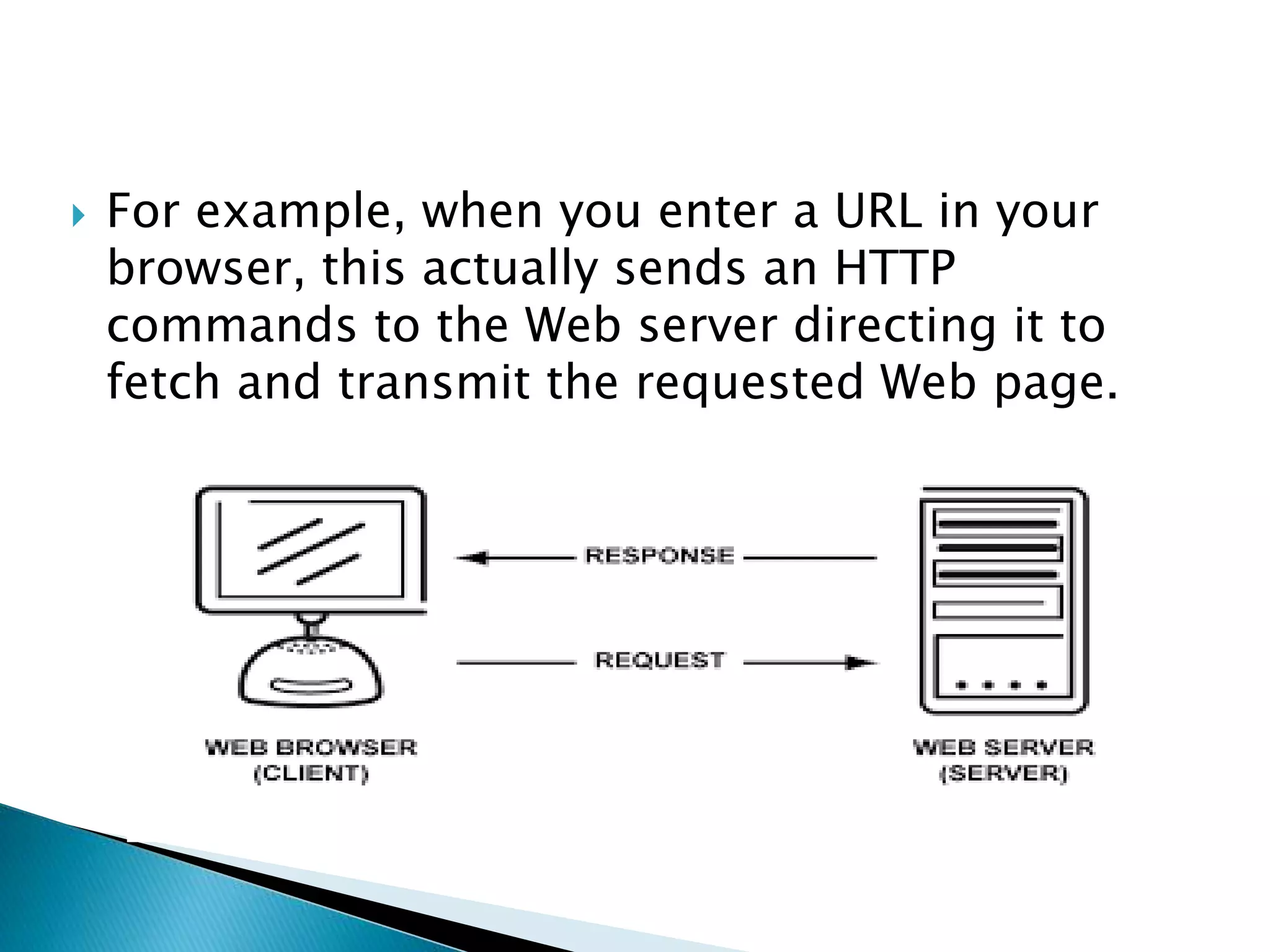
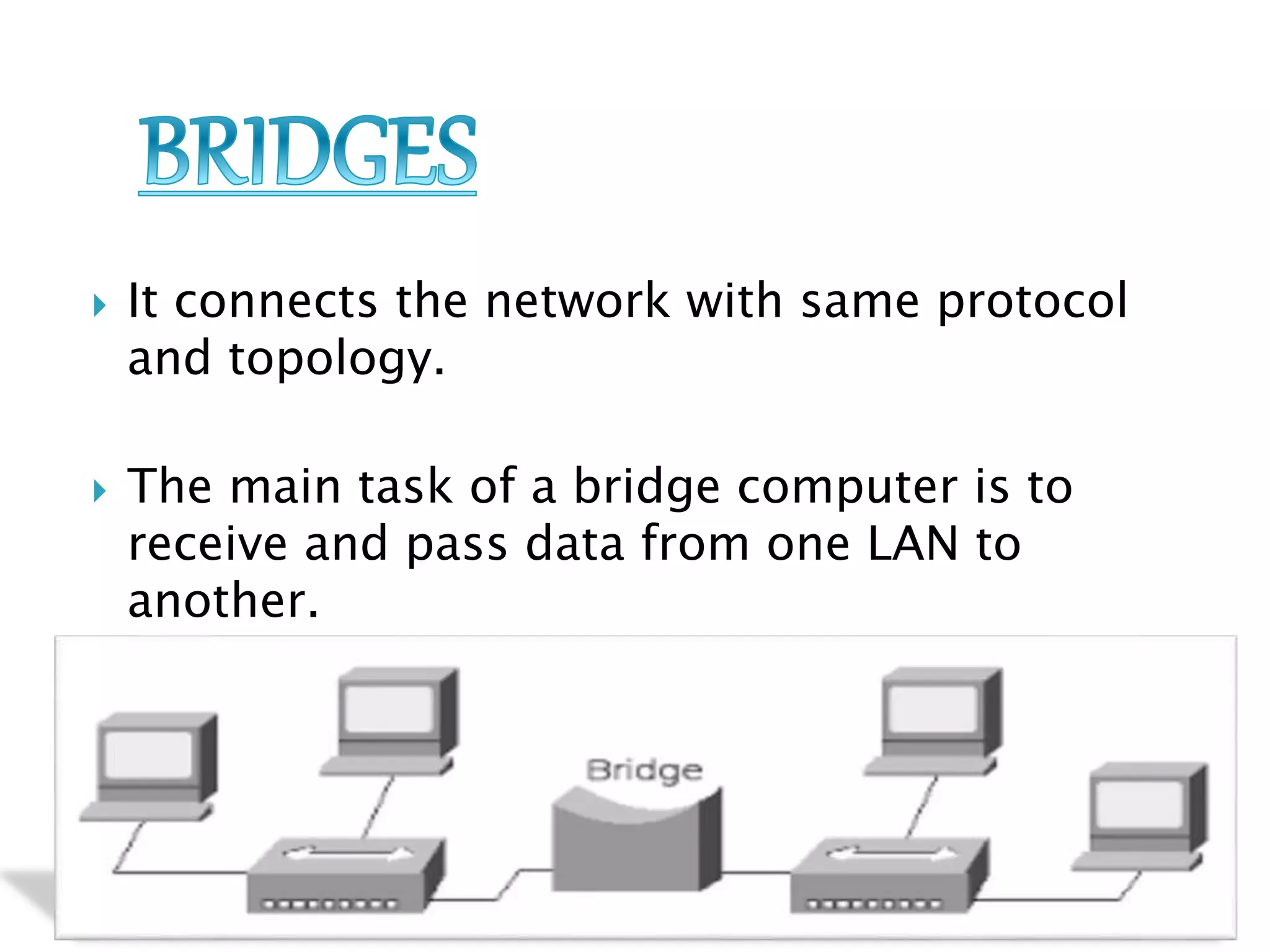
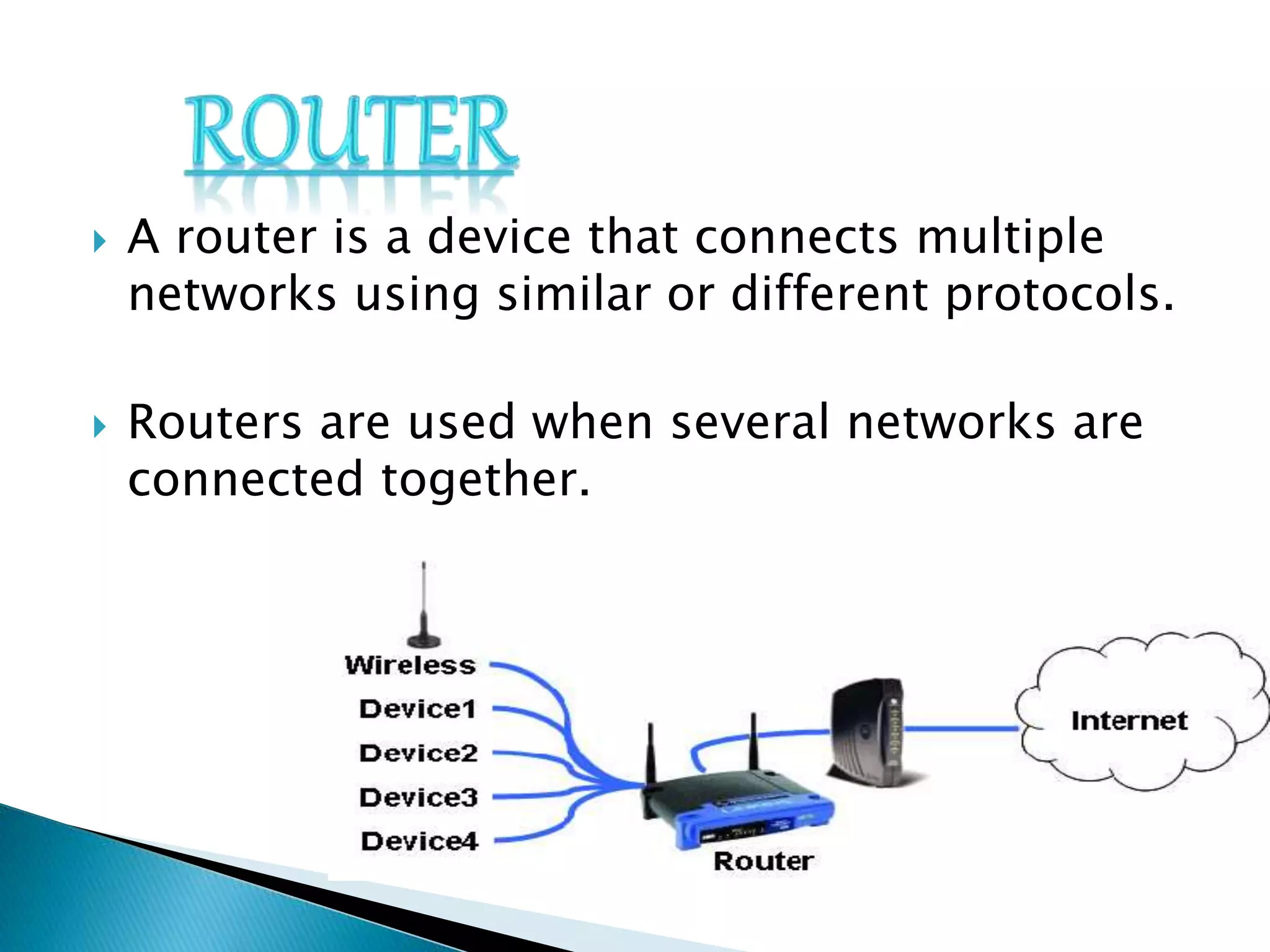
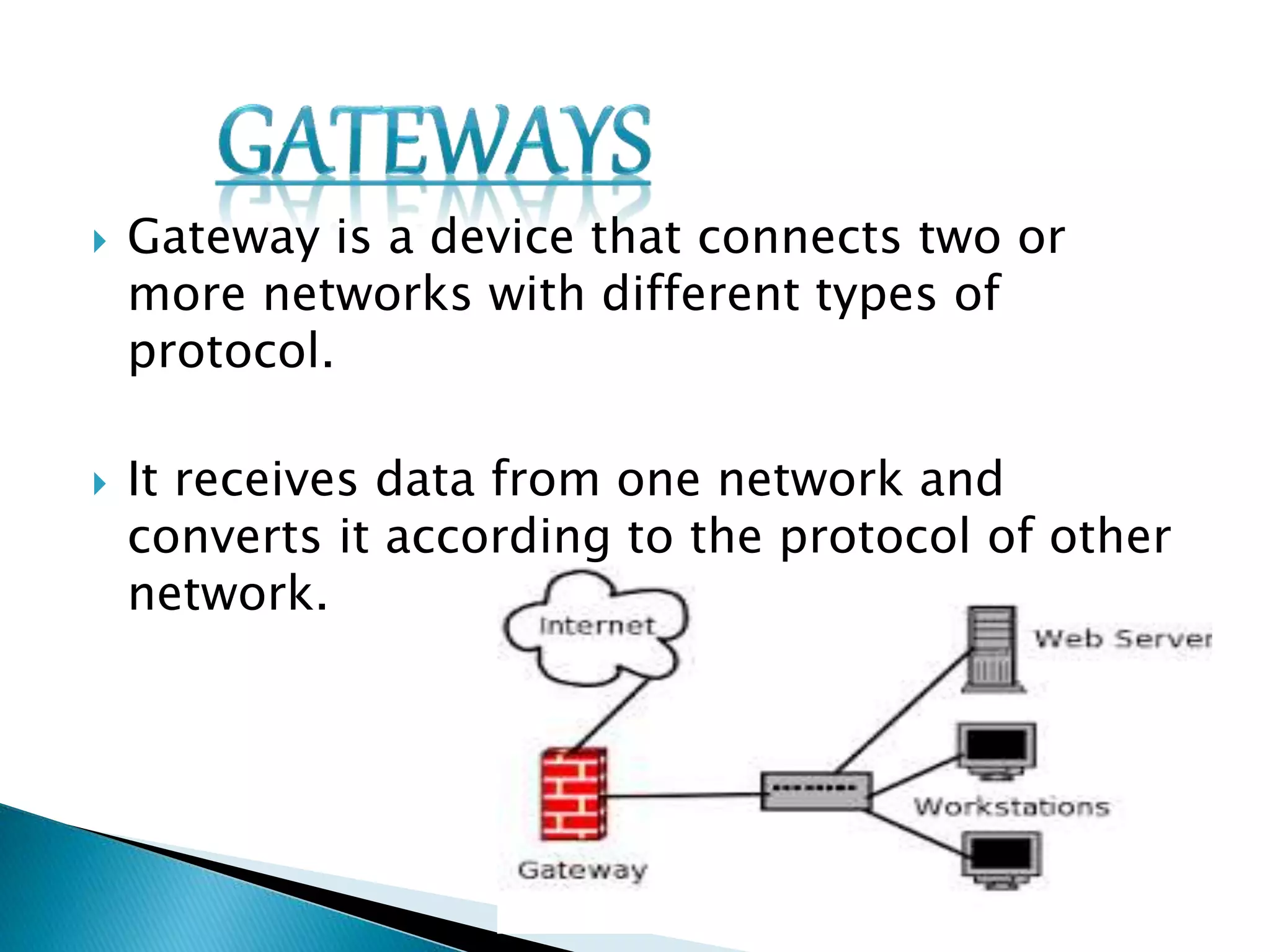
This document provides information about computer networks. It discusses that a computer network allows two or more computers to exchange information via data communication links. It then describes different types of networks like LAN, MAN, WAN based on size. It also discusses different network topologies like star, bus, ring and tree and network devices like hub, repeater, bridge, router and gateway. It finally explains common network protocols like TCP, IP, HTTP, FTP and HTTPS.