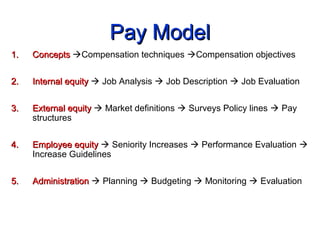
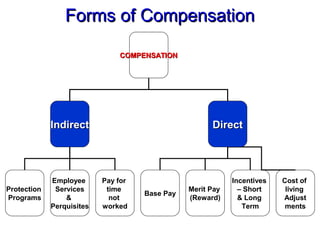
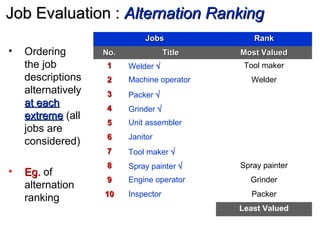
The document discusses concepts related to compensation and reward management including pay models, internal equity, external equity, and employee equity. It covers forms of compensation including base pay, incentives, and cost of living adjustments. Key aspects of designing pay structures are also outlined such as determining pay level policies by leading, meeting, or following competition. Methods for evaluating jobs like ranking, classification, factor comparison, and point plans are explained. The importance of conducting pay surveys and using the data to construct policy lines and design pay ranges is also highlighted.








![Job Evaluation :Job Evaluation : Paired ComparisonPaired Comparison
• Comparing all
possible pairs of
jobs
• No. of pairs to
compare =
[n (n-1)] / 2
• Eg.Eg. If you have 5
jobs then there are
10 paired
comparisons
• Jobs with highest
total no. of “MostMost
ValuableValuable” ranking
becomes the
highest-ranked job.
Job NumbersJob Numbers
11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99
11 AA AA BB AA BB BB AA AA
22 BB
33 BB AA
44 AA
55 BB
66 AA BB
77 AA
88 BB
99 BB
A = Better B = Worse](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paycompensation-151201151059-lva1-app6892/85/Pay-and-Compensation-12-320.jpg)