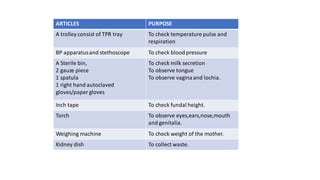
The document outlines the responsibilities and procedures for postnatal assessment and management, emphasizing the importance of thorough examination for early identification of complications in mothers and newborns. It covers the definitions, purposes, aims, and the systematic assessment process, including monitoring vital signs, physical examinations, and postpartum care guidelines. Postnatal management recommendations include hygiene, diet adjustments, early ambulation, and necessary immunizations for both mother and child.