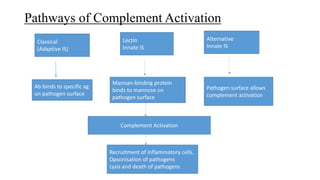
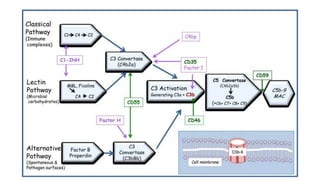
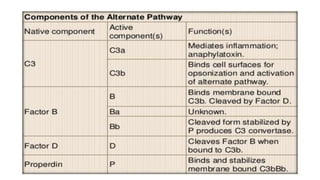
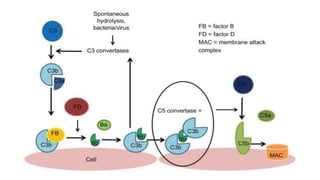
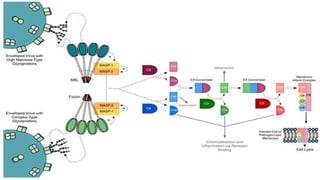
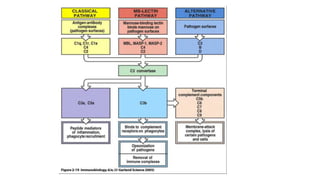
The complement system is a complex network of over 30 proteins that enhance the immune response by destroying pathogens, facilitating phagocytosis, and increasing inflammation. It can be activated via different pathways: classical, alternative, and lectin, each triggered by various signals such as antibodies, pathogens, or carbohydrates. The system plays a crucial role in defense against infections, and deficiencies in complement components can lead to serious health issues, including increased susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases.