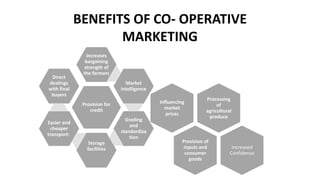
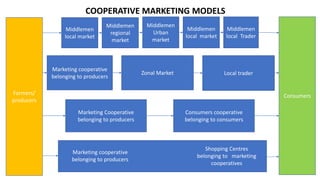
The document discusses several topics related to agricultural marketing, including market analysis, cooperative marketing, branding, and organic certification. Market analysis involves researching customer preferences, prices, supply and demand trends, and identifying new market opportunities. Cooperative marketing allows farmers to achieve economies of scale, increase bargaining power, and access resources like credit, storage, and transport jointly. Branding differentiates products and builds customer loyalty and trust. Organic certification verifies that products were grown without chemicals, communicating quality to consumers.