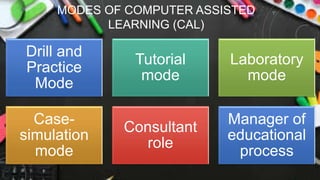
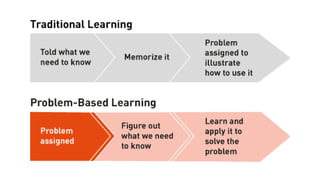
The document discusses various instructional methods including Computer Assisted Learning (CAL), Microteaching, and Problem-Based Learning (PBL). CAL enhances learning through multimedia and has advantages like time-saving and rapid information access, but faces limitations like cost and a lack of human interaction. Microteaching focuses on skill development in a controlled, small-group setting, while PBL emphasizes student-centered learning through problem-solving in groups, fostering skills like critical thinking and self-directed learning.