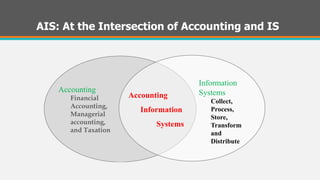
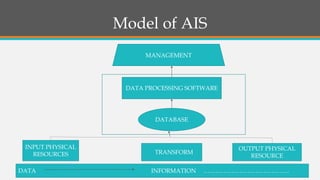
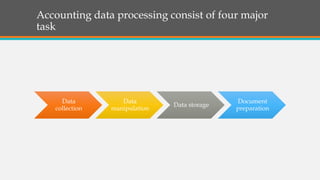
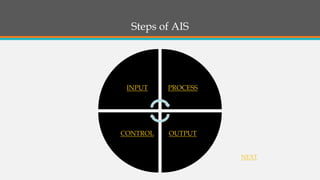
This document provides an overview of accounting information systems (AIS). It defines AIS and discusses their key components, including people, procedures, data, software, infrastructure, and controls. The document also outlines the history of AIS, how technology has impacted the field, common AIS models and processes, objectives and uses of AIS, limitations, and career opportunities in AIS such as systems consulting and value-added reselling.