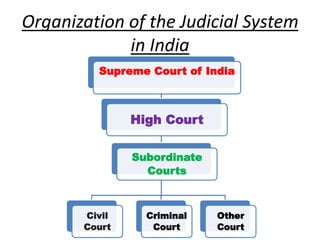
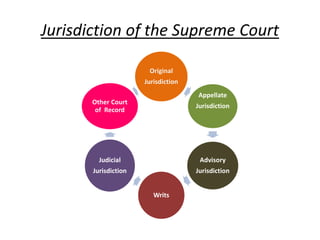
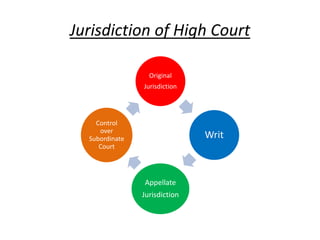
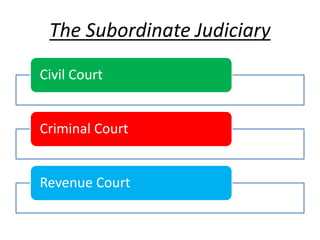
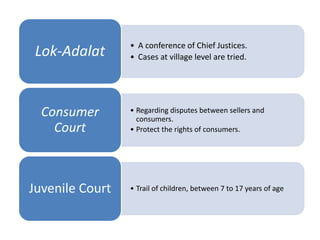
The document outlines the structure and functioning of the judicial system in India, detailing the roles of the Supreme Court, High Courts, and subordinate courts. It highlights key figures such as the Chief Justice of India and discusses judicial appointments, jurisdictions, and significant cases like the impeachment proceedings against Justice V. Ramaswami. Additionally, it mentions the role of the Attorney General and various types of courts established to resolve specific disputes.