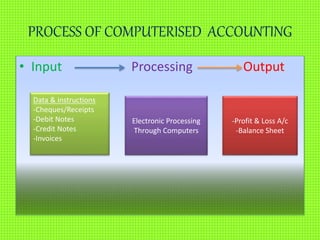
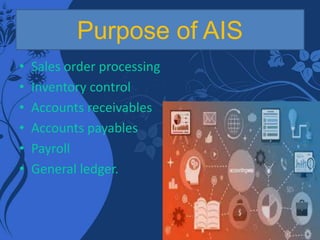
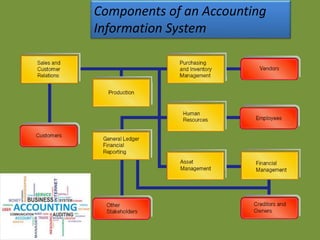
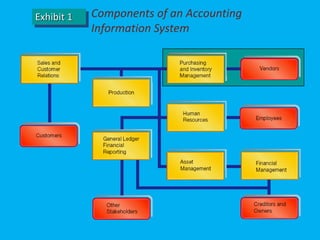
This document discusses computerized accounting systems and their components. It explains that a computerized accounting system processes financial transactions and generates reports according to accounting principles and user-defined structures. The key components of a computerized accounting system include input, processing, output, and control subsystems. The input subsystem collects accounting data, processing converts it into useful information, output produces reports, and control ensures accuracy, security and compliance. The system handles modules for sales, purchasing, inventory, human resources, production, assets, and financial reporting to support the accounting process.