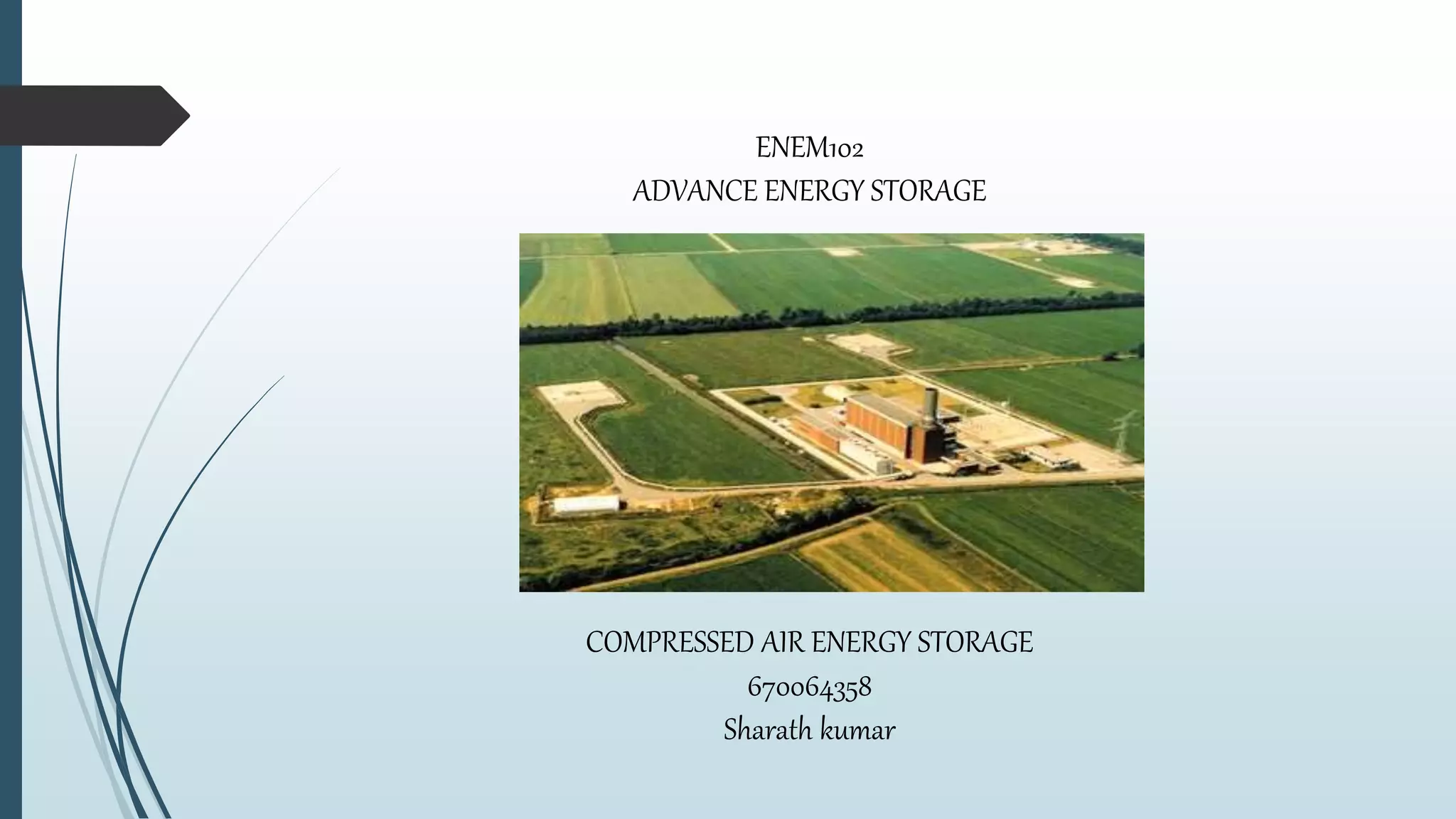
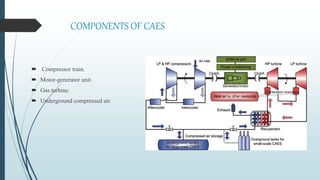
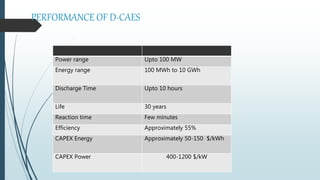
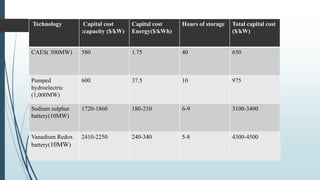
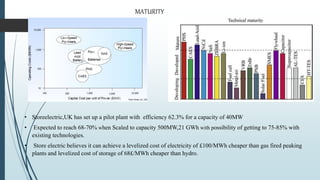
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) is a technology that temporarily stores energy in the form of compressed air, addressing market concerns related to renewable energy intermittency. It encompasses two main types: diabatic CAES, which uses combustion for energy generation, and adiabatic CAES, which captures heat from compression for improved efficiency. CAES offers advantages like high storage capacity, fast start-up times, and significant potential for integrating renewable energy, while facing challenges related to costs and physical storage infrastructure.