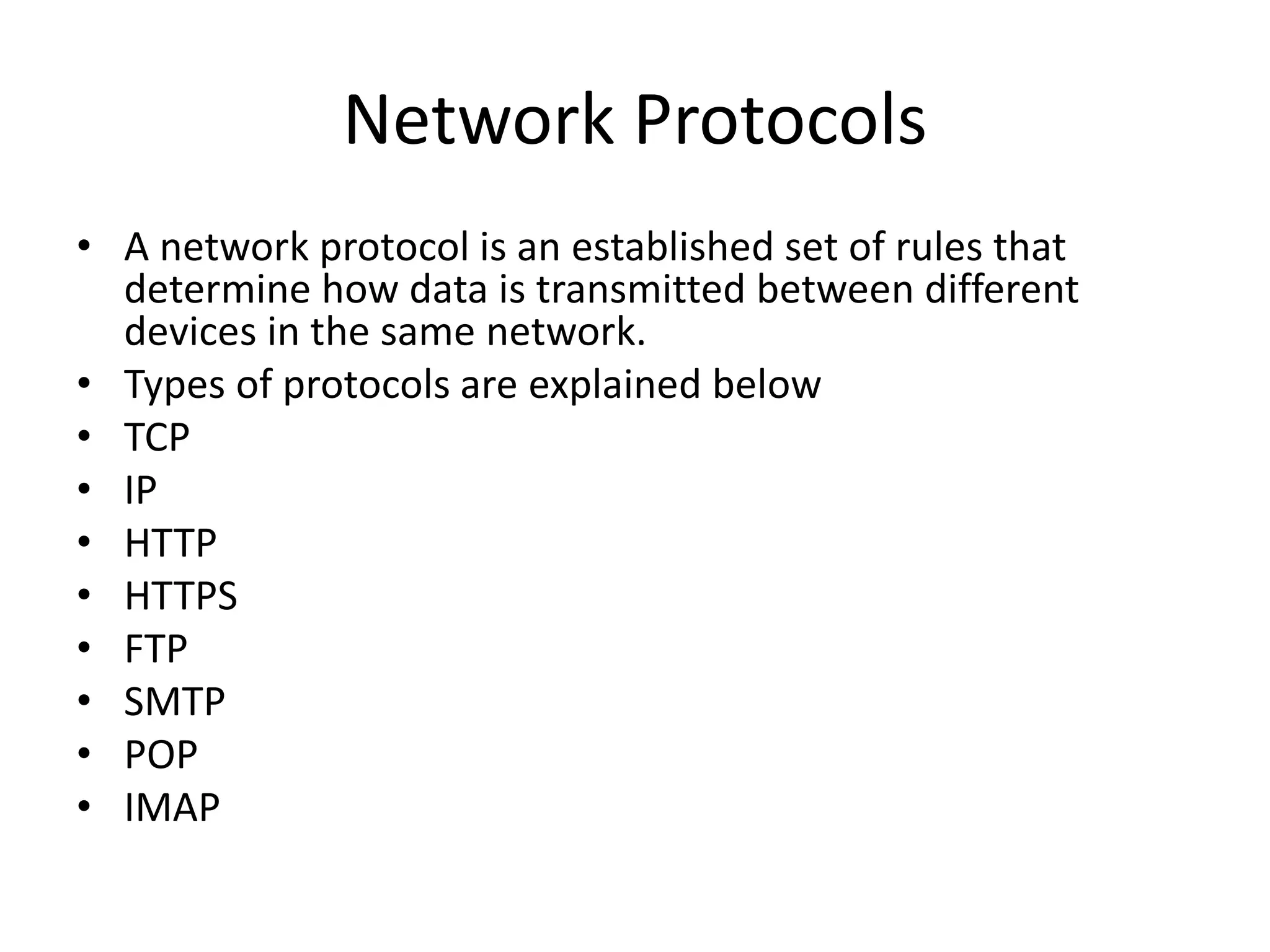
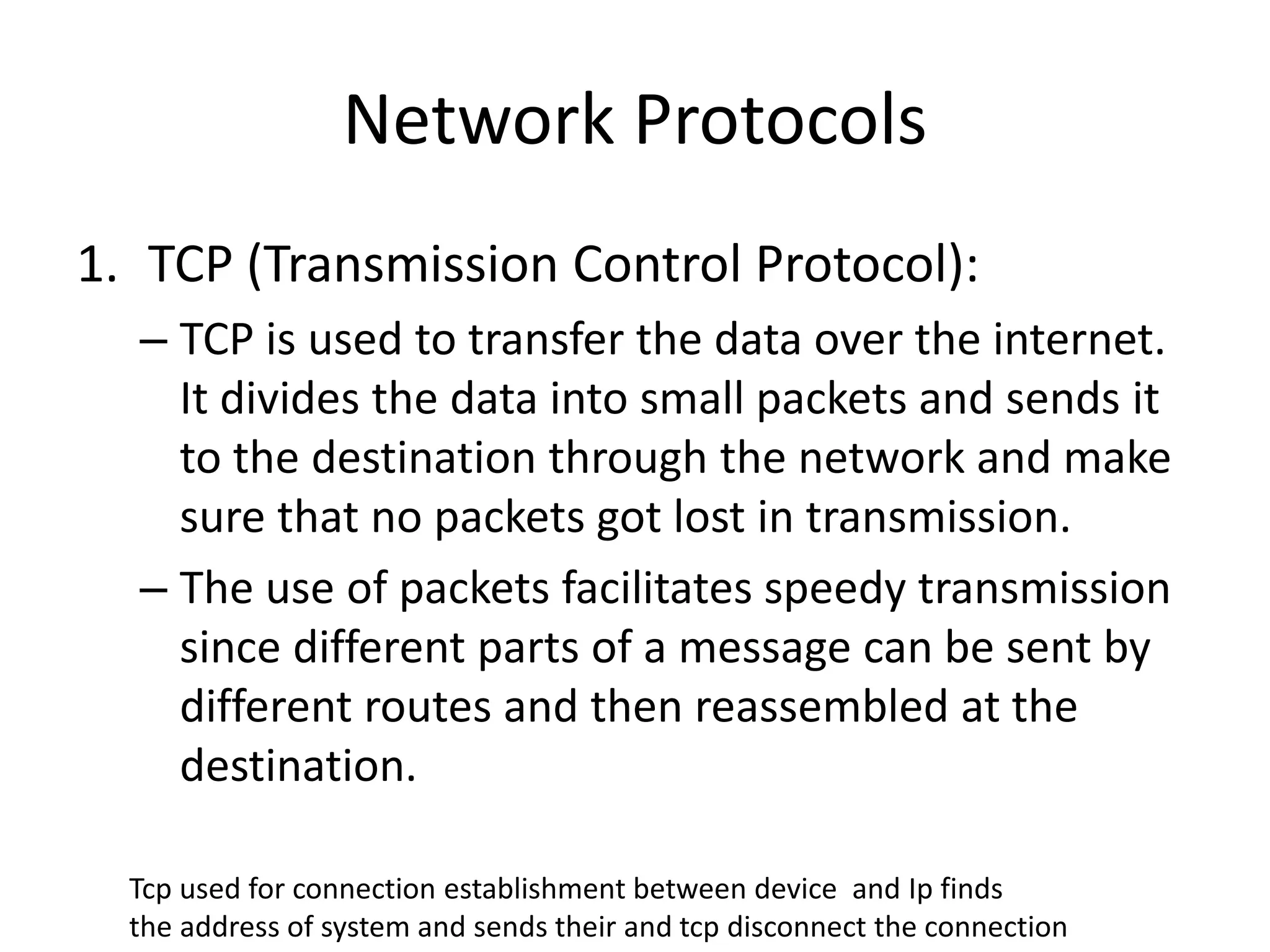
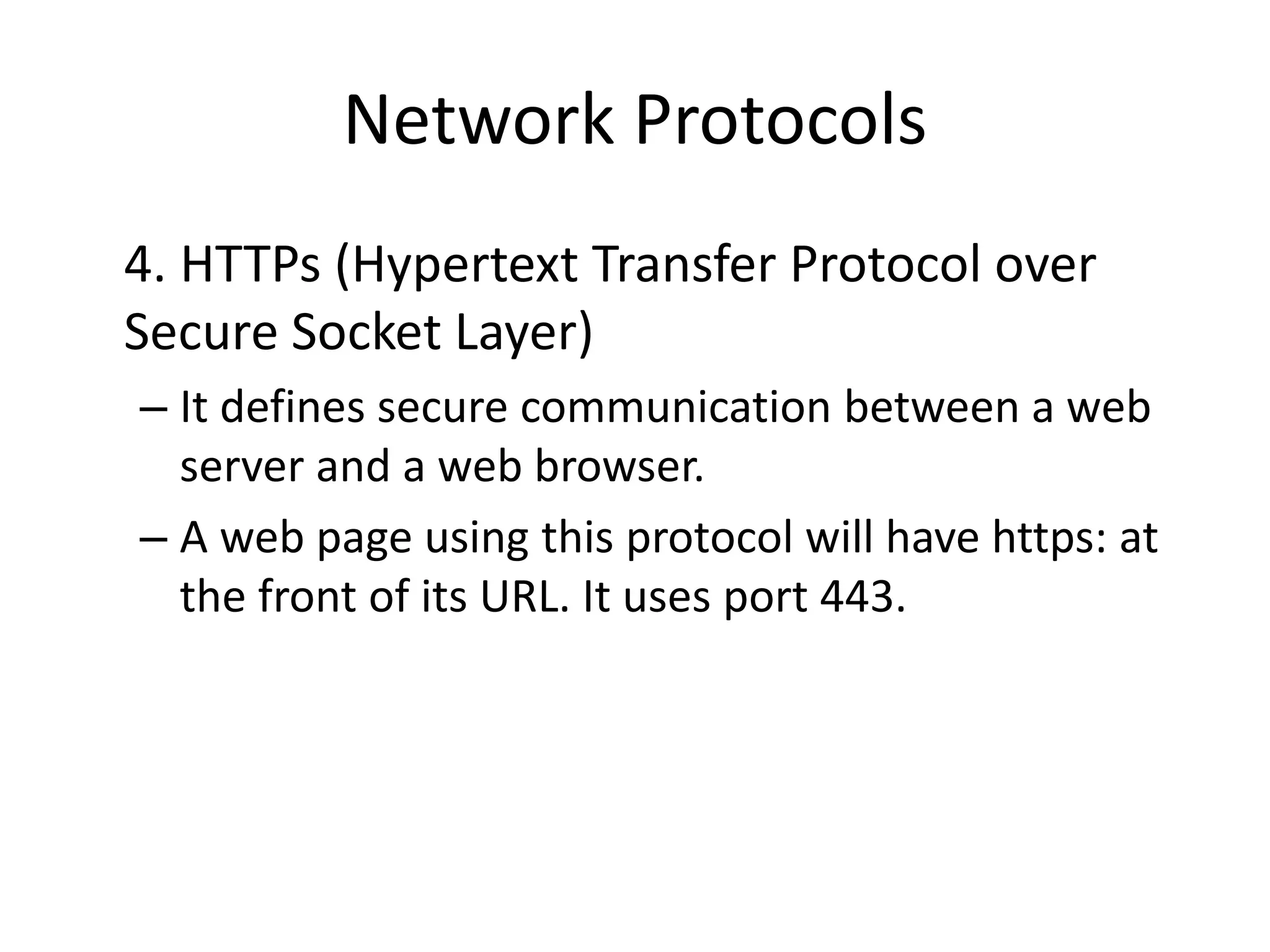
