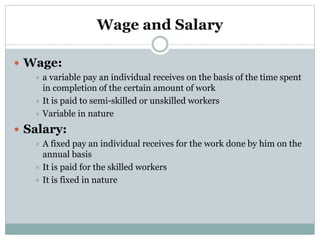
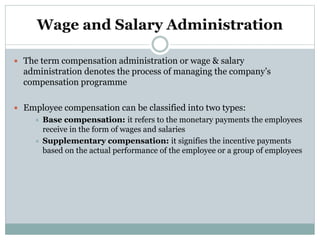
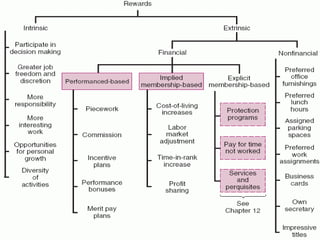
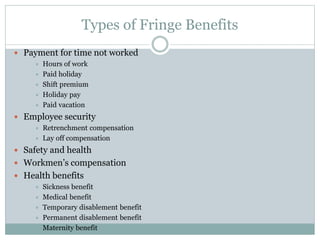
This document discusses compensation planning and administration. It defines compensation as what employees receive in exchange for their services, which can include base pay, variable pay, and benefits. The objectives of compensation planning are to ensure fairness, attract and retain talent, and reward desired behaviors. Base compensation includes wages and salaries, while supplementary compensation includes incentive payments based on performance. Effective compensation administration establishes equitable pay scales and controls costs while attracting qualified employees and complying with legal regulations.