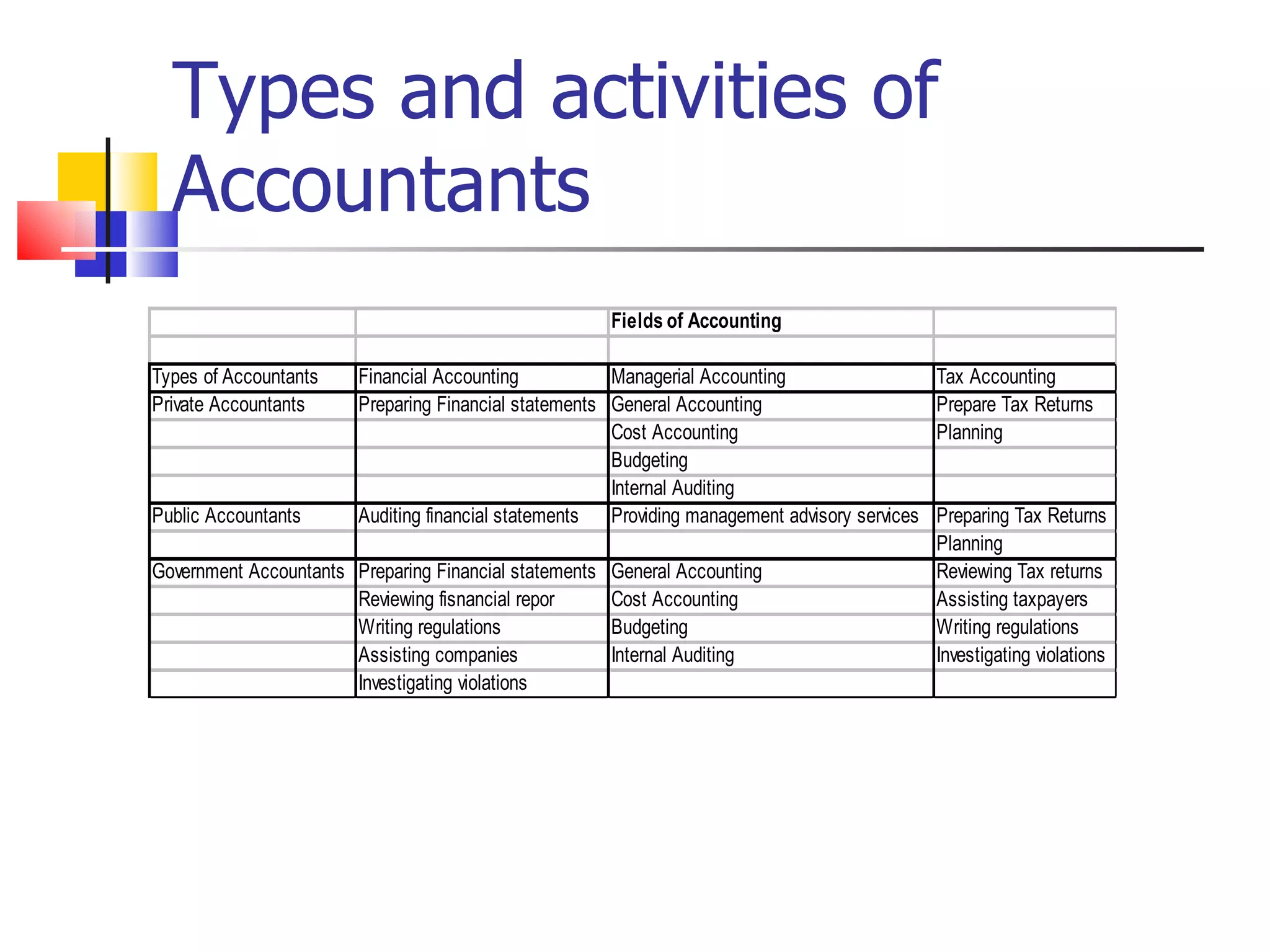
1. Accounting involves systematically recording, analyzing, classifying, summarizing, and interpreting business transactions and financial information.
