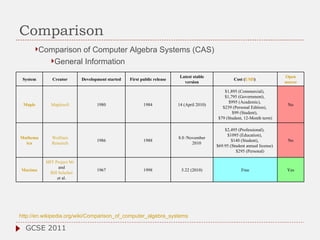
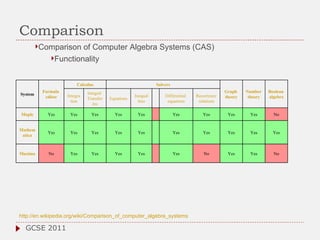
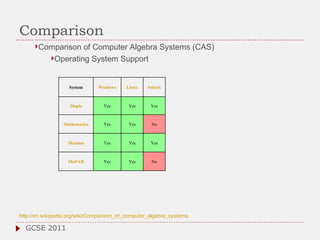
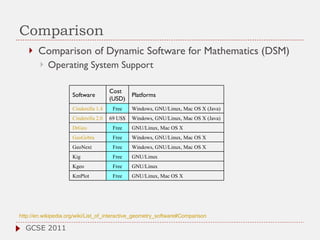
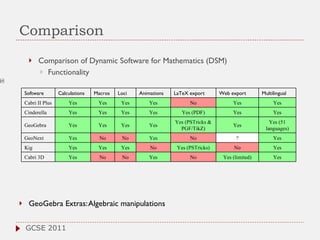
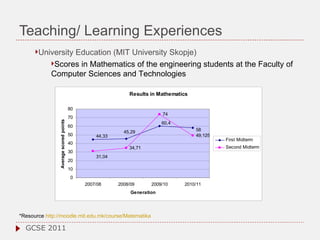
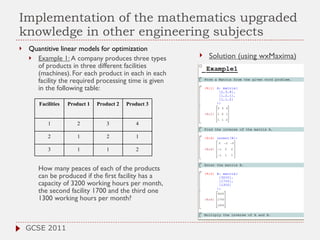
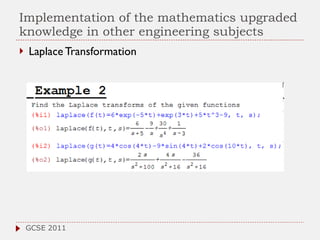
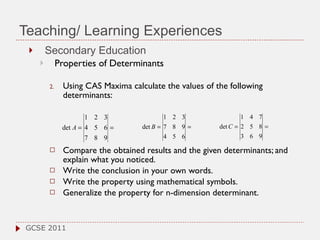
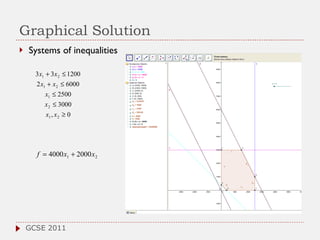
The document discusses the role of computer algebra systems (CAS) in teaching linear algebra, comparing several CAS such as Maple, Mathematica, and Maxima regarding their functionalities and costs. It emphasizes the need for university students to be familiar with CAS to enhance their mathematical understanding and provides examples of their applications in education. Additionally, the document highlights teaching experiences and solutions to mathematical problems using CAS, particularly in high school and university settings.