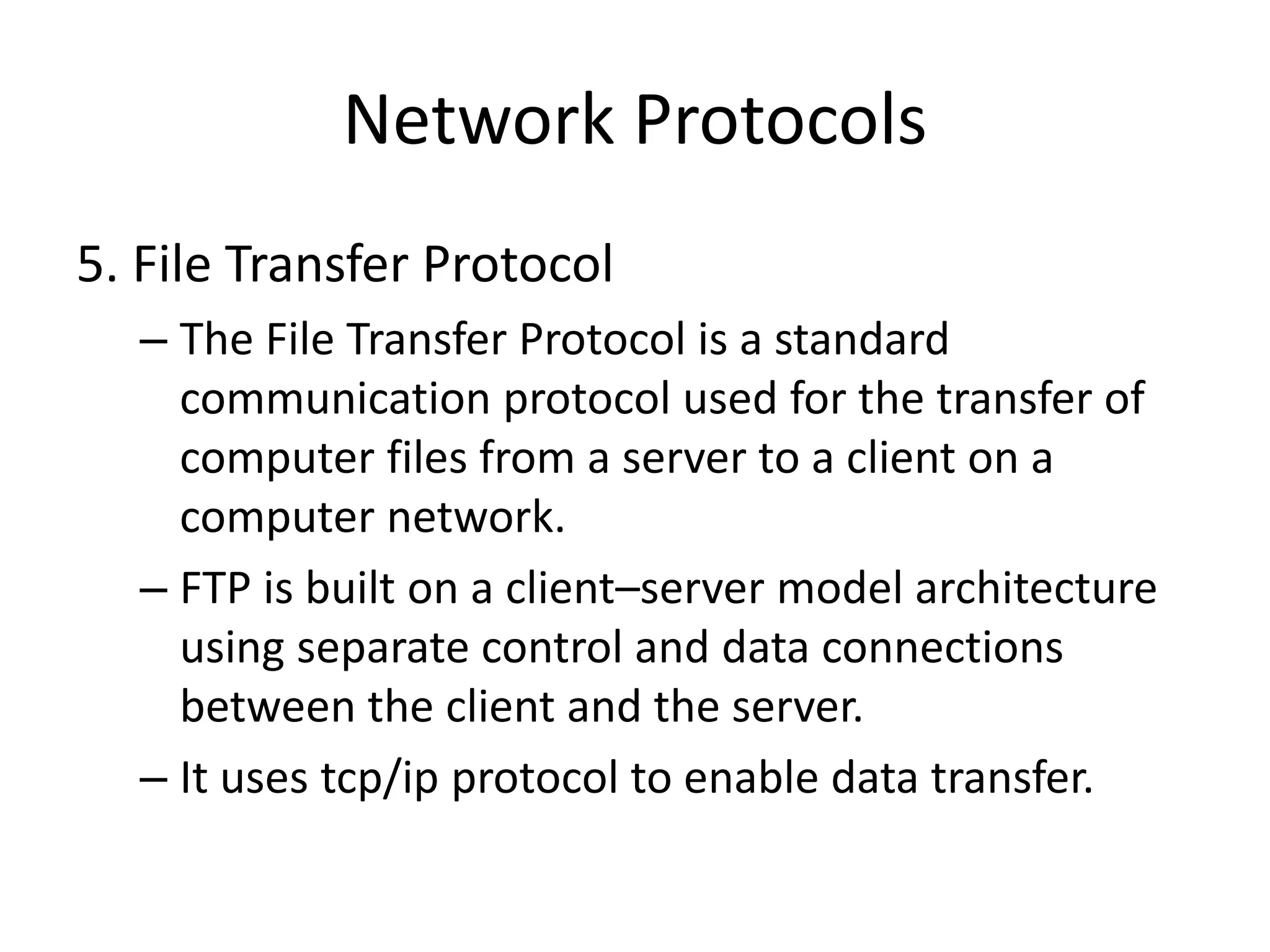
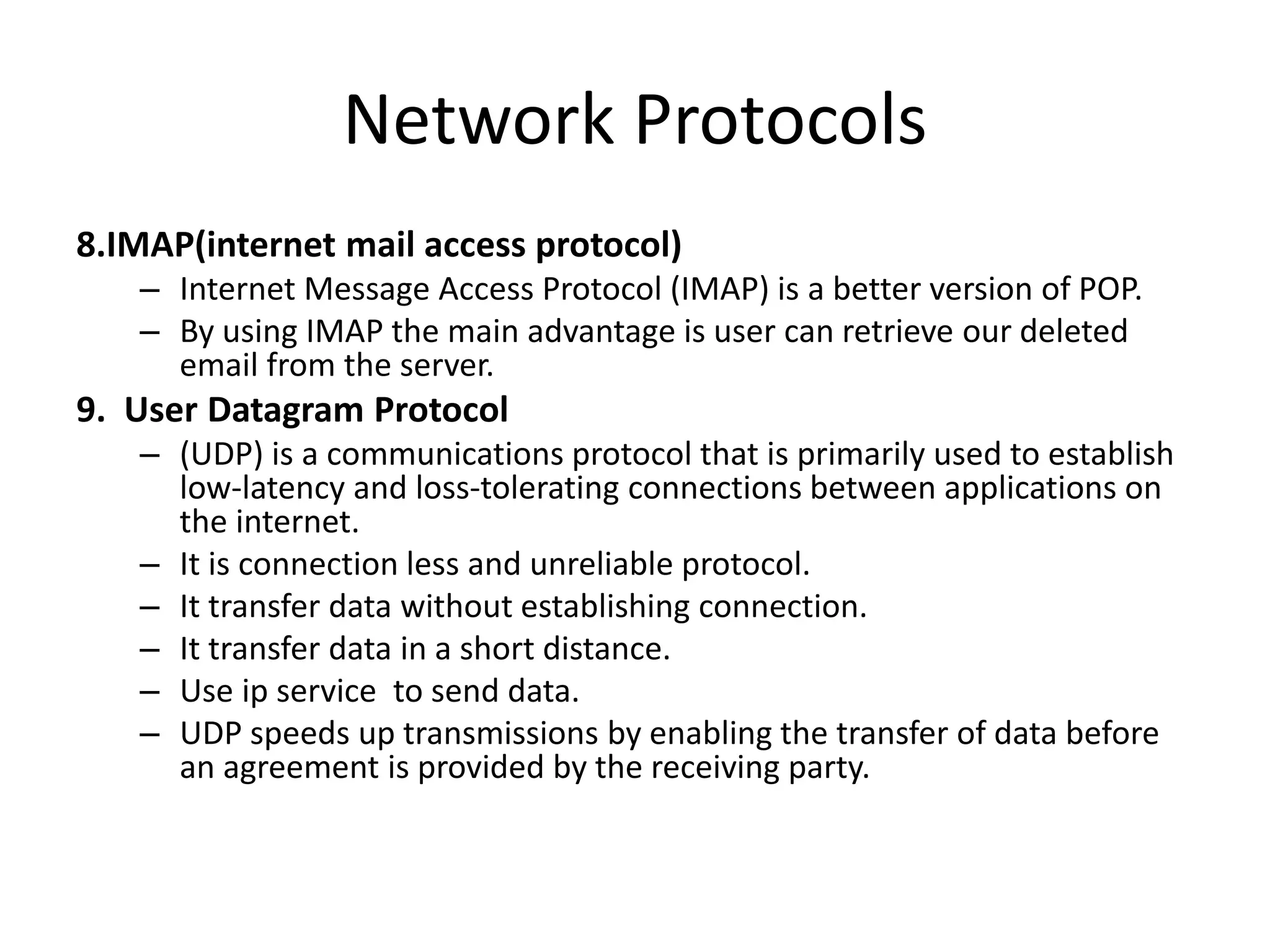
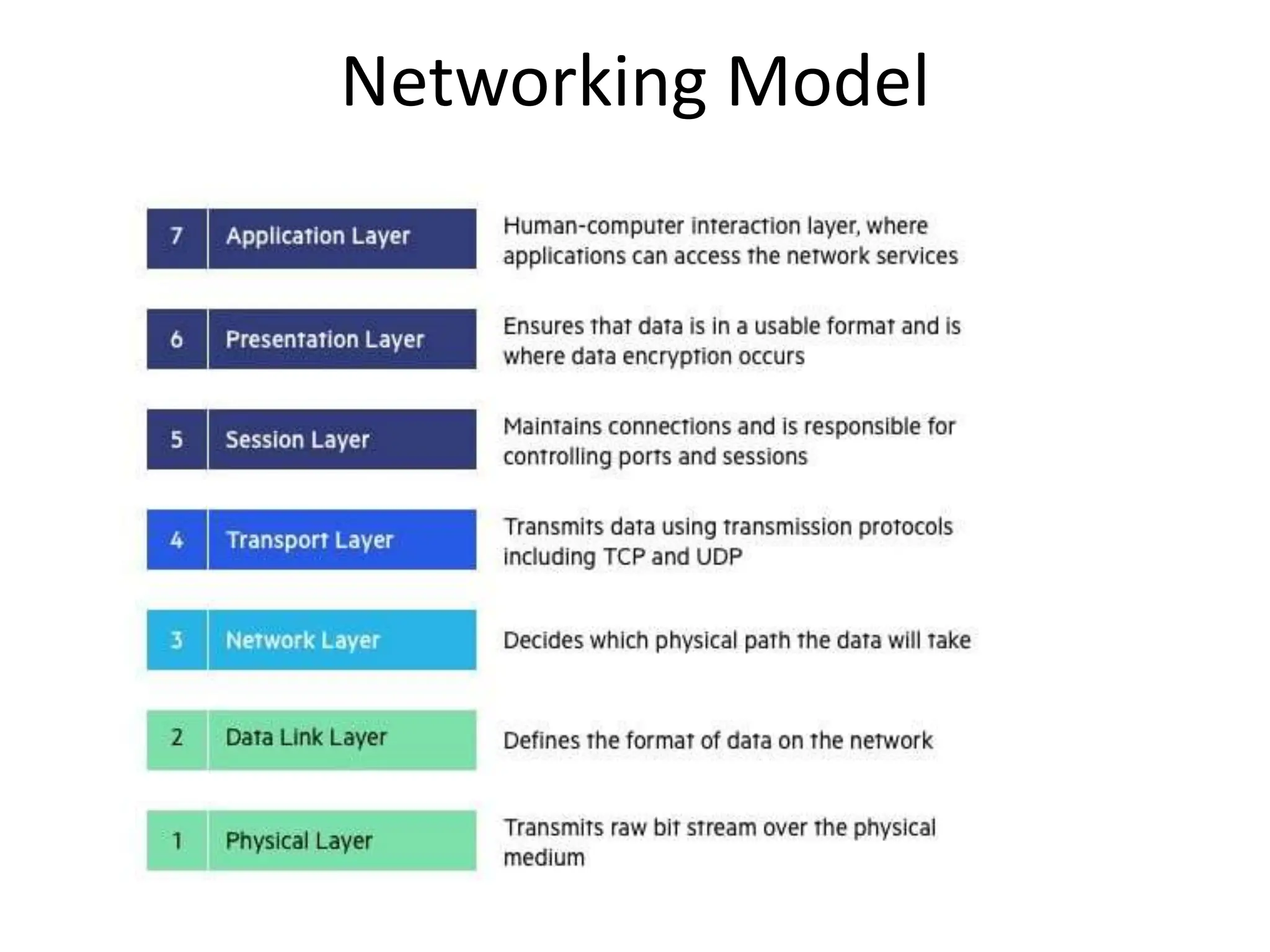
