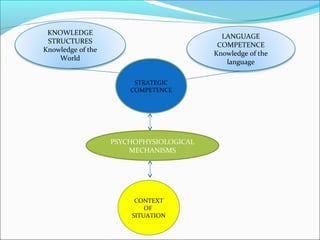
This document discusses theories of communicative competence. It describes how communicative competence involves understanding sociocultural contexts and interactive communication. Theories discussed include Paulston and Hymes' notion of linguistic and communicative competence, Cummins' ideas of CALP and BICS, and Canale and Swain's four components of communicative competence: grammatical, discourse, sociolinguistic, and strategic competence. The document also discusses Halliday's seven language functions and how context gives meaning to form and function.