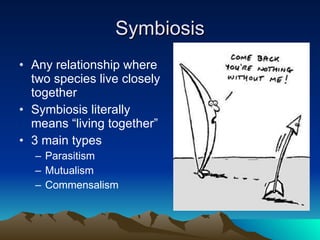
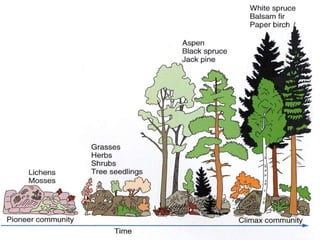
Community interactions include competition, predation, and symbiosis. Competition occurs when organisms attempt to use the same ecological resource, leading to winners and losers. Predation involves one organism capturing and feeding on another. Symbiosis is a close relationship between two species, and includes mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Ecosystems are constantly changing over time through ecological succession in response to disturbances. Succession involves predictable changes in a community's composition as older species decline and new species move in.