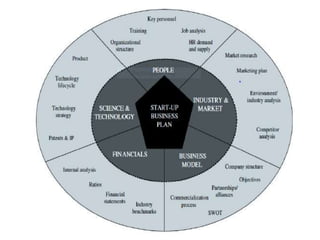
This document discusses entrepreneurship and biotechnology entrepreneurship opportunities. It defines an entrepreneur, discusses entrepreneurship theories over time, characteristics of successful entrepreneurs, and factors favoring entrepreneurship. It then discusses potential biotechnology entrepreneurship activities, the concept of biotechnology parks, and constraints faced by biotechnology entrepreneurs such as funding and commercializing innovations.