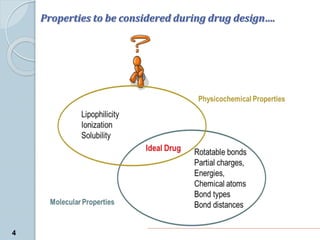
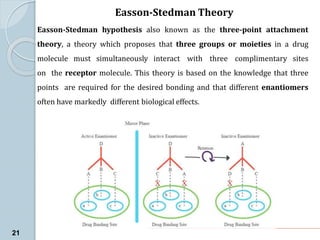
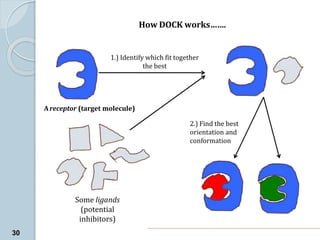
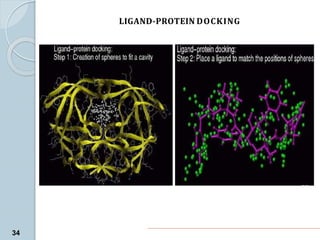
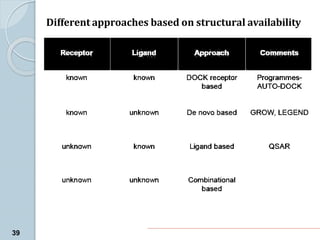
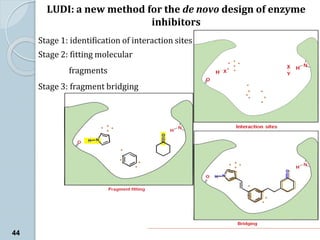
The document discusses drug design as the process of creating new medications by understanding biological targets, detailing two main methods: traditional trial-and-error and rational drug design. It highlights key factors affecting drug properties such as ionization, solubility, and stereoisomerism, and introduces computational chemistry techniques, including structure-based and ligand-based drug design. It also emphasizes the role of computer-aided drug design (CADD) in developing therapeutics and provides examples of drugs discovered through these methods.