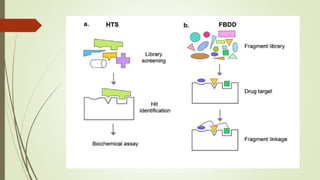
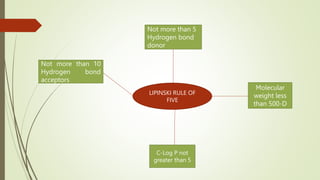
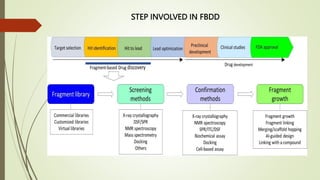
Fragment-based drug discovery is a process that begins with identifying low molecular weight fragments that weakly bind to the target of interest. These fragment hits are then optimized into lead compounds with higher affinity and selectivity. This approach has successfully identified several drug candidates, including Venetoclax which treats chronic lymphocytic leukemia by inhibiting BCL-2. Key techniques for fragment screening include differential scanning fluorimetry, isothermal titration calorimetry, NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Hit optimization is achieved through fragment growing, linking or hopping to develop potent inhibitors.