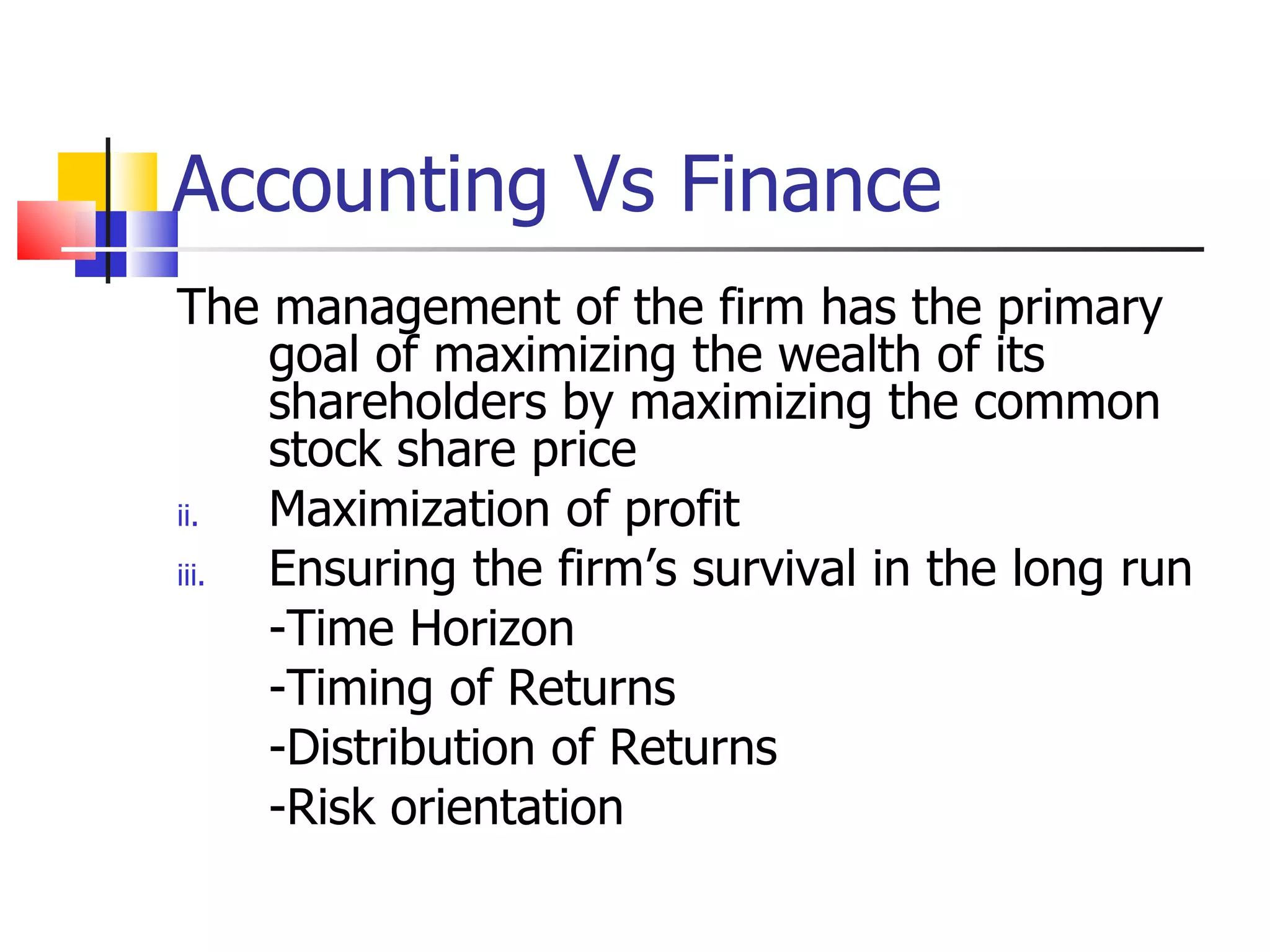
2. The main purposes of accounting are to plan finances, keep financial records, enable information sharing, and use data to make decisions.
