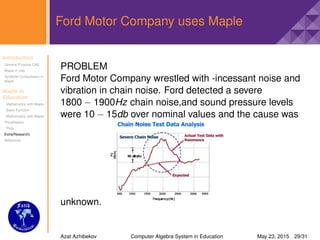
Maple is a general-purpose computer algebra system that is widely used for teaching and scientific purposes. It allows symbolic and numeric computation and can simplify mathematical expressions. The document discusses Maple's features and how it can be used for education in mathematics. Commands in Maple are demonstrated for performing calculus operations like differentiation, integration, limits, and plotting functions.








![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
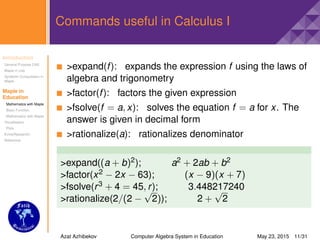
Commands useful in Calculus I
>Slope(p1,p2): computes the slope of the line
through the points p1 and p2
>limit(f, x = a): finds the limit of f as x approaches a
>solve(f = a, x): solves f(x) for x
>root(x, n): nth root of x
>limit(sin(x)/x,x = 0); 1
>limit(exp(b),infinity); ∞
>limit(−1/x, x = 0,right); −∞
>solve(sin(x) + y = 2, x); − arcsin(y − 2)
>solve(x2 − 9 = 0, x); ±3
>root(32, 5); 2
>Slope([0, 0], [1, 2]); 2
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 13/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-13-320.jpg)
![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
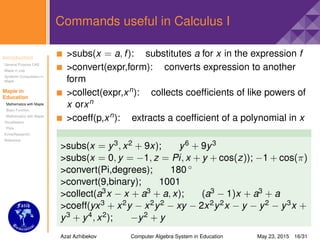
Commands useful in Calculus I
>int(a, x): computes the indefinite integral of
expression a with respect to x
>int(a, x = b..c): computes the definite integral of a
with respect to x
>maximize(a, opt1, opt2..optn): computes global
maximum value of a
>minimize(a, opt1, opt2..optn): computes global
minimum value of a
>int(2 + x, x); 2x + x2
2
>int(4x2 − 2/x5 + 7, x); 4x3
3 + 1
2x4 + 7x
>int(exp(x)/2, x); 1
2 ex
>maximize(x3 − 3x2 − 9x + 5, x = 0..4,location);
5, {[{x = 0}, 5]}
>minimize(x2 + 1, x = −1..2); 1
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 14/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-14-320.jpg)
![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
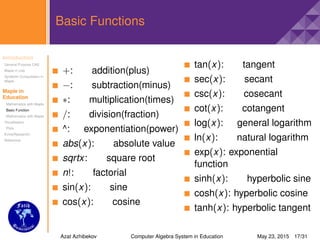
Some important commands II
restart: clears all previously assigned variables,makes
Maple act like as if just started
: executes the current expression
: executes the worksheet
[list] (ordered): z := [c, a, b]: >z [1]; c
{set} (unordered,no duplicates): >{a, b, a, c}; {a,b,c}
>=: ≥ (greater than or equal)
<>: = (not equal)
<=: ≤ (less than or equal)
@: composition operator(composition function)
"text": assigns nothing but only text
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 15/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-15-320.jpg)

![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
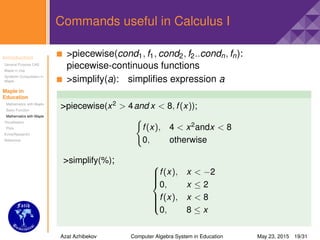
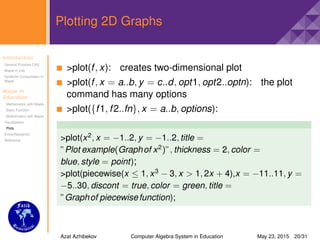
Some plot options
You can change the view of graphs by applying plot options
axes="boxed,frame,none or normal"
color="Orange,Silver,Gold,Green,Coral,BlueViolet,Lime,
Yellow,DeepSkyBlue,etc."
discont=true,false
filled=true,false
labels=[x,y]
labeldirections=[horizontal,vertical]
linestyle=solid,dot,dash,dashdot,longdash,spacedash,
spacedot
numpoints=n (default is 50 points)
style=line,point,patchnogrid,patch
thickness=n
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 22/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-22-320.jpg)
![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
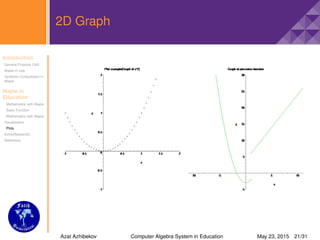
2D Graph
>plot([sqrt(x), 3log(x)], x = 0..400, numpoints =
1000, thickness = 3);
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 23/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-23-320.jpg)
![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
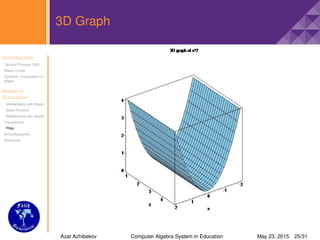
Plotting 3D Graphs
For some special plots you need special commands that
are in plots package
>plot3d(f, x = a..b, y = c..d): creates
three-dimensional plot
>plot3d([f, g, h], s = a..b, t = c..d):
>plot3d([f, g, h], a..b, c..b):
>plot3d([exprf, exprg, exprh], s = a..b, t = c..d):
>plot3d(x2, x = −2..2, y = 1..5, axes = boxed, scaling =
constrained, color = ”SkyBlue”, style = patch, title =
”3Dgraphof x2);
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 24/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-24-320.jpg)
![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
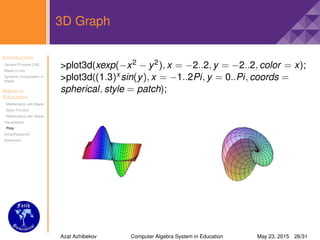
Some 3D Plot Options
axes=boxed
caption="c"
coords=polar,spherical,cylindrical,conical,bispherical
font=[family, style, size]
family=TIMES,HELVETICA,COURIER,SYMBOL
TIMES→ style=ROMAN,BOLD,ITALIC,BOLDITALIC
HELVETICA and COURIER→
style=BOLD,OBLIQUE,BOLDOBLIQUE
SYMBOL→ style=no style
lightmodel=none,light1,light2,light3,light4
scaling=constrained,unconstrained
style=surface,patch,contour,patchcontour,line,point
symbol=asterisk,box,circle,diagonalcross,diamondpoint,
solidsphere,sphere
symbolsize=n(default=10)
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 27/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-27-320.jpg)
![Introduction
General Purpose CAS
Maple in Use
Symbolic Computation in
Maple
Maple in
Education
Mathematics with Maple
Basic Function
Mathematics with Maple
Visualisation
Plots
Extra(Research)
Reference
Potting points
>plot([[x1, y2], [x2, y2], [x3, y3]..., [xn, yn]]): Plots points
>L:=[[0, 0], [1, 1], [2, 3], [3, 2], [4, −2]]:
>plot(L);
Azat Azhibekov Computer Algebra System in Education May 23, 2015 28/31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer-algebra-system-maple-160328162145/85/Computer-algebra-system-maple-28-320.jpg)