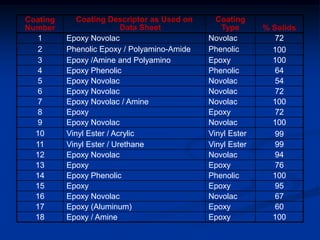
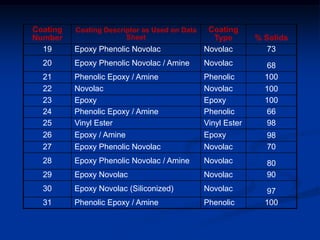
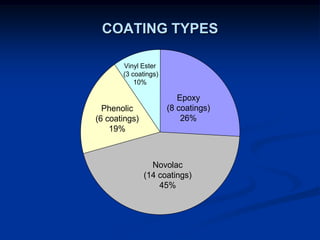
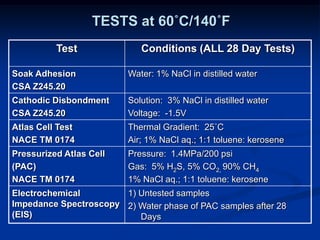
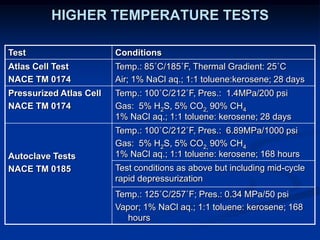
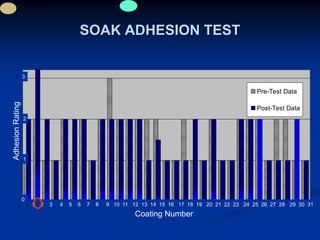
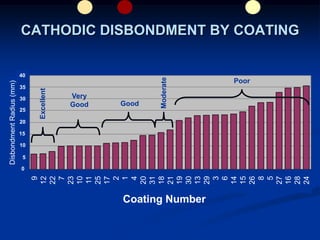
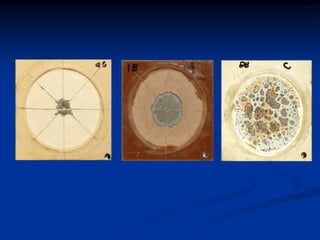
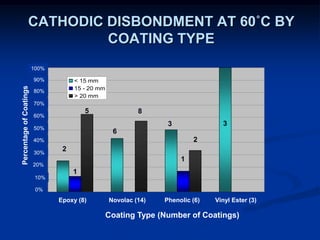
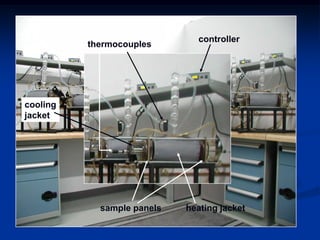
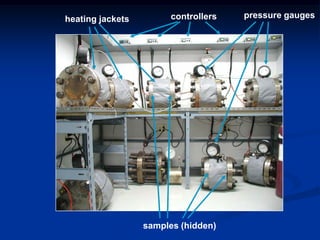
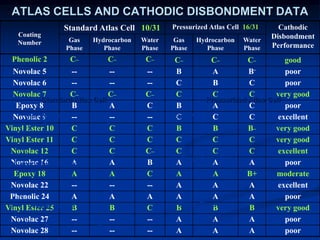
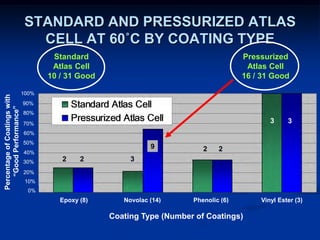
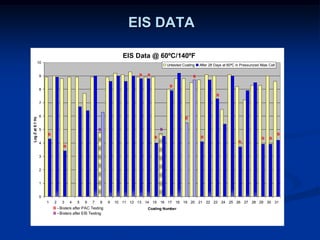
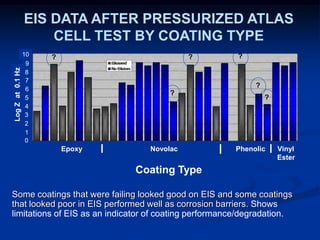
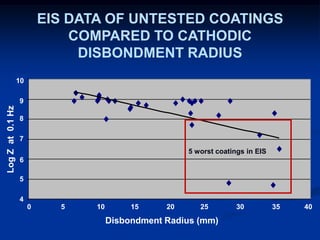
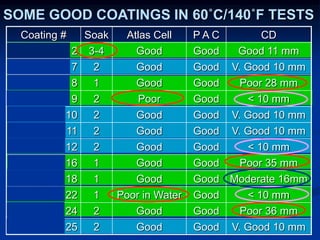
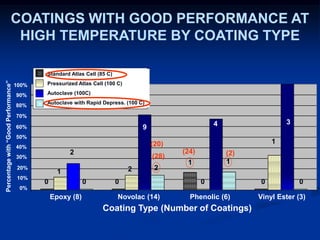
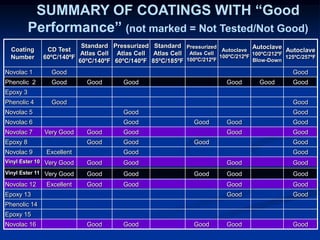
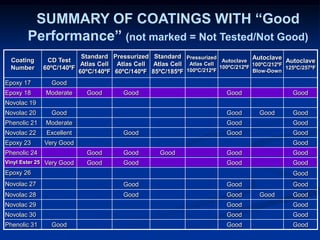
The document details comparative testing of 31 tank lining systems to evaluate their performance in various oil field environments, with the objective of aiding in the selection of appropriate coatings. Results include data on coating types and their respective performance metrics under specific conditions, such as adhesion, cathodic disbondment, and temperature resistance. The study encourages interaction between suppliers and end users to enhance coating selection processes.