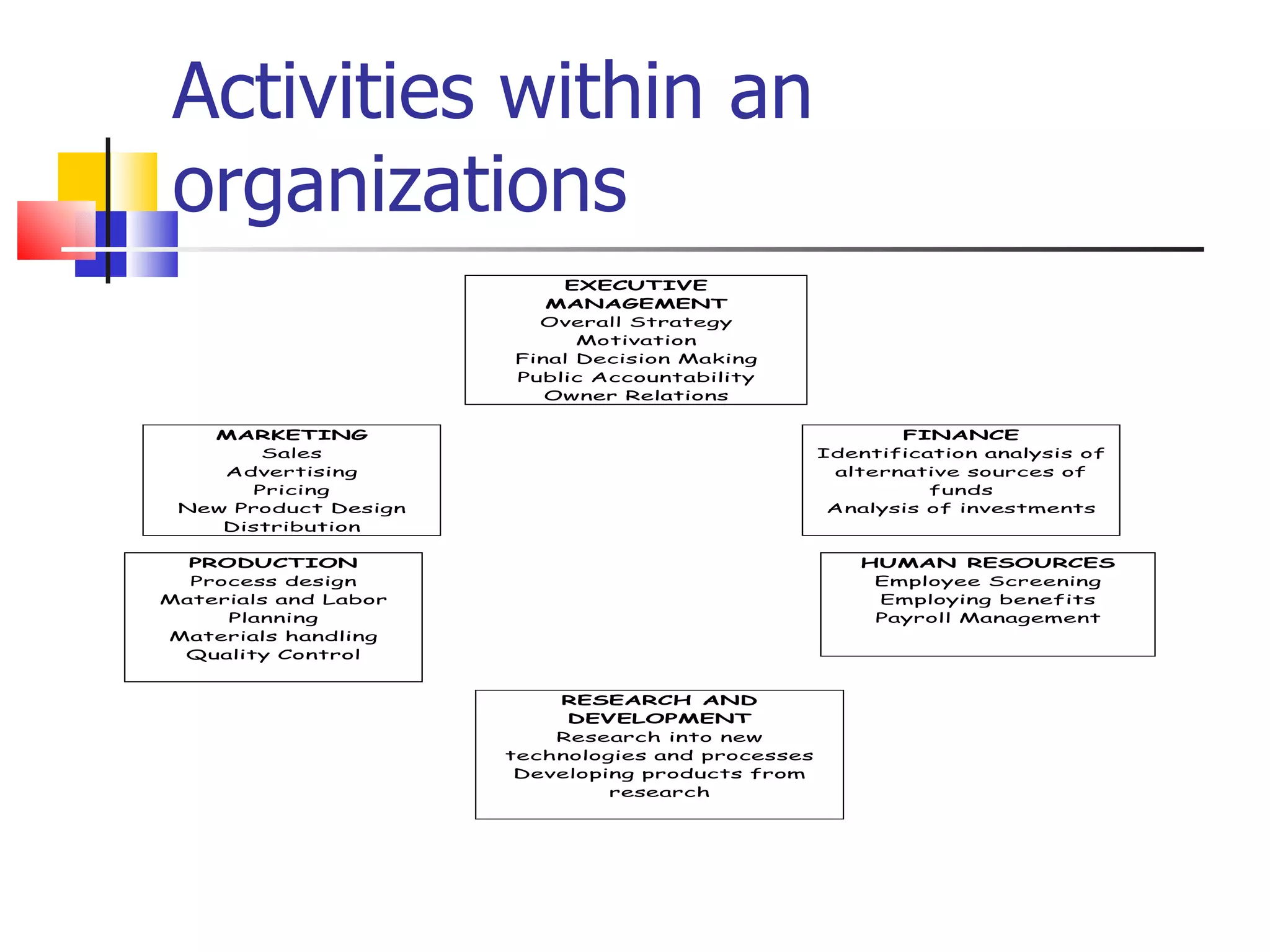
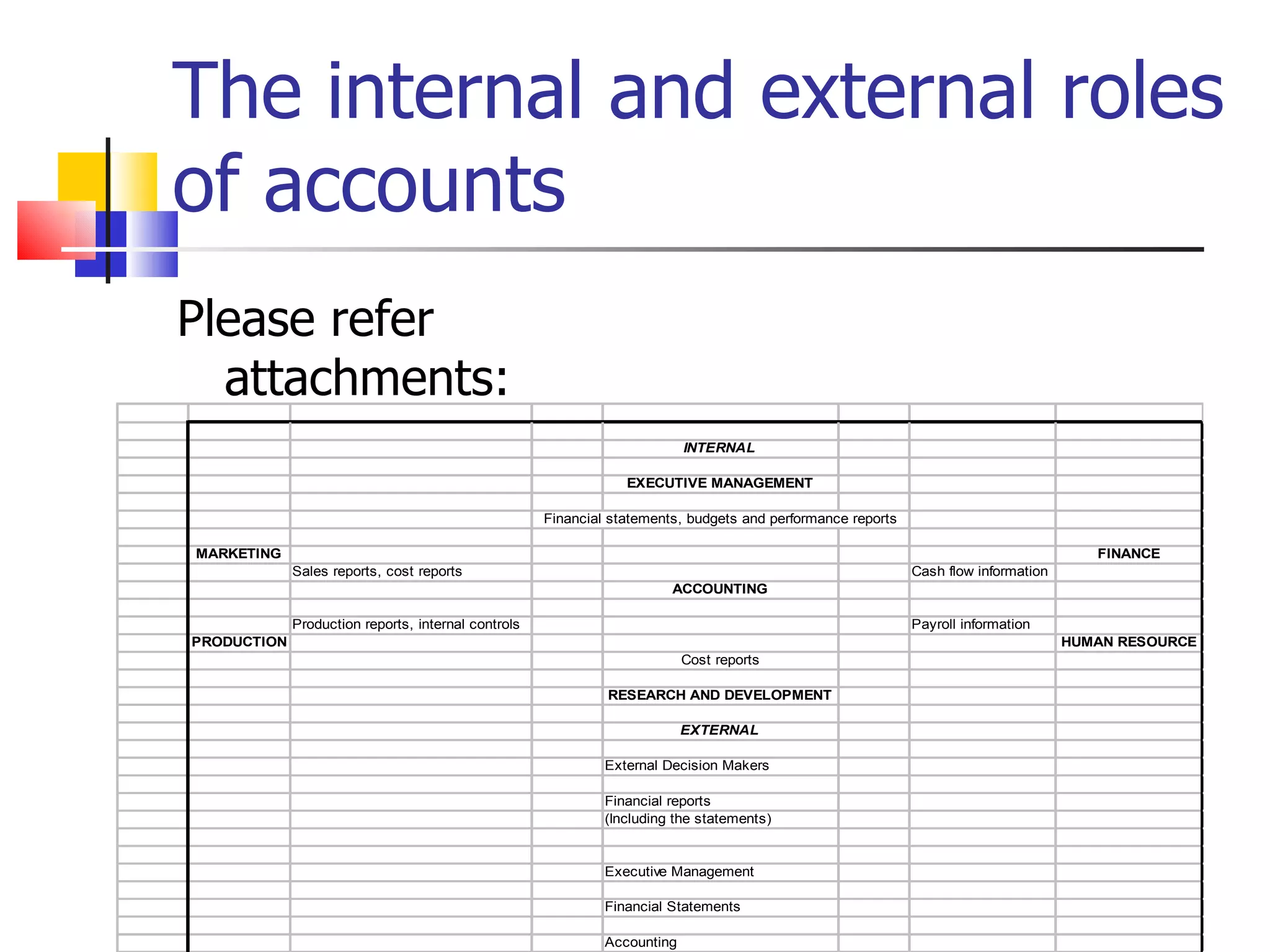
3. Accounting provides both internal and external users with financial information to assess a business's performance and financial position.