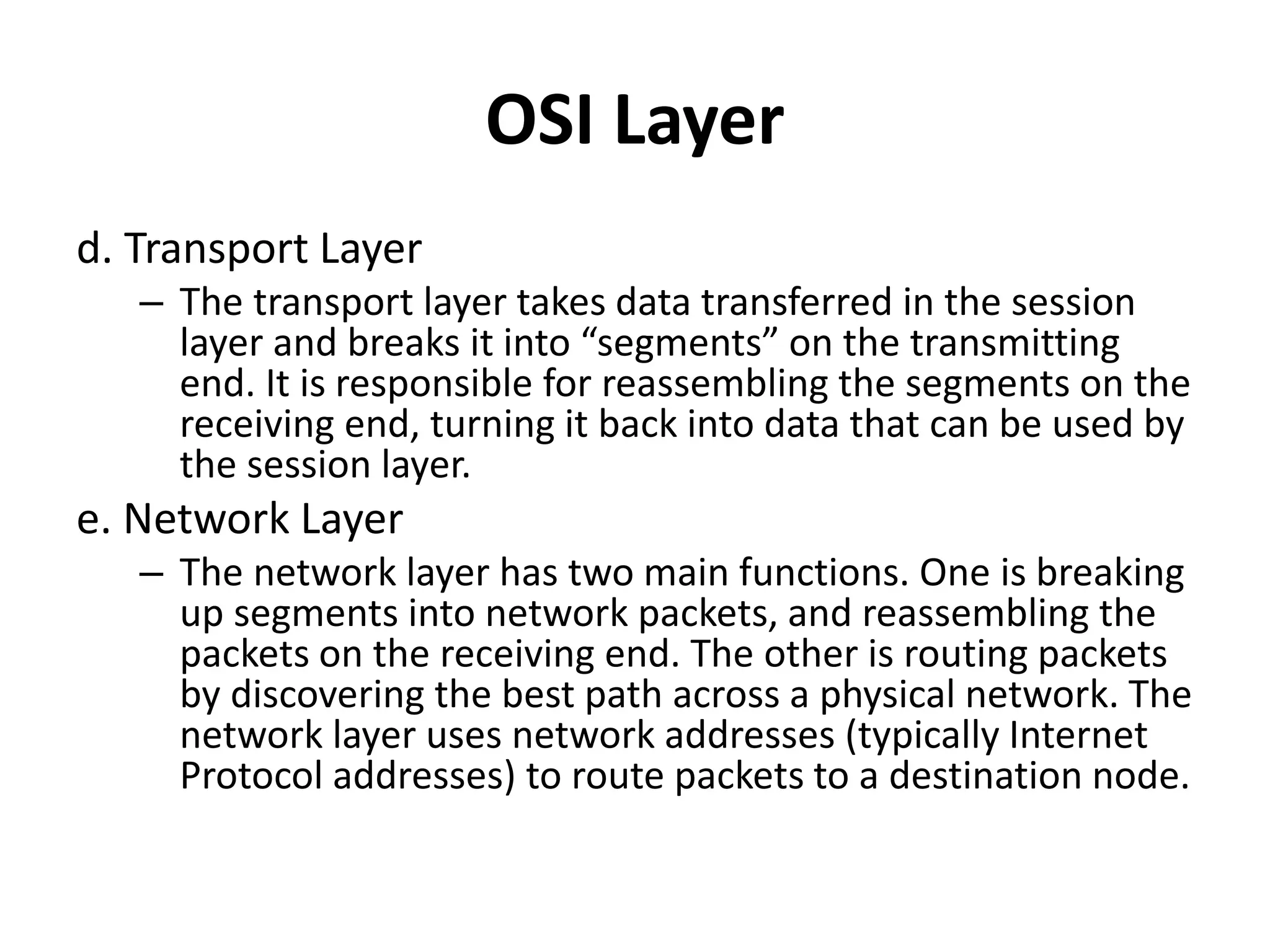
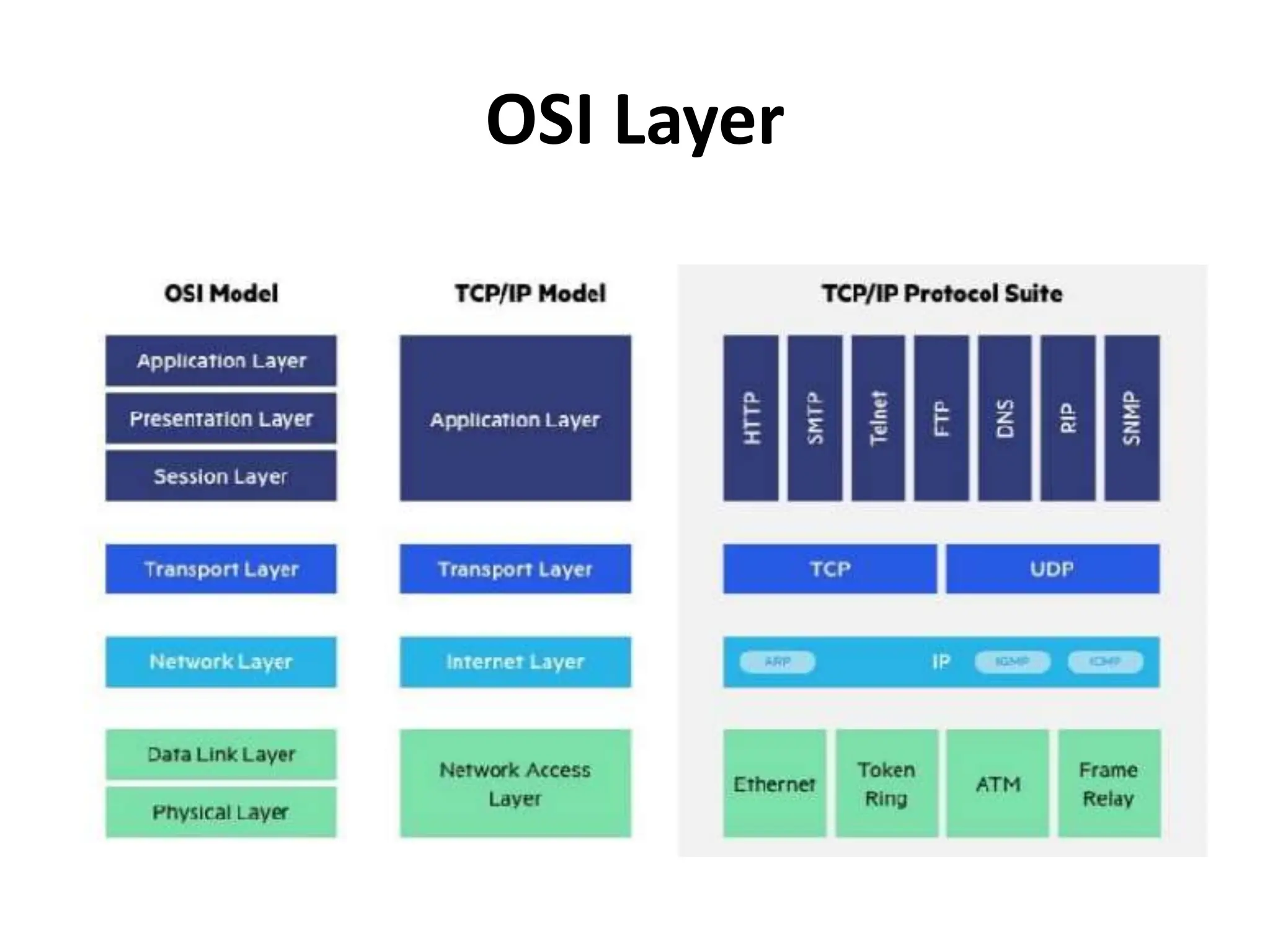
