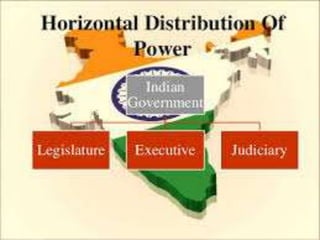
There are three branches of government in India: the legislature, executive, and judiciary. The central legislature is called Parliament, which has two houses - Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. The legislature is responsible for making laws, controlling the budget, amending the constitution, and some electoral and judicial functions. The executive implements laws and policies adopted by the legislature and handles day-to-day administration. The judiciary settles disputes between individuals and private parties, and also interprets the constitution and protects citizens' rights.