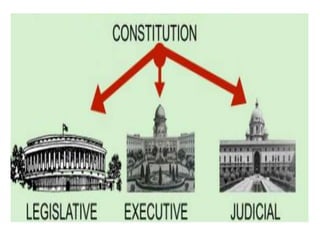
This document provides information about the three organs of government in India:
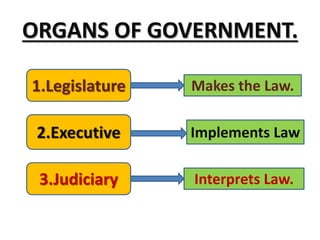
1. The legislature makes laws and consists of the Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha houses of parliament.
2. The executive implements laws and consists of the central government led by the president and state governments led by governors and chief ministers.
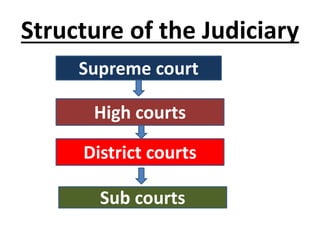
3. The judiciary interprets laws and resolves disputes, led by the Supreme Court, high courts, and subordinate courts like district courts.
The three organs must work together constitutionally for effective governance.