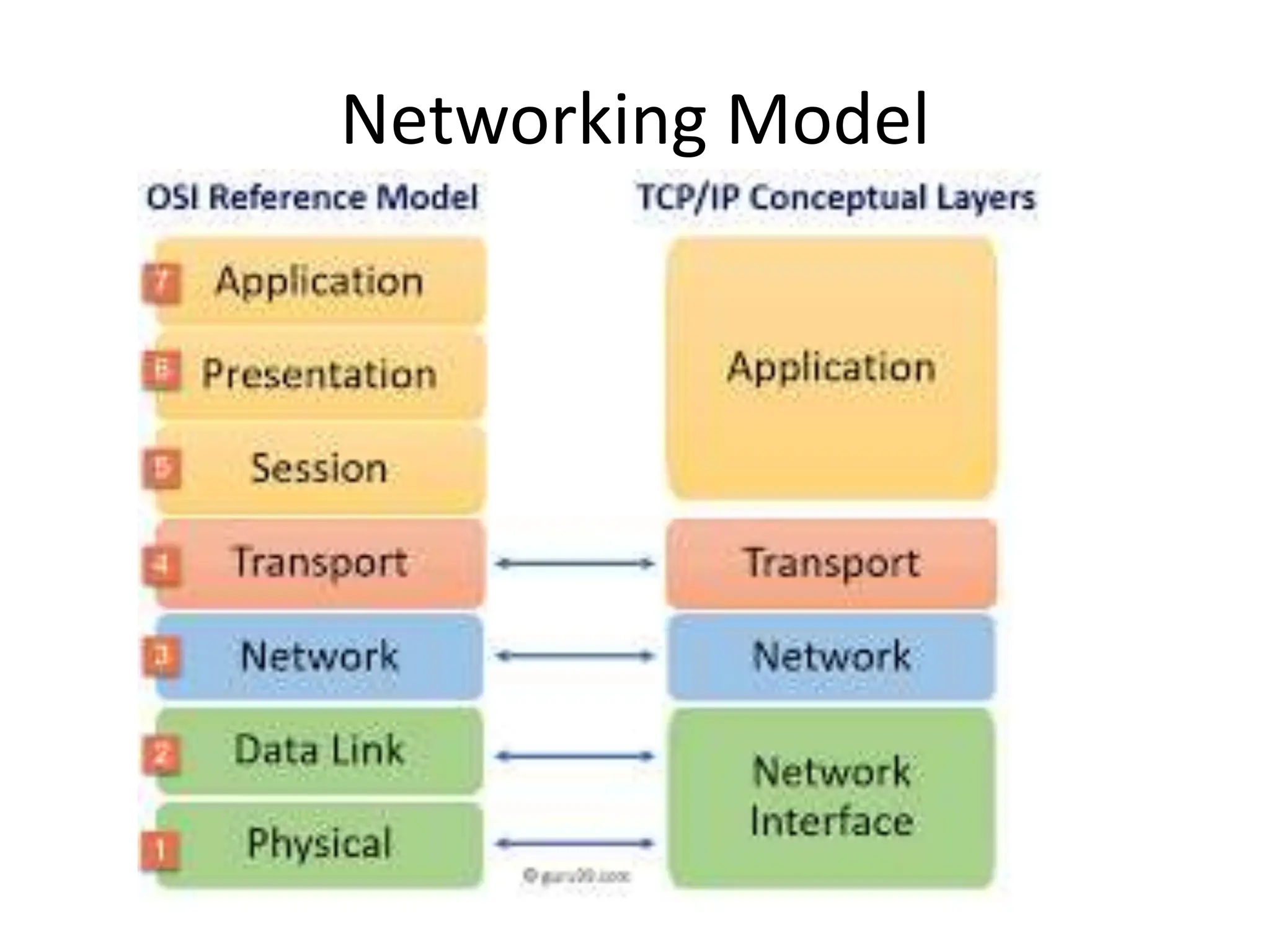
The document provides an overview of computer networking, highlighting the definition, purpose, and importance of computer networks in resource sharing, reliability, inter-process communication, and cost reduction. It details various networking protocols such as TCP, IP, HTTP, and others, explaining their functions in data transmission and communication. Additionally, the document outlines networking models like OSI and TCP/IP, as well as the applications and uses of networks in communication, resource access, and productivity enhancement.