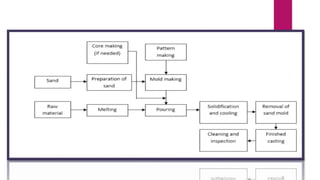
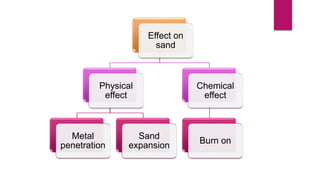
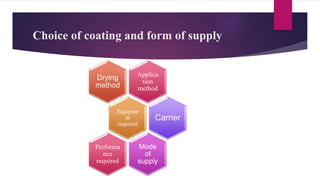
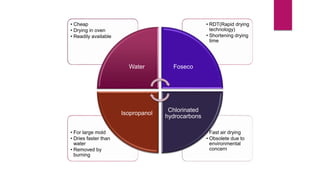
The document discusses mold and core coatings used in metal casting. It provides information on:
1) The physical and chemical effects that can occur between liquid metal and sand molds without a coating, such as metal penetration and sand burn-on.
2) The key characteristics an effective coating should possess, such as refractory properties and good adhesion.
3) The typical components of foundry coatings, including refractory fillers, liquid carriers, binders, and rheology control systems.
4) Common application methods for coatings like brushing, dipping, spraying, and overpouring. Equipment used in mixing and applying coatings is also discussed.